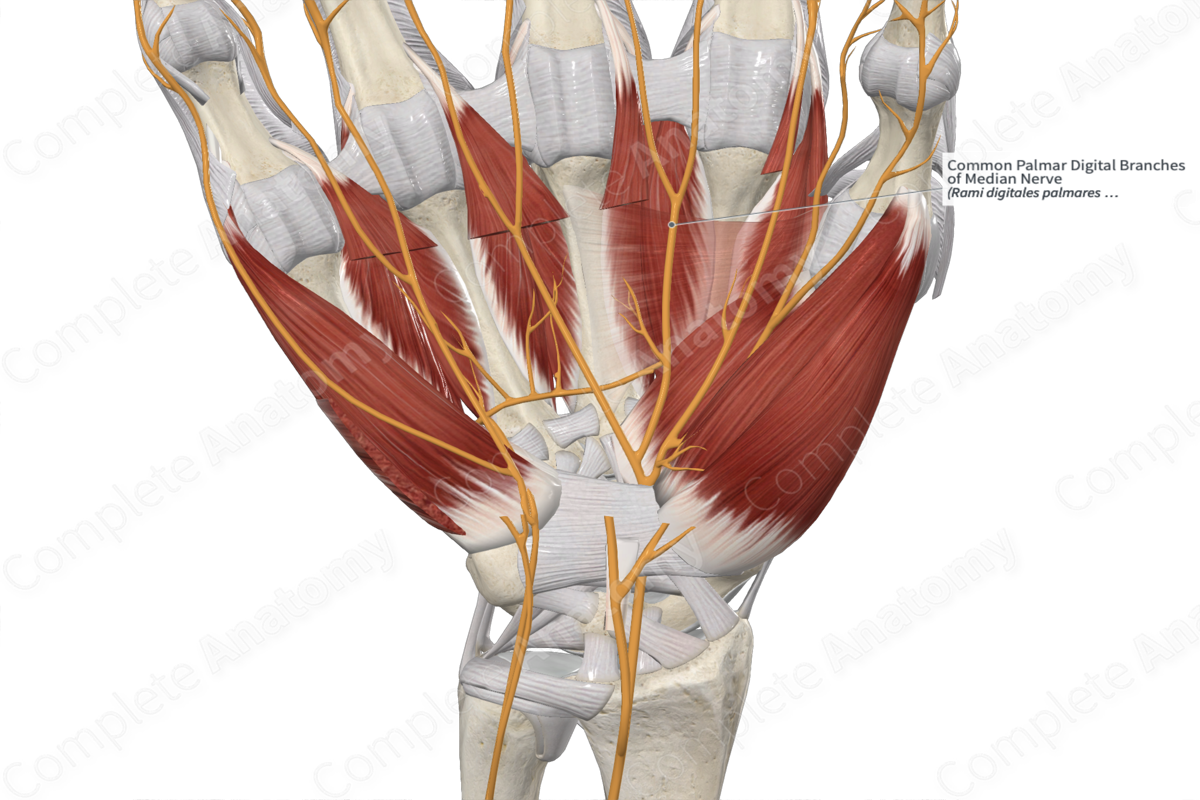
Common Palmar Digital Branches of Median Nerve
Rami digitales palmares communes nervi mediani
Read moreQuick Facts
Origin: Median nerve (C6—C8).
Course: Median nerve enters the palm underneath the flexor retinaculum and divides into medial and lateral division. The medial division gives off common palmar digital branches for second and third interdigital clefts, which further give off proper palmar digital branches.
Branches: Proper palmar (or volar) digital of median nerve.
Supply: Adjoining sides of index, middle, and ring fingers in the second and third interdigital clefts.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The common palmar digital branches of median nerve arise from the median nerve below the flexor retinaculum (C6—C8).
Course
The median nerve enters the palm by passing deep to the flexor retinaculum, where it lies in the narrow space of the carpel tunnel in front of the ulnar bursa enclosing the long flexor tendons of the forearm. Immediately below the retinaculum, the nerve divides into lateral and medial divisions.
The medial division divides into common palmar digital branches for the second and third interdigital clefts, supplying the adjoining sides of the index, middle, and ring fingers. The common palmar digital branches for the medial one and half digits come from the ulnar nerve. The lateral division gives off a muscular branch to thenar muscles and three digital branches for the lateral one and half digits (including thumb).
Branches
Proper palmar (or volar) digital nerves arise from the common digital branches of the median nerve inside the palmar aspect of the hand.
Supplied Structures
The common palmar digital branches of the median nerve supply the second and third interdigital clefts, and adjoining sides of the index, middle, and ring fingers. It also innervates the second lumbrical.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Median Nerve

The median nerve is a terminal branch nerve of the brachial plexus formed from the medial and lateral cords.




