Quick Facts
Sympathetic Contribution: Lumbar splanchnic nerves.
Parasympathetic Contribution: Pelvic splanchnic nerves.
Course: Forms on and follows the inferior mesenteric artery and its branches. Some fibers also contribute to the inferior hypogastric plexus nerves.
Sympathetic Supply: Hindgut, pelvic organs, perineum, and external genitalia.
Parasympathetic Supply: Hindgut (from the distal half to one third of the transverse colon and rectum), pelvic organs, perineum, and external genitalia.
Contributing Nerves
Preganglionic sympathetic nerve cell bodies are primarily located in the first to second lumbar (L1 and L2) spinal cord segments. They do not synapse in lumbar paravertebral ganglia but descend to the third to fourth lumbar (L3 and L4) spinal cord segments and emerge from this spinal level. Lumbar splanchnic nerves travel to the inferior mesenteric ganglion, often by way of the celiac and aortic plexuses, and synapse here.
Parasympathetic preganglionic fibers leave the spinal cord as the pelvic splanchnic nerves. These nerves join the periarterial plexus along the superior rectal artery, or join the inferior hypogastric nerves/plexus, to ascend out of the pelvis and join the inferior mesenteric plexus.
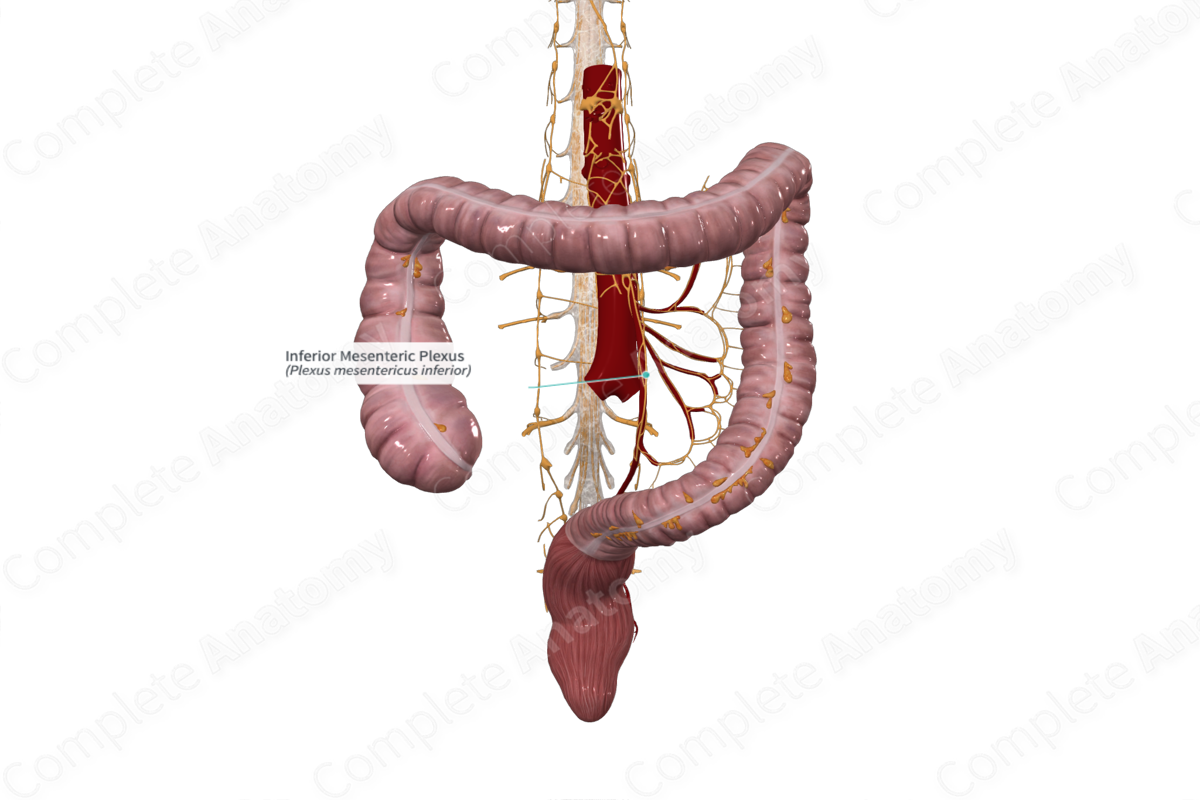
Course
The inferior mesenteric plexus forms a periarterial network of postganglionic sympathetic and preganglionic parasympathetic nerves, that surround the inferior mesenteric artery and its branches, or connects with the superior hypogastric plexus.
Branches
Subplexuses branch from the inferior mesenteric plexus, and follow the course of the left colic, sigmoid, and superior rectal arteries. Other subplexuses join the superior hypogastric plexus.
Supplied Structures
The plexus supplies postganglionic sympathetic and preganglionic parasympathetic nerves to the hindgut abdominal organs: the distal half to two thirds of the transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, and superior rectum. Other pelvic, perineal, and external genital organs receive sympathetic innervation by fibers passing along the superior rectal artery or the superior hypogastric plexus. These nerves join sacral and pelvic splanchnic nerves.
Visceral sensory fibers carrying afferents from the aforementioned organs pass through the inferior mesenteric plexus.
List of Clinical Correlates
—Urinary or fecal retention/incontinence
—Erectile dysfunction



