Quick Facts
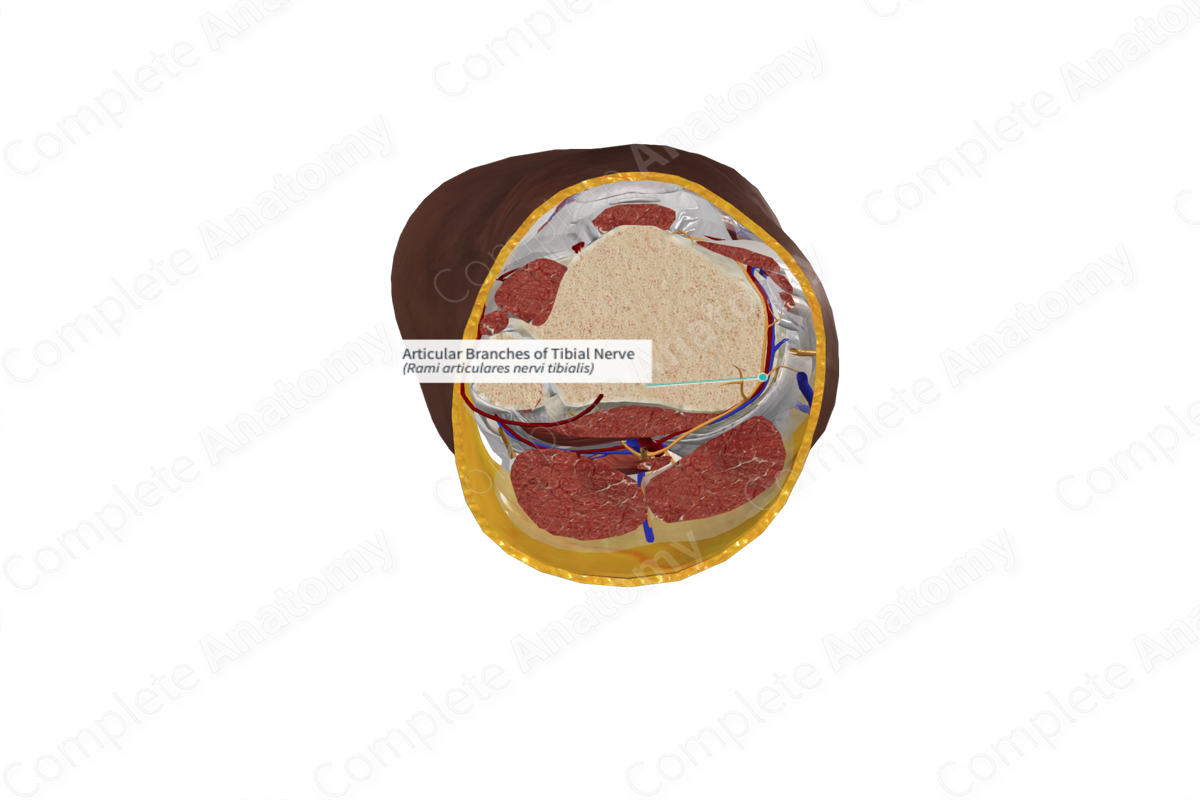
Origin: Tibial nerve.
Course: Accompany the genicular arteries around the knee joint.
Branches: None.
Supply: Posterior knee joint capsule, menisci, cruciate ligaments, and infrapatellar fat pad.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The articular branches arise at variable levels from the tibial nerve, either many centimeters above the knee or within the popliteal fossa. The number of articular branches may also vary, ranging from one to as many as five (Hines et al., 1996).
Course
The articular branches of the tibial nerve accompany the superior and inferior medial genicular arteries and the middle genicular artery.
Branches
There are no named branches.
Supplied Structures
The articular branches of the tibial nerve innervate the posterior knee joint capsule. Small ramifications (especially in fetal life) might also innervate external parts of the menisci. Others might perforate the joint capsule to travel in the synovial tissue, staying in close proximity to the cruciate ligaments. Some even extend as far as the infrapatellar fat pad (Hines et al., 1996).
References
Hines, A. E., Birn, H., Teglbjaerg, P. S. and Sinkjaer, T. (1996) 'Fiber type composition of articular branches of the tibial nerve at the knee joint in man', Anat Rec, 246(4), pp. 573-8.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products




