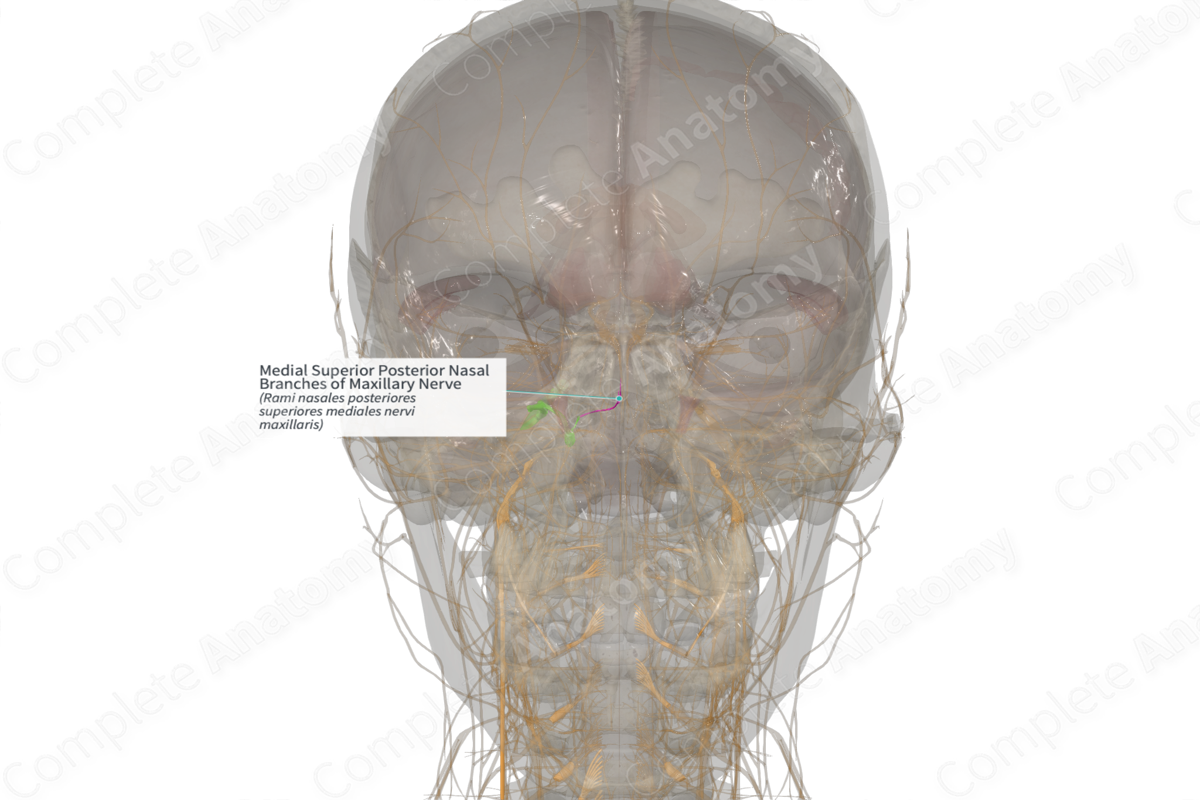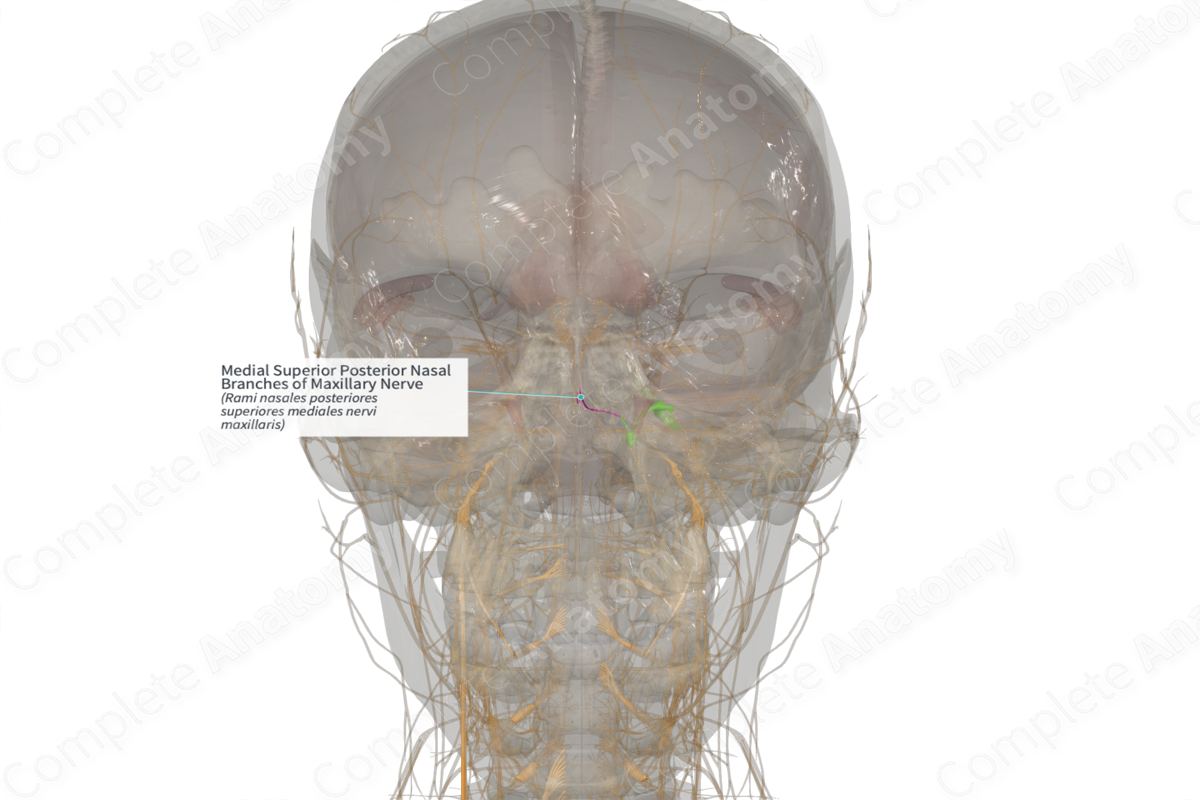
Medial Superior Posterior Nasal Branches of Maxillary Nerve (Right)
Rami nasales posteriores superiores mediales nervi maxillaris
Read moreQuick Facts
Origin: Posterior superior nasal nerve.
Course: Run medially and then anteriorly on the posterior part of the nasal septum.
Branches: None.
Supply: Sensory: conveys general sensation from the mucosa of the posterior nasal septum; Parasympathetic: innervation to mucosal glands of the same territories.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The medial superior posterior nasal branches of the maxillary nerve originate as branches from the posterior superior nasal nerve just after its entrance into the nasal cavity.
Course
From its origin, the medial superior posterior nasal branches run medially to the nasal septum and then inferiorly and anteriorly along the posterior portion of the nasal septum.
Branches
There are no named branches.
Supplied Structures
The medial superior posterior nasal branches of the maxillary nerve are mixed nerves carrying sensory and parasympathetic fibers. The sensory fibers have cell bodies located in the trigeminal ganglion while the parasympathetic fibers originate in the pterygopalatine ganglion.
The sensory fibers convey general sense information from the mucosal lining of the posterior nasal septum.
The parasympathetic fibers innervate the small mucosal glands of the same nasal territory.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Maxillary Nerve

The maxillary nerve, or second division of the trigeminal, is a sensory nerve that crosses the pterygopalatine fossa, traverses the orbit in the infraorbital groove and canal in the floor of the orbit, and appears upon the face at the infraorbital foramen as the infraorbital nerve.