Quick Facts
Origin: Continuation of the internal and external carotid plexuses, fibers from the cervical ganglia.
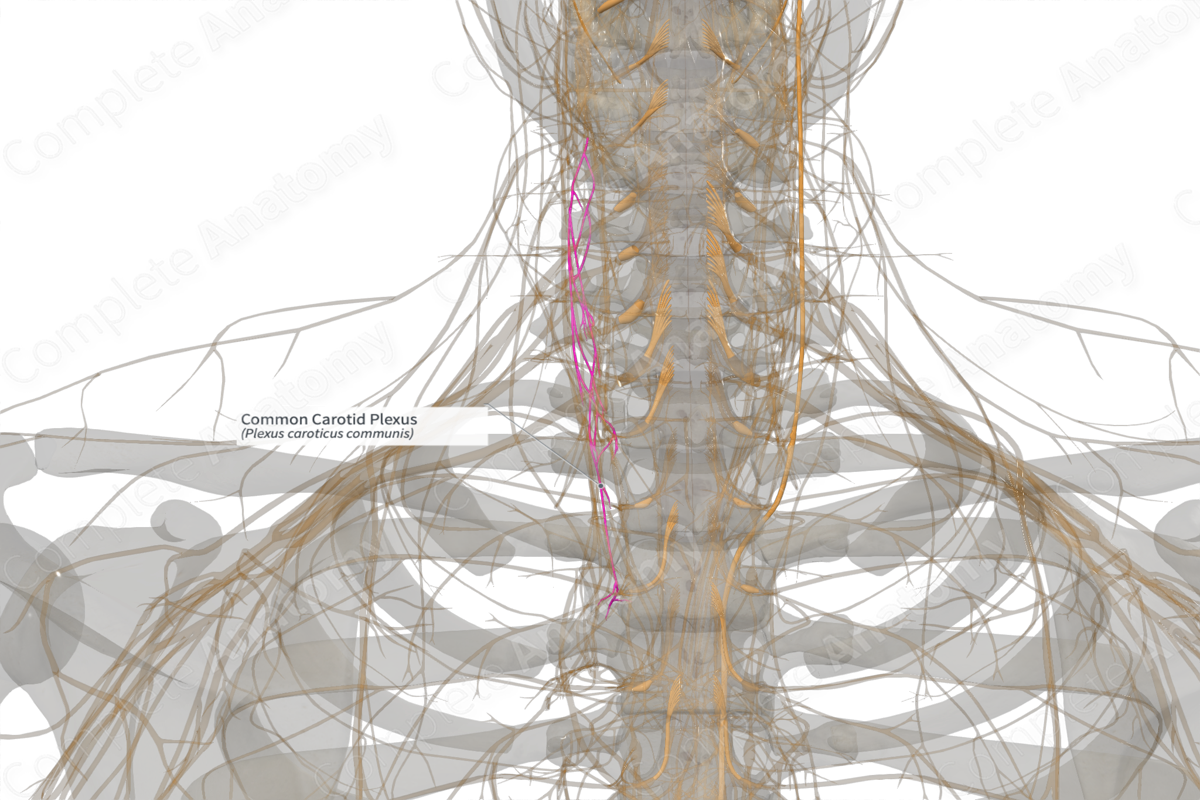
Course: Travels along the common carotid artery.
Branches: None.
Supply: Sympathetic efferent fibers to the glands and mucosa of the neck.
Origin
The common carotid plexus is formed by the continuation of the external and internal carotid plexuses, with contributions from the superior cervical ganglion of the sympathetic trunk (Dorland, 2011).
Course
As the common carotid artery ascends through the neck, the sympathetic fibers forming the plexus follow it, traveling on the surface of the common carotid artery.
Branches
There are no named branches.
Supplied Structures
The common carotid plexus supplies sympathetic efferent innervation to the glands and mucosal linings of the neck.
List of Clinical Correlates
—Horner’s syndrome
—Anhidrosis
—Myosis
—Ptosis
References
Dorland, W. A. (2011) Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. 32nd edition.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products





