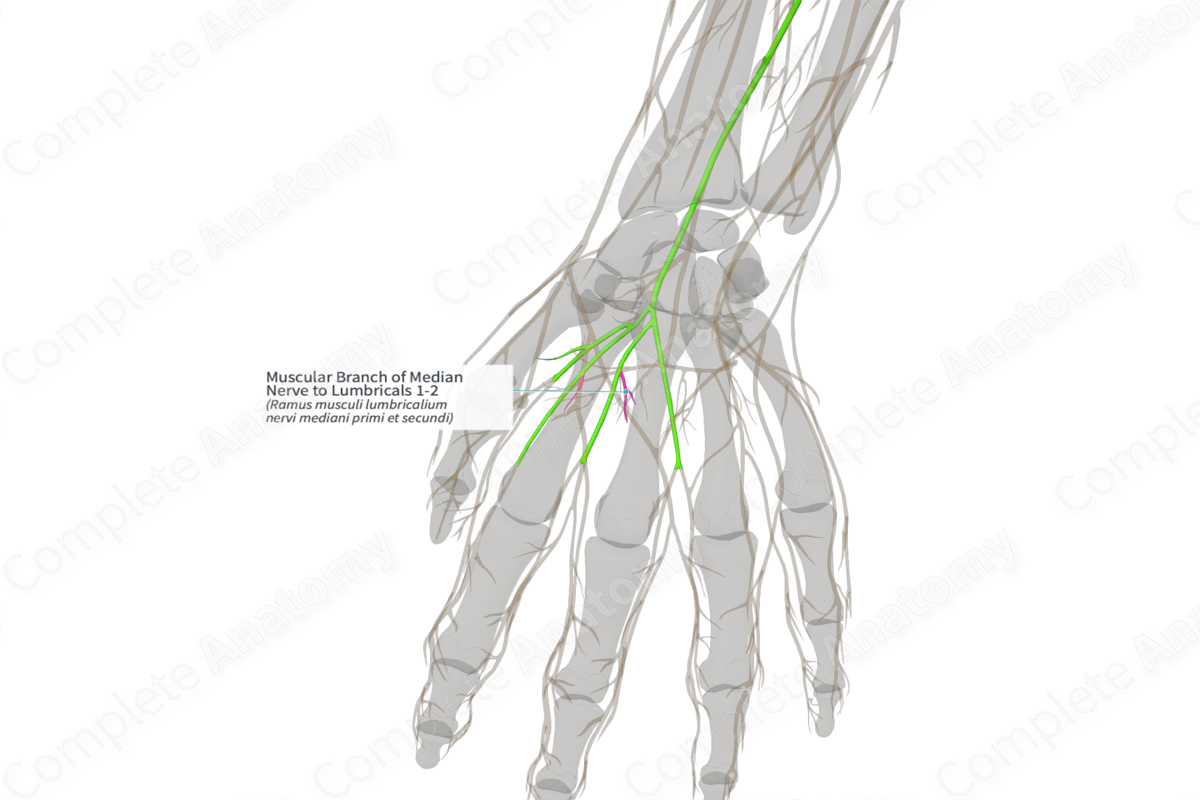
Muscular Branch of Median Nerve to Lumbricals 1-2 (Left)
Ramus musculi lumbricalium nervi mediani primi et secundi
Read moreQuick Facts
Origin: Common palmar digital branches of median nerve (C8, T1).
Course: As the median nerve splits into common palmar digital branches, a branch to the lateral side of the index finger also innervates the first lumbrical. The common palmar digital branch for the medial side of the index finger also innervates the second lumbrical.
Branches: None.
Supply: First and second lumbricals.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The median nerve enters the hand by passing through the carpal tunnel (i.e., deep to the flexor retinaculum) along with the long flexor tendons. After emerging from carpal tunnel, it divides into the common palmar digital branches. These innervate the first and second lumbricals.
Course
The common palmar digital branches can be divided into lateral and medial divisions. The lateral division supplies a muscular branch to the thenar muscles and three proper palmar digital branches. Out of the three digital branches, two supply the thumb and one lateral side of the index finger. The common palmar digital branch to the index finger also innervates the first lumbrical.
The medial division divides into two common digital branches for the second and third interdigital clefts, supplying the adjoining sides of the index, middle, and ring fingers. The common digital branch for the second interdigital cleft also innervates the second lumbrical.
Occasionally the first and second lumbricals could receive their innervation from the ulnar nerve.
Branches
There are no named branches.
Supplied Structures
The muscular branch of median nerve to lumbricals 1–2 provides motor innervation to the first and second lumbrical muscles.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products





