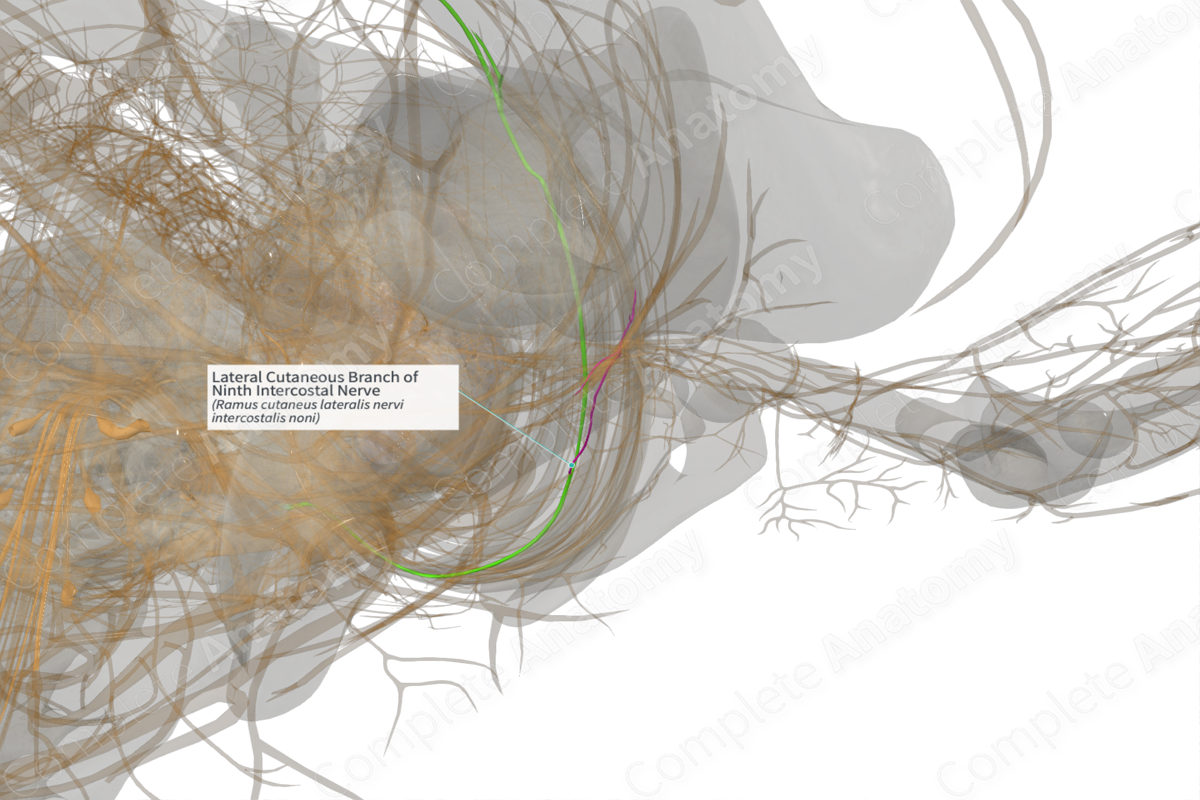
Lateral Cutaneous Branch of Ninth Intercostal Nerve (Right)
Ramus cutaneus lateralis nervi intercostalis noni
Read moreQuick Facts
Origin: Ninth intercostal nerve.
Course: Pierces the chest wall along the mid-axillary line.
Branches: Anterior and posterior branches.
Supply: Skin of the lateral abdominal wall.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The lateral cutaneous branch of anterior ramus of ninth thoracic nerve (or ninth intercostal nerve) arises from the anterior ramus of the ninth thoracic nerve roughly along the mid-axillary line.
Course
The lateral cutaneous branch may travel for a short distance with its parent nerve (the anterior ramus) within the intercostal space. It then pierces the thoracic wall through the internal and external intercostal muscles.
Branches
The lateral cutaneous branch further subdivides into anterior and posterior branches. The anterior branches extend anteriorly towards the rectus sheath, while the posterior branches extend backwards towards the latissimus dorsi muscle.
Supplied Structures & Function
The lateral cutaneous branch of the ninth intercostal nerve (or anterior ramus of ninth thoracic nerve) conveys sensory innervation from the skin overlying the lateral abdominal wall. See our dermatome map for cutaneous innervation.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Intercostal Nerve

Slipping rib syndrome is produced by impingement of an intercostal nerve between two costal cartilages, secondary to the subluxation of an interchondral articulation.




