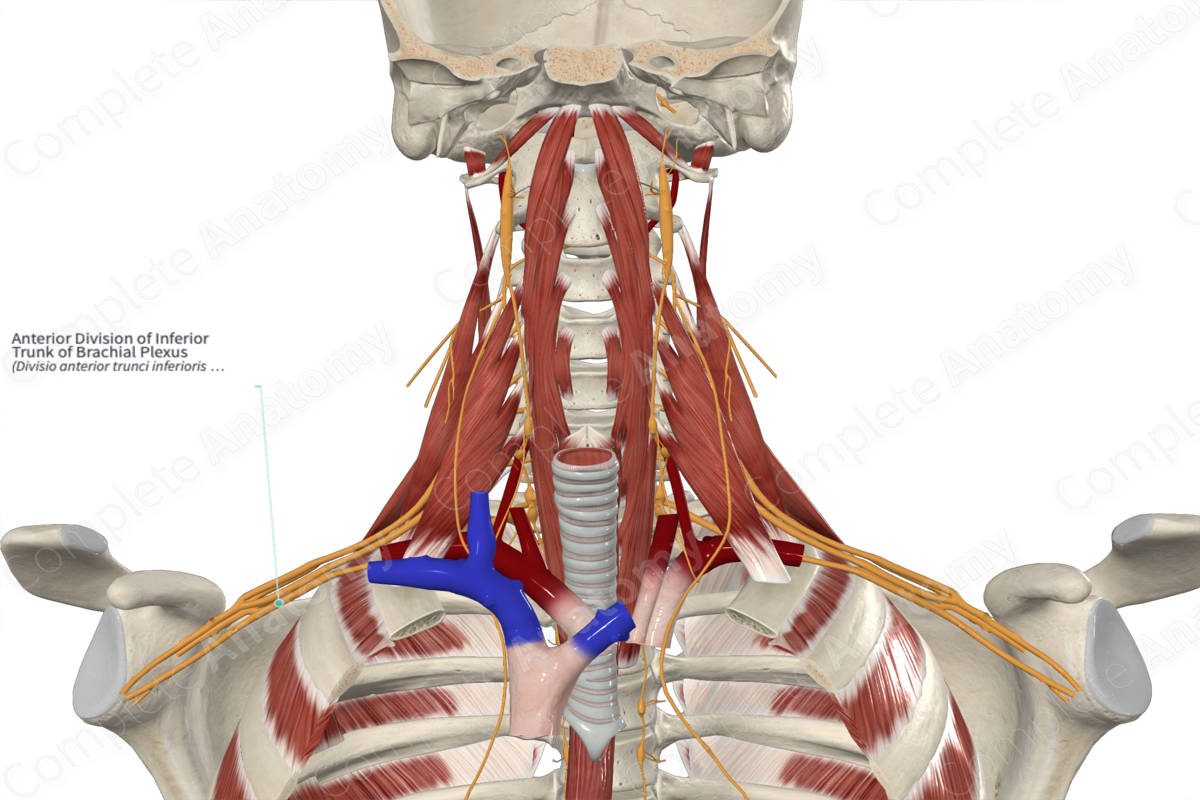
Anterior Division of Inferior Trunk of Brachial Plexus
Divisio anterior trunci inferioris plexus brachialis
Read moreQuick Facts
Origin: Inferior trunk of the brachial plexus.
Course: Forms posterior to the mid-clavicle and runs inferolaterally to the formation of the medial cord, posterior to the first segment of the axillary artery.
Branches: No branches. Becomes the medial cord which in turn gives rise to five nerves, two of which are terminal branches.
Supply: Sensory and motor innervation. Supplies sensory innervation for the skin of the palmar and medial surfaces of the hand, the tips of the digits, and the anteromedial surfaces of the arm and forearm. Motor innervation is to the muscles of the hand, anterior compartment muscles of the forearm, and pectoralis muscles.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The origin of the anterior division of the inferior trunk is from the inferior trunk itself. This occurs when the trunk bifurcates into anterior and posterior divisions. It carries fibers from the C8 and T1 spinal segments.
Course
The anterior division forms roughly posterior to the mid-clavicle. It runs inferolaterally, posterior to the first segment of the axillary artery. Here, the anterior division of the inferior trunk becomes the medial cord.
The divisions of the brachial plexus run within the prevertebral fascia or its inferior extension, the axillary sheath.
Branches
The anterior division of the inferior trunk itself has no branches as it generally does not give rise to any nerves. However, it becomes the medial cord and this cord gives rise or contributes to the following nerves:
—medial pectoral nerve;
—medial cutaneous nerve of the arm;
—medial cutaneous nerve of the forearm;
—ulnar nerve;
—median nerve.
Although typically considered to have no branches, reports from cadaveric investigations have suggested that in a majority of cases, the medial pectoral nerve may originate from the distal end of the anterior division of the inferior trunk, rather than the medial cord (Loukas et al., 2006).
Supplied Structures
The anterior division of the inferior trunk supplies the structures innervated by the medial cord. In general, this represents anterior and medial surfaces of the arm, forearm, hand, and fingers (sensory) and the muscles of the hand, anterior compartment of the forearm, and pectoralis muscles (motor).
Broken down by nerve, the structures supplied by the anterior division of the inferior trunk are listed below.
—Medial pectoral nerve, which supplies the pectoralis minor and pectoralis major muscles;
—Medial brachial cutaneous nerve supplying the skin of the medial arm;
—Medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve supplying the skin of the anterior and medial forearm;
—Ulnar nerve, which supplies the skin of the medial surface of the hand and all intrinsic muscles of the hand and forearm flexors not innervated by the median nerve;
—Median nerve innervates the skin of the lateral palmar surface of the hand and finger tips and all intrinsic muscles of the hand and forearm flexors not innervated by the ulnar nerve.
References
Loukas, M., Louis, R. G., Fitzsimmons, J. and Colborn, G. (2006) 'The surgical anatomy of the ansa pectoralis', Clin Anat, 19(8), pp. 685-93.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products