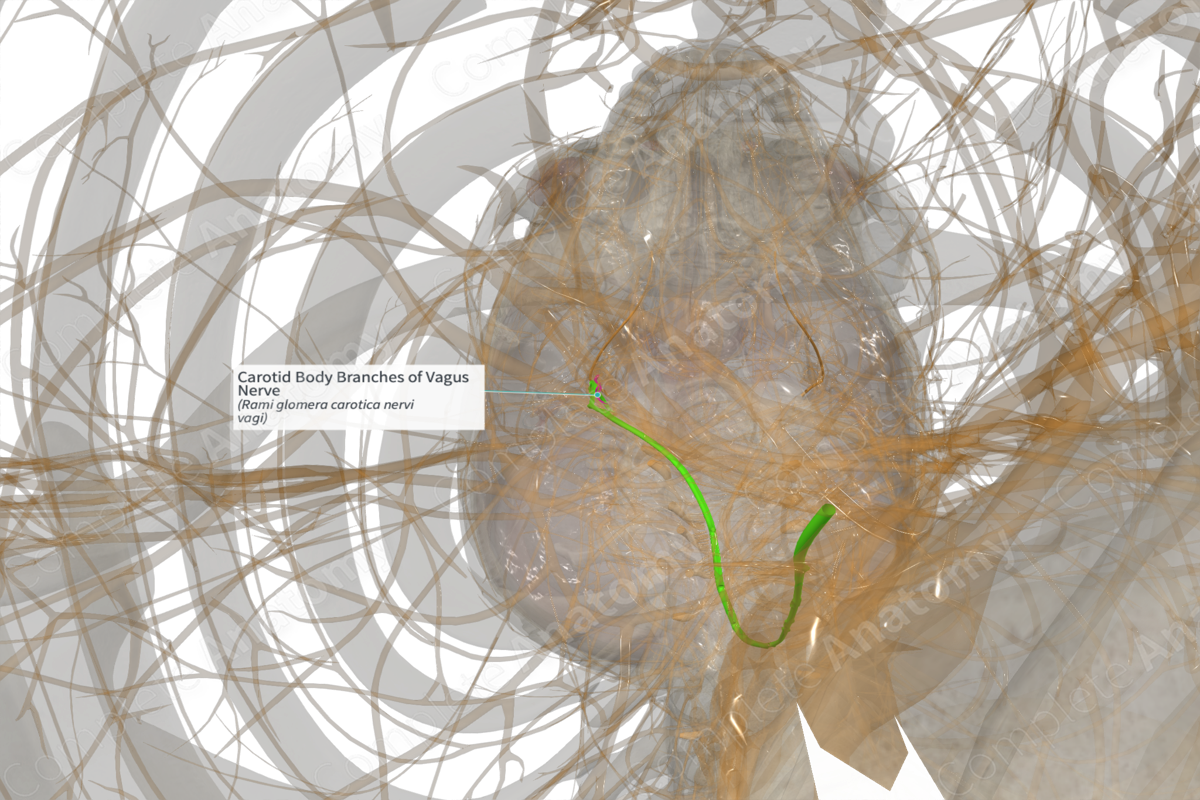
Carotid Body Branches of Vagus Nerve (Left)
Rami glomera carotica nervi vagi
Read moreQuick Facts
Origin: Inferior ganglion of vagus nerve, or the vagus nerve itself.
Course: Descends with the carotid sinus nerve of the glossopharyngeal nerve.
Branches: None
Supply: Sensory: conveys sensation from a minor portion of the chemoreceptors in the carotid body.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The branches of the vagus nerve to the carotid body originate either from the vagus nerve itself, or the inferior ganglion of the vagus nerve.
Course
The branches of the vagus nerve to the carotid body run from their origin down and towards the anterior surface of the internal carotid artery. Here they anastomose with the descending glossopharyngeal fibers of the carotid plexus, and particularly the carotid sinus nerve.
Branches
There are no named branches.
Supplied Structures
The branches of the vagus nerve to the carotid body are thought to convey sensation from a minor portion of the chemoreceptors in the carotid body. It is unclear if there is any functional significance to these fibers as the carotid body is largely innervated by the carotid sinus nerve from the glossopharyngeal nerve. Additionally, the branches of the vagus nerve to the carotid body are not always present (Toorop et al, 2009).
References
Toorop, R. J., Scheltinga, M. R., Moll, F. L. & Bleys, R. L. (2009) Anatomy of the carotid sinus nerve and surgical implications in carotid sinus syndrome. J Vasc Surg, 50(1), 177-82.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Vagus Nerve

The vagus nerve (10th cranial nerve) is a bilateral nerve bundle that is composed of axons of both efferent and afferent neurons.




