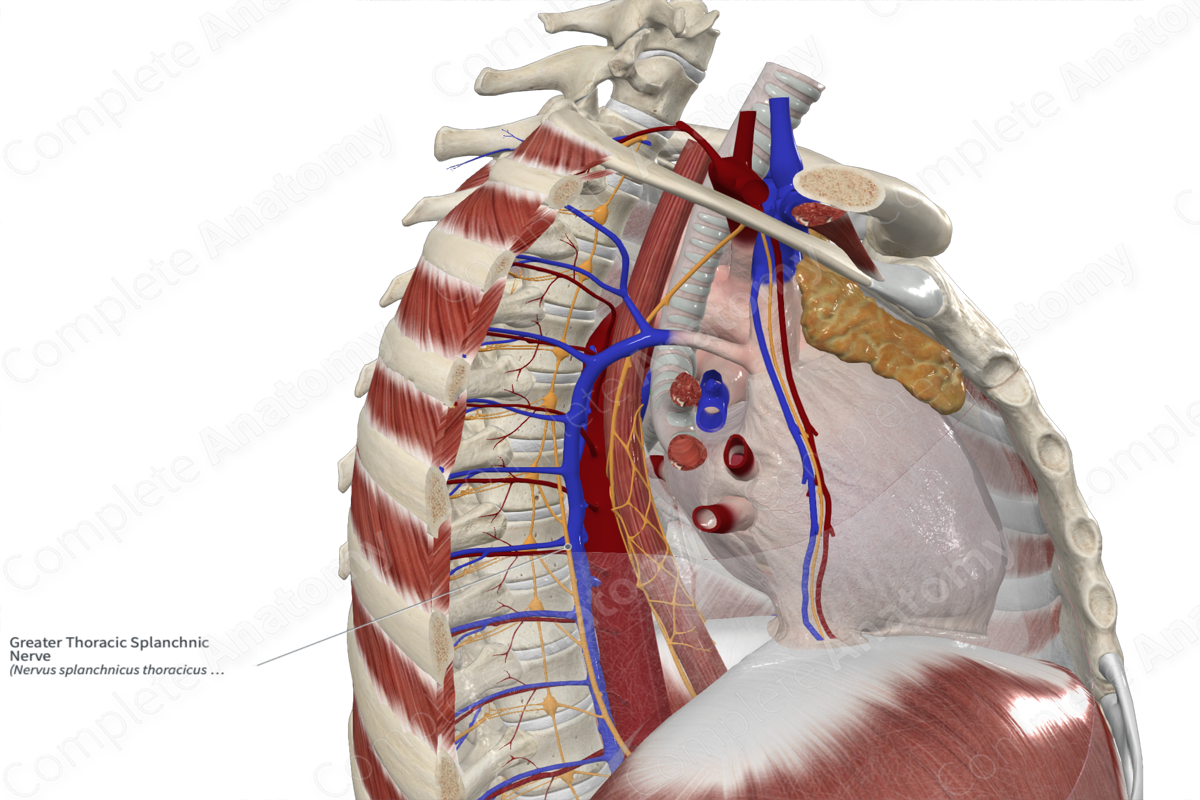
Quick Facts
Origin: Fifth to ninth thoracic nerves (T5—T9).
Course: Anteriorly and inferiorly from the thoracic sympathetic chain, piercing the diaphragm and running down through the abdomen to the celiac and superior mesenteric ganglia.
Branches: No branches.
Supply: Sympathetic innervation to the vessels and viscera associated with the celiac trunk, including the liver, gallbladder, spleen, and foregut.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The greater splanchnic nerve emerges from the sympathetic trunk ganglia, associated with the fifth to ninth thoracic nerve levels. These coalesce into the greater splanchnic nerve.
Course
The greater splanchnic nerve runs anteriorly towards the anterolateral surface of the vertebral bodies and inferiorly towards the abdomen. It pierces the diaphragm and runs through the abdomen to the celiac and superior mesenteric ganglia.
Branches
There are no branches of the greater thoracic splanchnic nerve.
Supplied Structures & Function
The sympathetic fibers of the greater splanchnic nerve synapse in the celiac ganglia. Postganglionic neurons in the celiac ganglia target the visceral organs of the foregut. This includes the liver, gallbladder, spleen, stomach, pancreas, and duodenum.
Visceral sensory fibers from the abdomen travel back to the central nervous system along the greater splanchnic nerve.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Splanchnic Nerve

The lumbar splanchnic nerves are extensions of the sympathetic trunk, originating from the L1-L3 nerve roots, and provide sympathetic innervation to the rectum and pelvic organs.