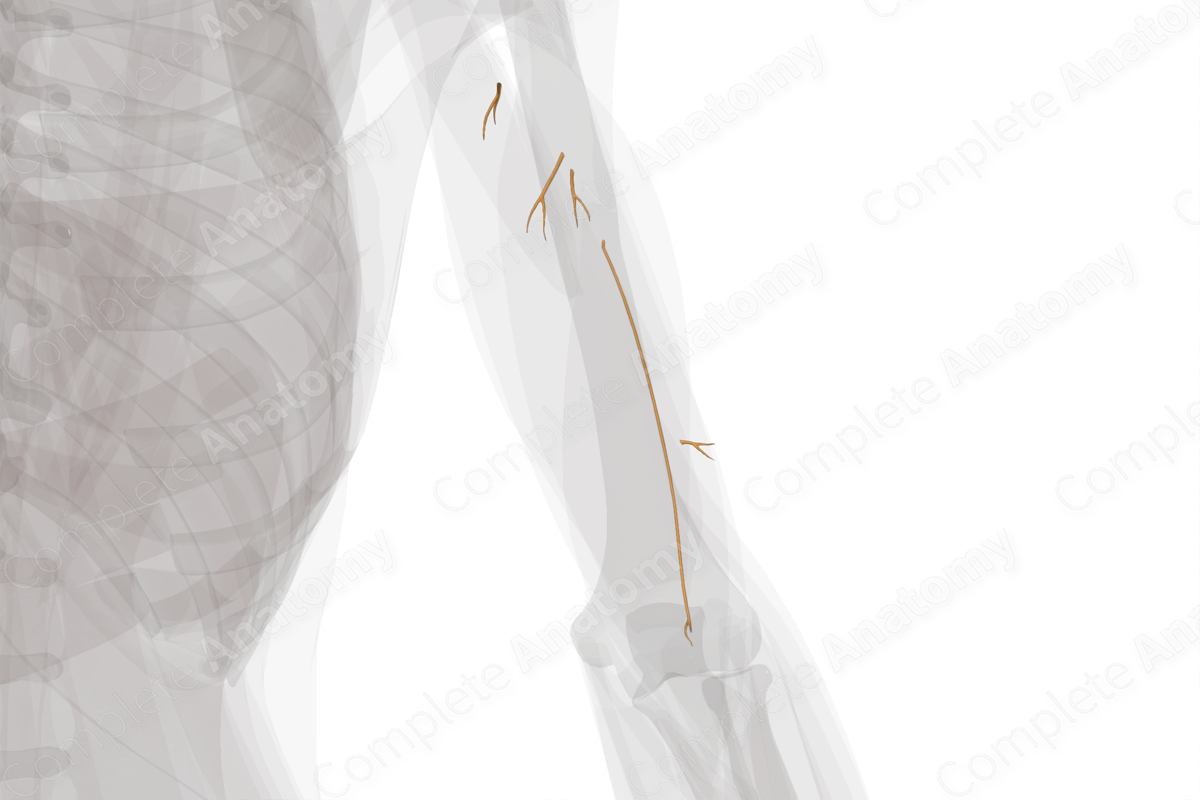
Muscular Branches of Radial Nerve (Arm, Left)
Rami musculares nervi radialis
Read moreDescription
The radial nerve arises from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. It descends against the posterior axillary wall and passes through the lower triangular space to descend further within the spiral radial groove. It pierces the lateral intermuscular septum to enter the anterior arm before reaching the cubital fossa.
Along its course it gives off numerous muscular branches.
—In the axilla (before entering the radial groove): two muscular branches to the long and medial heads of triceps brachii muscle.
—In the radial groove: three muscular branches to the lateral and medial heads of triceps brachii and the anconeus muscles.
—Inside the cubital fossa: three muscular branches to brachialis (lateral half), brachioradialis, and extensor carpi radialis longus muscles. Additionally, there are two terminal branches, the superficial and the deep branches. The posterior antebrachial interosseous nerve is generally considered to be a branch or continuation of the terminal deep branch of radial nerve; however, some authors use these names of these nerves interchangeably. The deep branch of radial nerve supplies the brachioradialis and extensor carpi radialis longus muscles, and then descends between the two heads of supinator muscle. Once the deep branch exits underneath the supinator muscle, it is referred to as the posterior antebrachial interosseous nerve. It innervates the extensor carpi radialis brevis, supinator, abductor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis brevis, extensor pollicis longus, extensor digitorum, extensor indicis, extensor digiti minimi, and extensor carpi ulnaris muscles. The superficial branch is given off inside the cubital fossa and runs on the lateral side of the forearm accompanied by the radial artery. It then curves posteriorly to descend until it reaches the anatomical snuff box where it ends by innervating the skin on the dorsum of hand.
Related parts of the anatomy




