Description
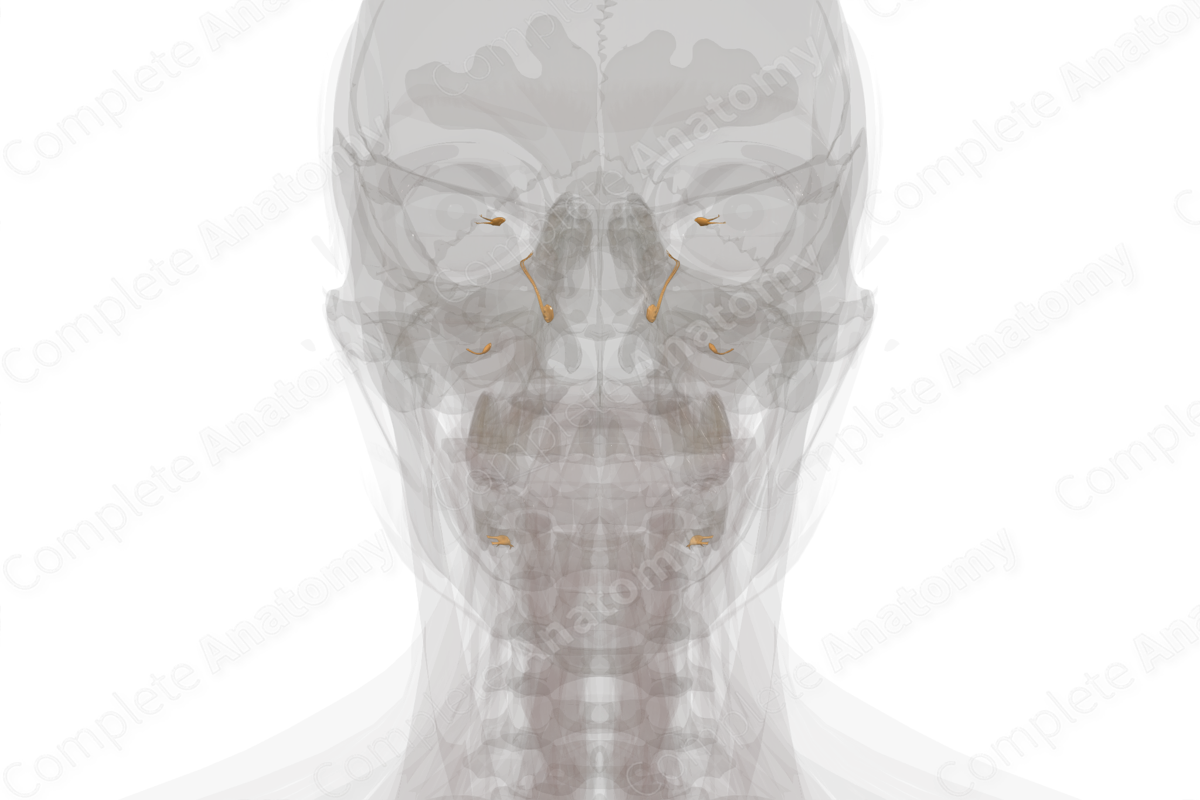
The cranial part of the craniosacral autonomic division is the parasympathetic part of the autonomic division that originates in the brainstem.
Neurons of the cranial division contribute in part to the following cranial nerves.
- Oculomotor nerve (CN III): Parasympathetic fibers associated with the oculomotor nerve control pupillary constriction and the accommodation reflex.
- Facial nerve (CN VII): Parasympathetic fibers associated with the facial nerve innervate most glands of the face, as well as the mucosa of the nasal cavity, palate, and paranasal sinuses.
- Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX): Parasympathetic fibers associated with the glossopharyngeal nerve control the parotid gland and some labial glands.
- Vagus nerve (CN X): Parasympathetic fibers associated with the vagus nerve control glands, mucosa, and smooth muscle in the pharynx, larynx, thorax, and abdomen, including all parasympathetic innervation to the foregut and midgut.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products





