Quick Facts
Origin: Anterolateral sulcus of spinal cord.
Course: Laterally towards intervertebral foramen.
Branches: None.
Supply: Motor innervation to epaxial muscles of upper trunk, intercostal muscles of third intercostal space. Sympathetic targets in the thorax and territories of third thoracic nerve.
Related parts of the anatomy
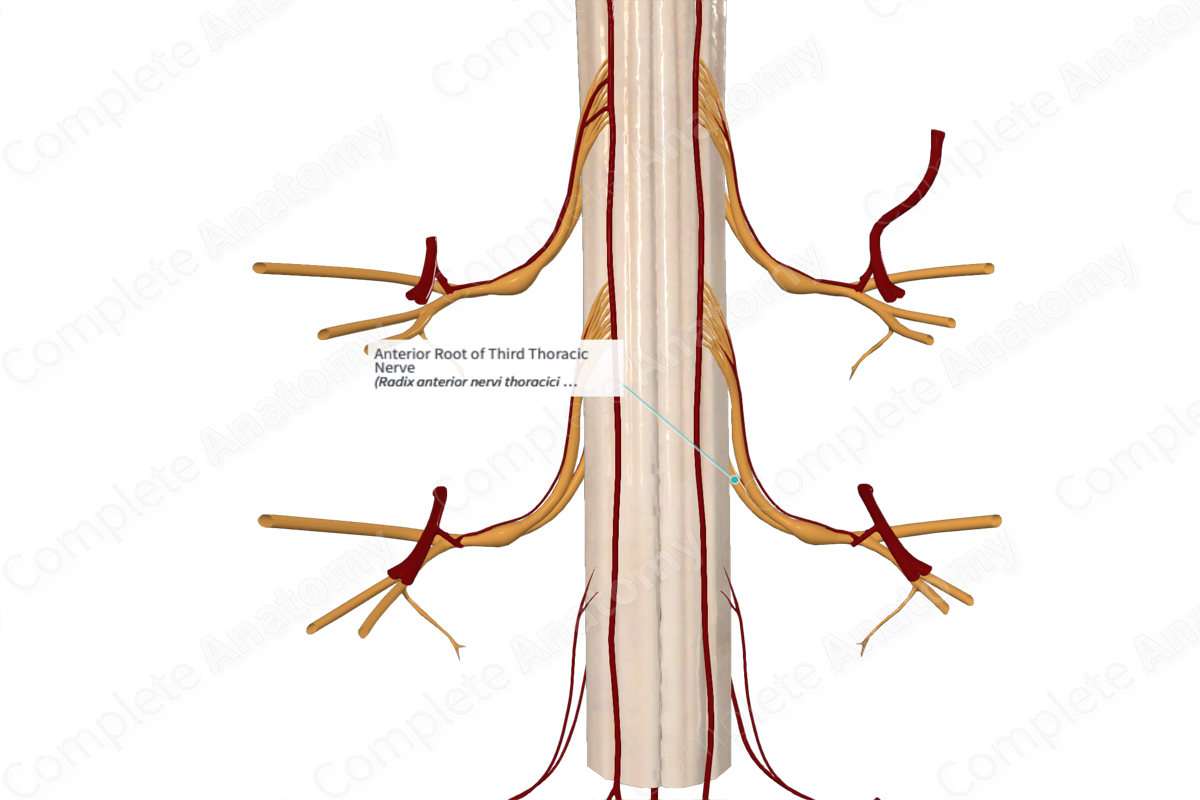
Origin
The anterior root of the third thoracic nerve forms from a series of rootlets that emerge from the anterolateral sulcus of the third thoracic spinal segment.
Course
The anterior root of the third thoracic nerve runs laterally and inferiorly away from the third thoracic spinal segment towards the intervertebral foramen located between the third and fourth thoracic vertebrae. Roughly within this intervertebral foramen, the anterior root merges with the posterior root to form the third thoracic nerve.
Branches
The anterior root of the third thoracic nerve merges with the posterior root to form the third thoracic nerve and does so without branching.
Supplied Structures & Function
The anterior root of the third thoracic nerve supplies all efferents for the third thoracic nerve, both somatic and sympathetic.
The somatic efferents pass through the spinal nerve itself and into either the posterior or anterior ramus of the third thoracic nerve.
—Those fibers that enter the posterior ramus convey motor innervation to the epaxial muscles, including the erector spinae (iliocostalis, longissimus, spinalis), transversospinal (rotatores, multifidus, semispinalis), and deep segmental back muscles (interspinales, levatores costarum).
—Those fibers that enter the anterior ramus of the third thoracic nerve (or third intercostal nerve) innervate the muscles of the third intercostal space (external intercostal, internal intercostal, innermost intercostal) and transversus thoracis muscle. A lateral branch of the intercostal nerve will innervate the serratus posterior superior muscle.
Preganglionic sympathetic efferents travel from the lateral horn of the third thoracic spinal cord segment, through the anterior root, and into the third thoracic nerve. Just past the intervertebral foramen, sympathetic efferents leave the thoracic nerve via the white rami communicans to enter the sympathetic chain. The preganglionic sympathetic efferents of the third thoracic anterior root primarily affect sympathetic innervation of thoracic organs, such as the lungs and heart. Additionally, they control the sympathetic response in the glands and vessels of the upper thoracic dermatomes.

