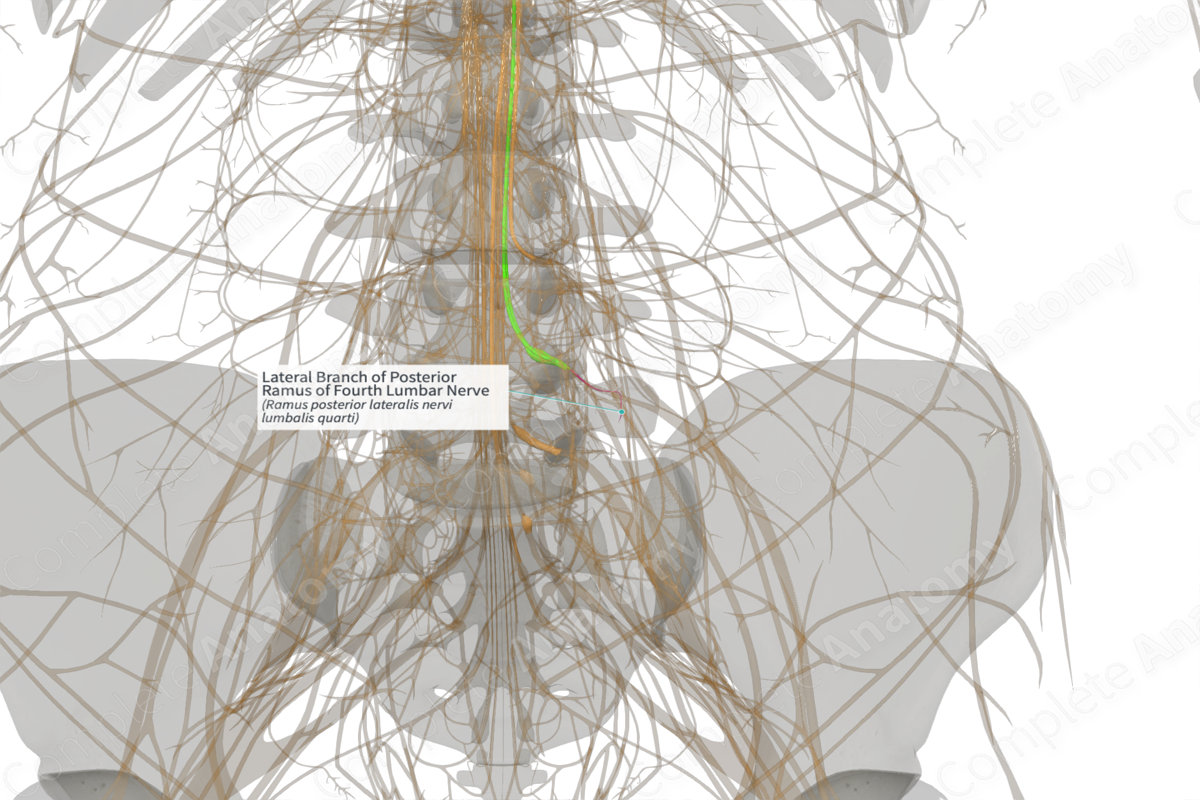
Lateral Branch of Posterior Ramus of Fourth Lumbar Nerve (Left)
Ramus posterior lateralis nervi lumbalis quarti
Read moreQuick Facts
Origin: Posterior ramus of fourth lumbar nerve.
Course: Crosses over the subjacent L5 transverse process to course laterally deep to longissimus and iliocostalis parts of the lumbar erector spinae. It remains entirely intramuscular.
Branches: None.
Supply: Motor innervation to longissimus and iliocostalis muscles.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
After the posterior ramus of the fourth lumbar nerve has traversed through intertransverse ligament and medial intertransverse muscle, a large lateral branch is given off, between the fourth and fifth lumbar vertebrae. In addition, the small medial neuronal branch is given off.
Course
The lateral branch crosses the subjacent fourth lumbar transverse process and pursues a sinuous course caudally, laterally, and dorsally through the longissimus and iliocostalis components of lumbar erector spinae muscle. Often, the muscular branch to longissimus comes off from the posterior ramus as a separate intermediate branch. These forms interneuronal loops with the corresponding branches of other posterior rami to innervate the muscle. The lateral branch of fourth lumbar nerve remains entirely intramuscular throughout its course (Bogduk, 2016, Boelderl et al., 2002).
Branches
There are no named branches.
Supplied Structures
The lateral branch supplies the longissimus and iliocostalis components of the lumbar erector spinae muscle.
List of Clinical Correlates
—Rhizolysis
References
Boelderl, A., Daniaux, H., Kathrein, A. and Maurer, H. (2002) 'Danger of damaging the medial branches of the posterior rami of spinal nerves during a dorsomedian approach to the spine', Clin Anat, 15(2), pp. 77-81.
Bogduk, N. (2016) 'Functional anatomy of the spine', Handb Clin Neurol, 136, pp. 675-88.

