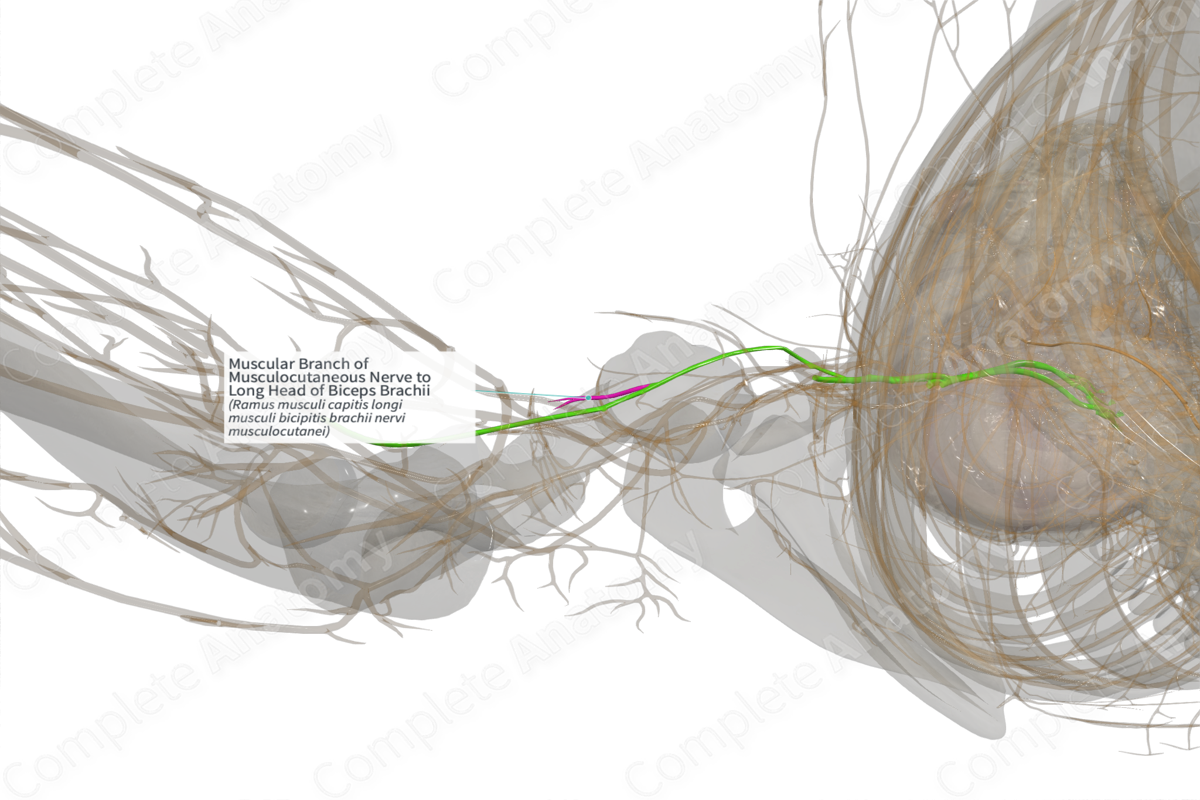
Muscular Branch of Musculocutaneous Nerve to Long Head of Biceps Brachii (Left)
Ramus musculi capitis longi musculi bicipitis brachii nervi musculocutanei
Read moreQuick Facts
Origin: Musculocutaneous nerve (C5—C7).
Course: Musculocutaneous nerve descends between brachialis and biceps brachii muscles, sending branches to innervates these muscles.
Branches: None.
Supply: Long head of the biceps brachii muscle.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The muscular branch to the long head of the biceps brachii muscle arises from the musculocutaneous nerve (C5—C7).
Course
Following its origin from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus, the musculocutaneous nerve leaves the axilla and enters the anterior compartment of the arm by piercing the coracobrachialis muscle. In the arm, it runs downwards and laterally between the biceps brachii superficially and brachialis deeper to reach the lateral side of the tendon of the biceps.
As the nerve descends between the two muscles, the muscular branches to biceps brachii are given off from the main nerve, at a distance of 11–13 cm from the acromial process. Usually a single branch arises from the main musculocutaneous nerve, which then splits into two secondary branches. One of these branches innervates the long head while the other innervates the short head (Type 1 pattern). In some other cases, the two branches are issued directly from two distinct points of the main nerve trunk and each branch makes its own way to each muscular head of the biceps (Type 2). In fewer cases, there are two branches given off from the musculocutaneous nerve. The proximal one splits into two secondary branches and each one supplies one head of the biceps muscle. The distal primary branch innervates the common belly of the biceps brachii (Type 3) (Pacha Vicente et al., 2005).
Branches
There are no named branches.
Supplied Structures
Muscular branches from the musculocutaneous nerve provide motor innervation to the flexor muscles of the anterior arm, including the muscular branch to the long head of biceps brachii.
List of Clinical Correlates
—Biceps reflex
—Nerve transfer surgery
References
Pacha Vicente, D., Forcada Calvet, P., Carrera Burgaya, A. and Llusá Pérez, M. (2005) 'Innervation of biceps brachii and brachialis: Anatomical and surgical approach', Clin Anat, 18(3), pp. 186-94.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Musculocutaneous Nerve

The musculocutaneous nerve is a terminal branch of the lateral cord of the brachial plexus that penetrates the conjoined tendon and innervates the brachialis and biceps muscles.




