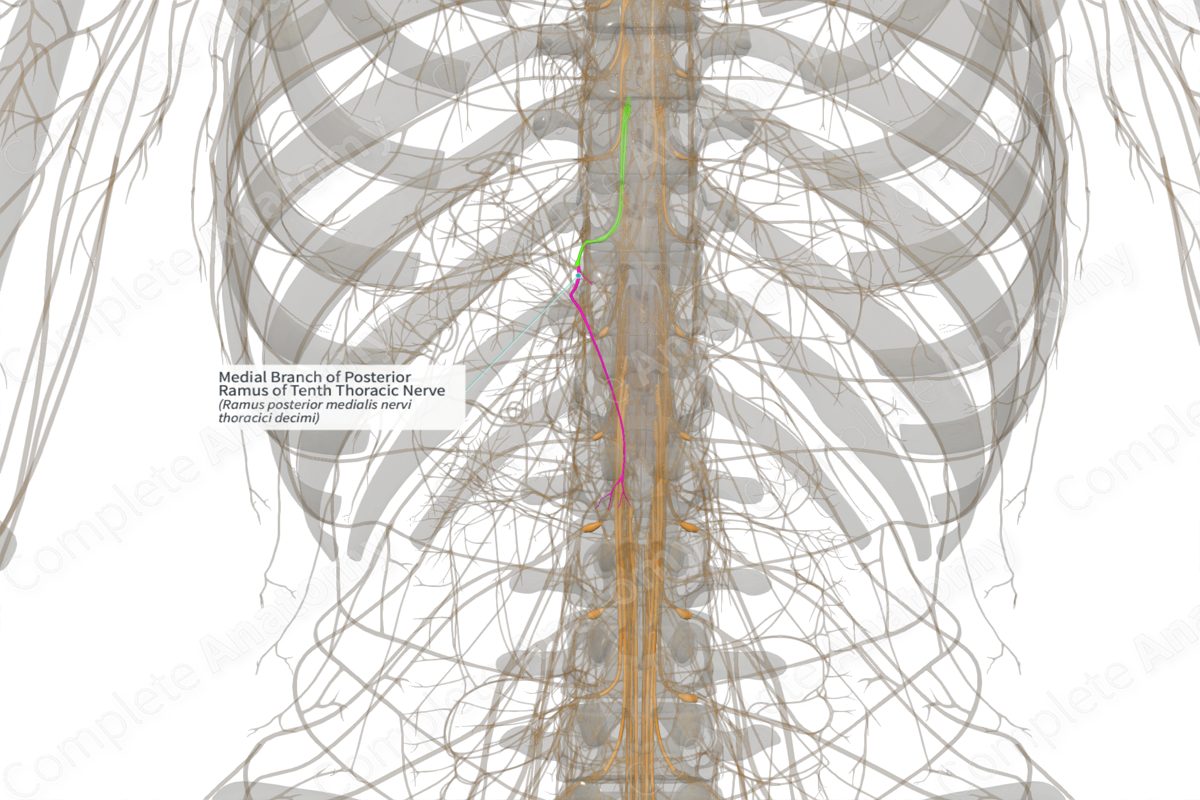
Medial Branch of Posterior Ramus of Tenth Thoracic Nerve (Right)
Ramus posterior medialis nervi thoracici decimi
Read moreQuick Facts
Origin: Posterior ramus of the thoracic nerve.
Course: Extends laterally over the transverse process of underlying vertebra, then passes medially between semispinalis thoracis and multifidus muscles.
Branches: Articular and cutaneous branches.
Supply: Motor innervation to intrinsic muscles of the back. Sensory innervation to zygapophyseal joints and to skin of the back (T1-T6).
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The medial branch is one of two branches that arise from of the posterior ramus of the thoracic nerves, the other being the lateral branch.
Course
Near the zygapophyseal joint, the posterior ramus of the thoracic nerve divides into medial and lateral branches. The medial branches continue laterally, briefly, to extend over the transverse process of the underlying vertebra. They then turn inferiorly and medially, coursing between the multifidus and semispinalis muscles.
The upper medial branches (T1-T6) continue to travel inferomedially, piercing through the rhomboid and trapezius muscles to reach the skin, adjacent to the spinous processes of the vertebrae. The lower medial branches (T7-T12) remain intramuscular, however, occasionally supply filaments to the skin.
Branches
The medial branches give rise to articular branches. The upper medial branches (T1-T6) also give rise to cutaneous branches as they pierce through the rhomboid and trapezius muscles to access the skin.
Supplied Structures
The medial branches of the posterior rami of thoracic nerves primarily supply motor innervation to the intrinsic muscles of the back, including multifidus, semispinalis thoracis, spinalis thoracis, interspinales thoracis, and rotatores muscles. All medial branches provide an articular branch to the zygapophyseal joint. The upper medial branches of the posterior rami (T1-T6) provide sensory innervation from the skin of the back (see our dermatome map for cutaneous innervation), while the lower medial branches (T7-T12) convey sensory innervation from its target epaxial muscles.




