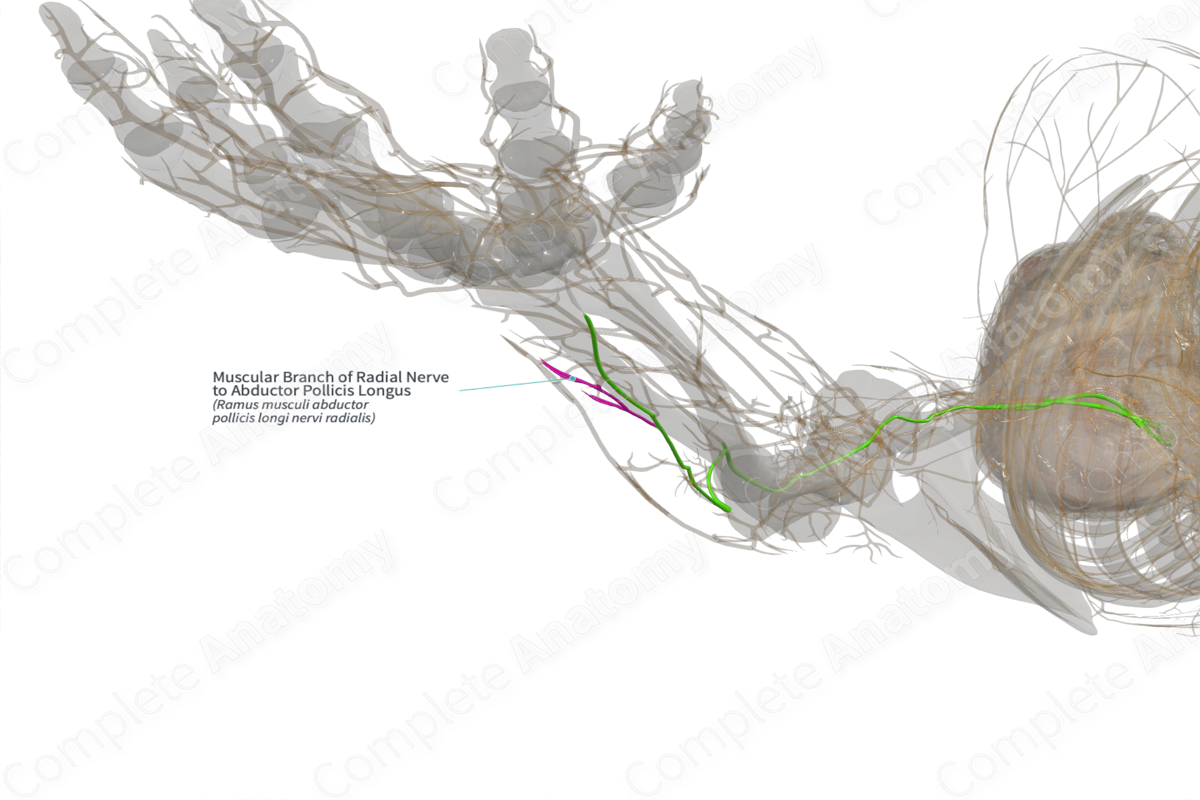
Muscular Branch of Radial Nerve to Abductor Pollicis Longus (Left)
Ramus musculi abductor pollicis longi nervi radialis
Read moreQuick Facts
Origin: Posterior antebrachial interosseous nerve (C7-C8).
Course: Arises from the posterior interosseous nerve as it descends and emerges distally from the supinator muscle.
Branches: None.
Supply: Abductor pollicis longus muscle.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
A motor nerve branch to abductor pollicis longus muscle originates from the posterior antebrachial interosseous nerve (distal continuation of the deep branch of radial nerve). It contains motor nerve fibers from the C7—C8 cervical spinal segments.
Course
The posterior antebrachial interosseous nerve is a continuation of the deep branch of radial nerve as it passes between the two heads of supinator muscle. The nerve changes its name to posterior antebrachial interosseous nerve after it has crossed the supinator muscle. It contains motor fibers which originate from the anterior horns of the C7-C8 cervical segments of the spinal cord. As it descends in the forearm, it gives of muscular branches to the extensor muscles of the forearm including extensor digitorum, extensor digiti minimi, extensor carpi ulnaris, supinator muscle, abductor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis brevis, extensor pollicis longus, and extensor indicis.
Branches
There are no named branches.
Supplied Structures
The muscle branch of radial nerve to abductor pollicis longus provides motor innervation to abductor pollicis longus muscle.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Radial Nerve

Radial tunnel syndrome: The radial tunnel refers to the segment of the radial nerve between the lateral intermuscular septum and the supinator.




