Quick Facts
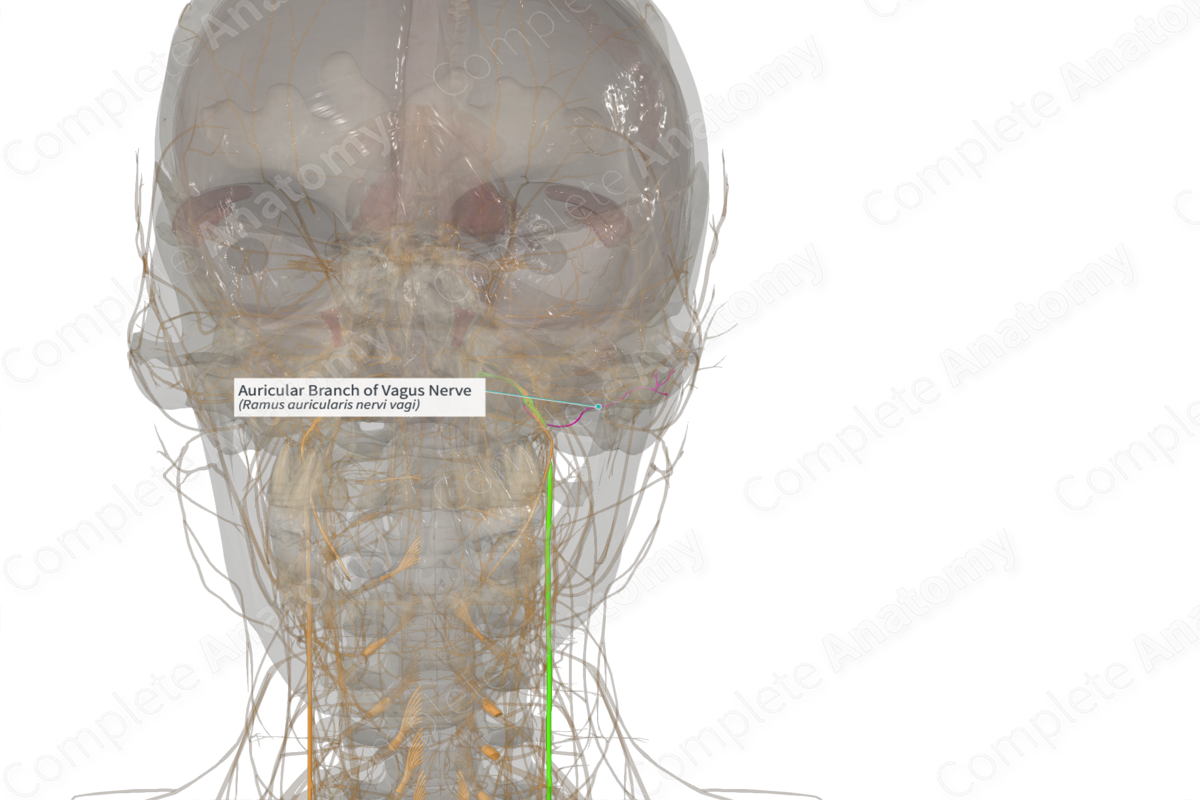
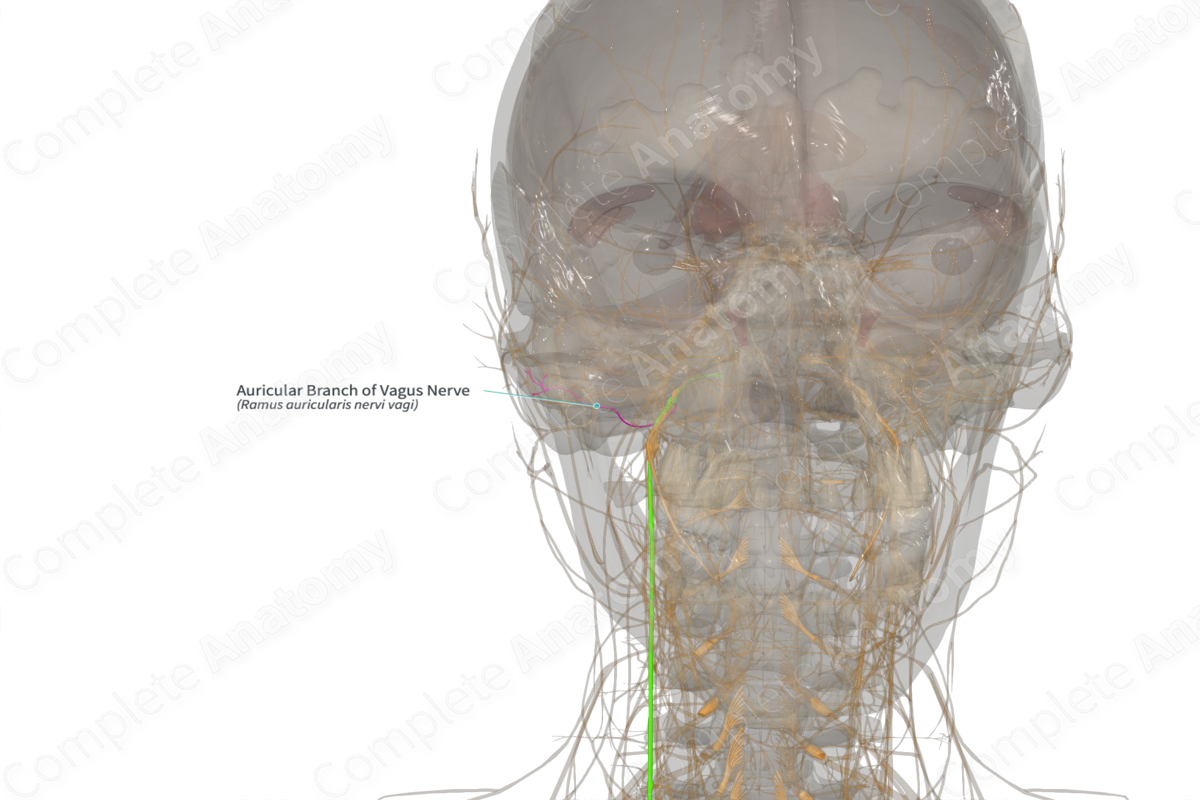
Origin: Superior ganglion of vagus nerve.
Course: Runs from the superior ganglion through the temporal bone to the area just anterior of the external acoustic meatus.
Branches: The auricular branch of the vagus nerve forms a posterior auricular branch and an anterior branch. It also has communications with the glossopharyngeal nerve and the facial nerve.
Supply: General somatic sensation from parts of the skin of the anterior auricle, the external acoustic meatus, and the external surface of the tympanic membrane.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The auricular branch is first seen splitting from the vagus nerve at the superior ganglion.
Course
From the superior ganglion, the auricular branch penetrates the temporal bone at the mastoid canaliculus. It runs through the temporal bone, passing close to the facial canal, reaching the surface at the tympanomastoid fissure, just anterior to the external acoustic meatus.
Branches
The auricular branch of the vagus nerve has two branches and forms two communications.
After emerging from the temporal bone, the auricular branch of the vagus nerve sends some fibers posteriorly to join the posterior auricular nerve of the facial nerve. The other fibers remain more anterior relative to the external ear. Both branches innervate parts of the skin of the auricle, the external acoustic meatus, and the external surface of the tympanic membrane.
Within the jugular foramen, shortly after its origin, the auricular branch of the vagus nerve sends a communication to the glossopharyngeal nerve. As the auricular branch of the vagus nerve moves through the temporal bone and passes by the facial canal, it sends a communication to the facial nerve. It should be mentioned that one of the two branches of the auricular nerve join the posterior auricular nerve which is also a branch of the facial nerve.
Supplied Structures
The auricular branch of the vagus nerve is a sensory nerve. Its fibers convey general somatic sensation from parts of the skin of the auricle, the external acoustic meatus, and the external surface of the tympanic membrane back to the spinal nucleus of the trigeminal nerve in the brainstem.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products