Quick Facts
Origin: Glossopharyngeal nerve.
Course: Runs inferiorly along the anterior surface of the internal carotid artery until it reaches the carotid bifurcation.
Branches: None.
Supply: General visceral afferents from the carotid body and carotid sinus to the brainstem.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
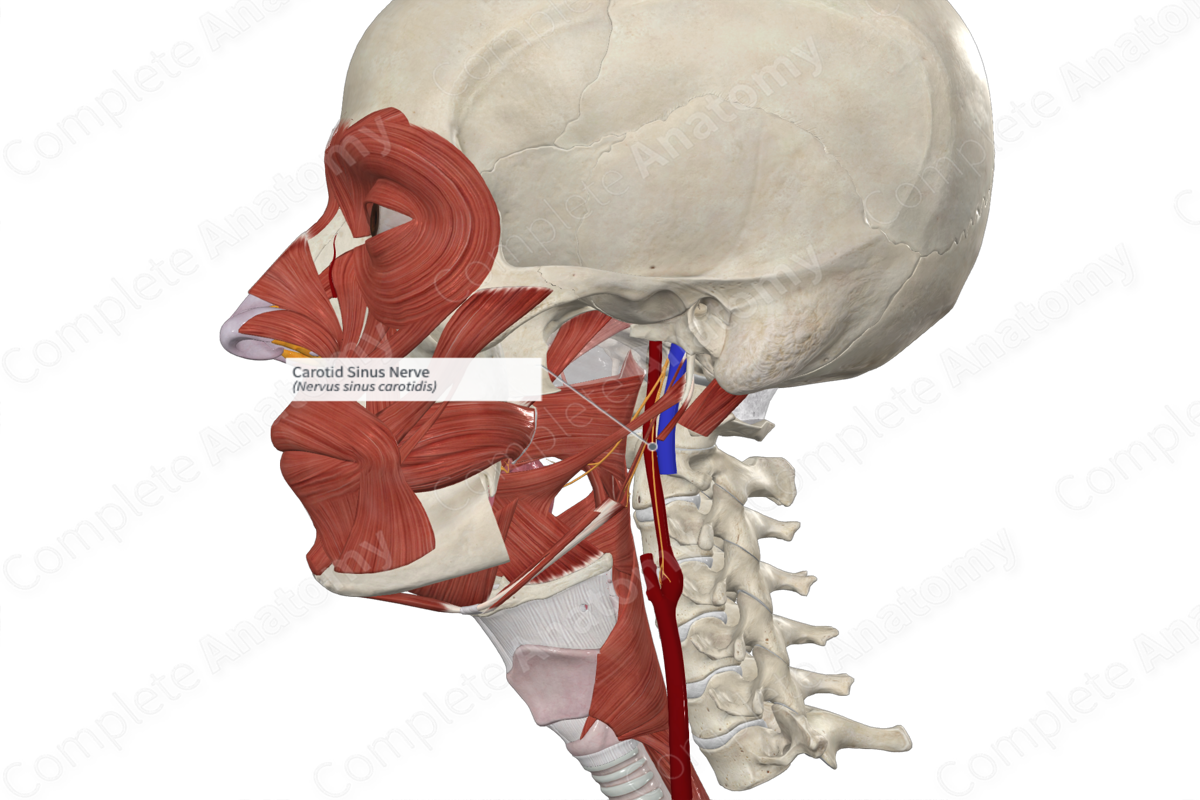
The carotid sinus nerve splits off the glossopharyngeal nerve early in its extracranial course. Shortly after the glossopharyngeal nerve emerges from the jugular foramen, or even at the level of the inferior ganglion of glossopharyngeal nerve, these fibers split from the main nerve.
Course
From its origin, the carotid sinus nerve runs inferiorly along the anterior surface of the internal carotid artery. It continues down until reaching the carotid bifurcation at which point the carotid sinus nerve splits into two terminal ramifications.
Branches
There are no named branches, however, the two terminal ramifications of the carotid sinus nerve extend to the carotid sinus the carotid body.
Supplied Structures
The carotid sinus nerve is a sensory nerve. It conveys general visceral sense fibers from the carotid body and carotid sinus back to the brainstem.
Fibers from the carotid body originate on chemoreceptors that measure blood O2 and CO2 levels. Fibers from the carotid sinus originate on baroreceptors that measure blood pressure.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Carotid Sinus Nerve

The carotid sinus nerve, another branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve, contains the primary afferent fibers of chemoreceptors in the carotid body and of baroreceptors lying in the carotid sinus wall.



