Quick Facts
Origin: From the coccygeal nerve (Co).
Course: The anterior rami of Co and S5 emerge from the sacral hiatus and run anteriorly to the coccygeal muscle. A communicating branch from the anterior ramus of S4 unites with these rami to form the coccygeal plexus.
Branches: Gray communicating branch and anococcygeal nerve.
Supply: Motor innervation to the coccygeus muscle. Sensory innervation to the perianal skin in the anal triangle.
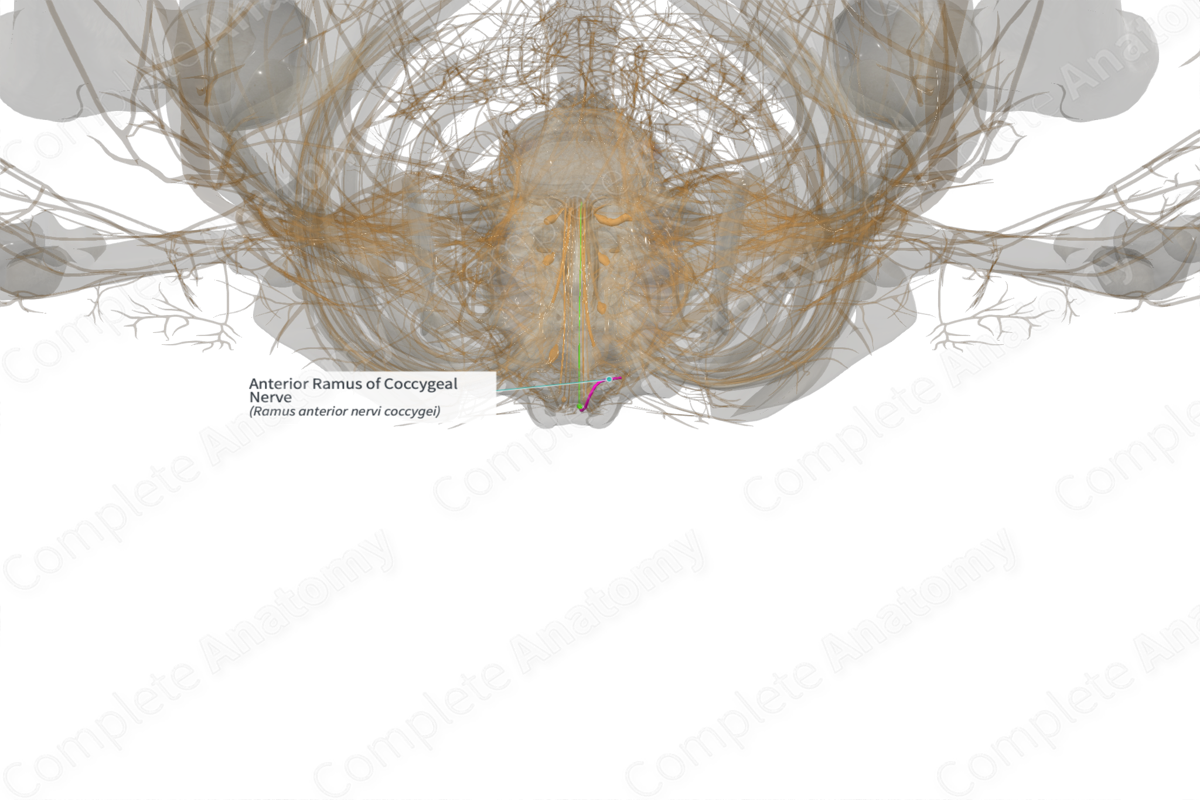
Origin
The anterior (ventral) ramus of coccygeal nerve originates as one of two branches of the fifth sacral nerve. The other branch is the posterior ramus of the same coccygeal nerve.
Course
The coccygeal nerve bifurcates into anterior and posterior rami. Both rami exit the sacral hiatus along with the fifth sacral nerve.
The anterior ramus of the coccygeal nerve, along with the anterior ramus of fifth sacral nerve (both of which originate caudal to the pelvic floor), penetrate the coccygeus muscle to enter the pelvic cavity, and join with the anterior ramus of fourth sacral nerve to form the coccygeal plexus. Anococcygeal nerves are given off from this coccygeal plexus.
Branches
The anterior ramus of coccygeal nerve is a mixed nerve as it contains both somatic efferent (motor) and afferent (sensory) neurons.
The somatic efferent neurons emerge from the anterior gray horn of the coccygeal segment of the spinal cord. These are lower motor neurons that exit the cord through the anterolateral sulcus, as they travel inside the anterior motor rootlets and root of the spinal segment. They subsequently travel through the coccygeal nerve to enter the anterior ramus, prior to reaching the coccygeal plexus and innervate the coccygeus muscle.
Somatic afferent neurons travel through the anococcygeal nerve to enter the sacral plexus. These descend to reach the coccygeal plexus. From there onwards, these neurons travel through the sensory root and rootlets of the coccygeal nerve. The cell bodies of these neurons are located inside the posterior root ganglion of the coccygeal nerve. The axons then travel through the posterolateral sulci to enter the right posterior sensory horn of the coccygeal cord segment.
The anterior ramus of coccygeal nerve is also connected to the sympathetic trunk through the gray communicating branch (gray ramus communicans), which serves as a conduit for the postganglionic sympathetic neurons.
Supplied Structures & Function
The anterior ramus of coccygeal nerve supplies motor innervation to the coccygeus muscle, through the general somatic efferent neurons, as they run inside the direct muscular branches of the anterior ramus of fourth sacral nerve.
The general somatic afferent neurons conduct cutaneous general sensory information from the perianal skin over the anal triangle via the anococcygeal nerve.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products





