Medial Branches of Posterior Rami of Lumbar Nerves (Left)
Rami posteriores mediales nervorum lumbalium
Read moreDescription
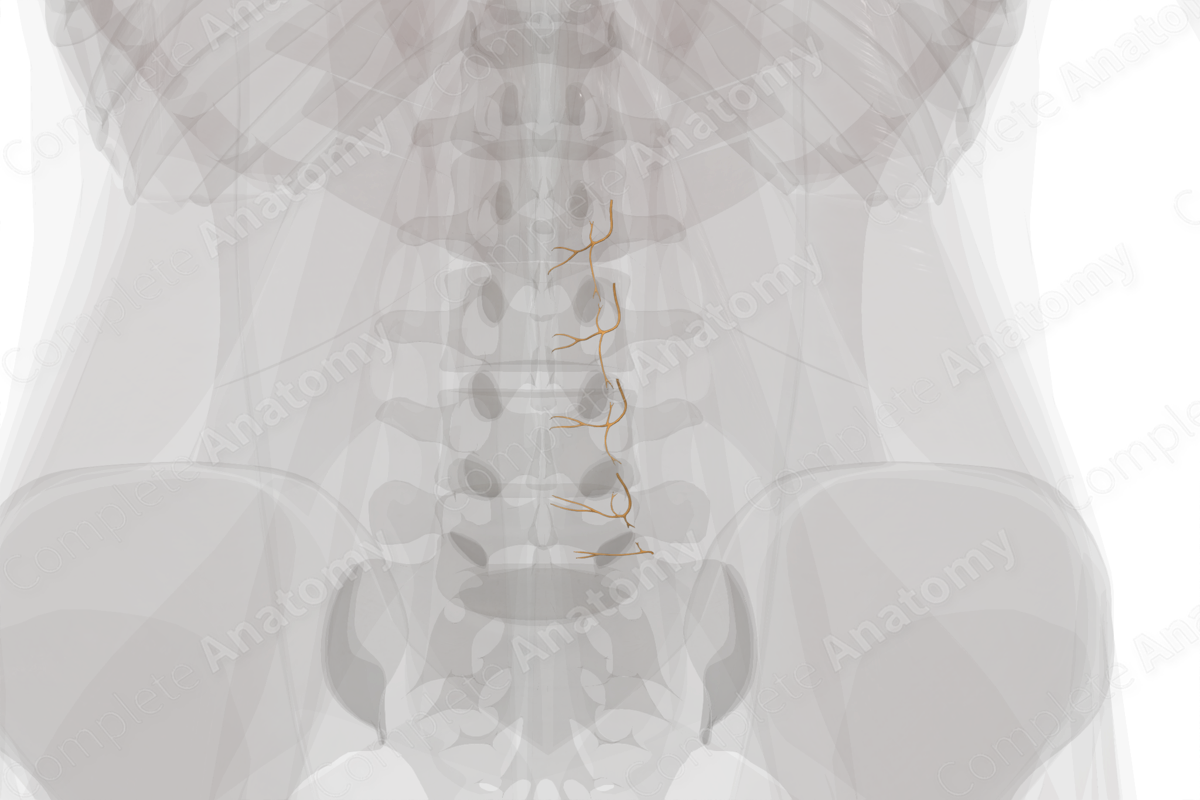
The posterior rami of each lumbar nerve give off a small medial neuronal branch, after the ramus has traversed through the intertransverse ligament and the medial intertransverse muscle. The medial branch continues dorsally and caudally, lying against the groove formed by the junction of the root of subjacent transverse process, with the root of the superior articular process of the vertebra below. Opposite the caudal border of the zygapophyseal joint, the medial branch turns medially through a groove between the mammillary process and accessory process. Here it is held tightly in the groove by the mamilloaccessory ligament, abridging these two processes. Beyond the mamilloaccessory ligament, the medial branch runs medially and caudally across the vertebral lamina. It lies deep to the multifidus muscle and gives off an interspinous branch. The medial branch eventually enters the multifidus muscle, via its deep surface, and breaks up into a separate division for each fascicle of multifidus of which it innervates (Bogduk, 2016).
Each medial branch gives off the following branches; muscular branches to the multifidus muscle fascicles; proximal and distal zygapophyseal nerves to the rostrally and caudally related zygapophyseal joints; and interspinous branches which emerge from the medial branch on the vertebral lamina (Boelderl et al., 2002).
Related parts of the anatomy
References
Boelderl, A., Daniaux, H., Kathrein, A. and Maurer, H. (2002) 'Danger of damaging the medial branches of the posterior rami of spinal nerves during a dorsomedian approach to the spine', Clin Anat, 15(2), pp. 77-81.
Bogduk, N. (2016) 'Functional anatomy of the spine', Handb Clin Neurol, 136, pp. 675-88.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products





