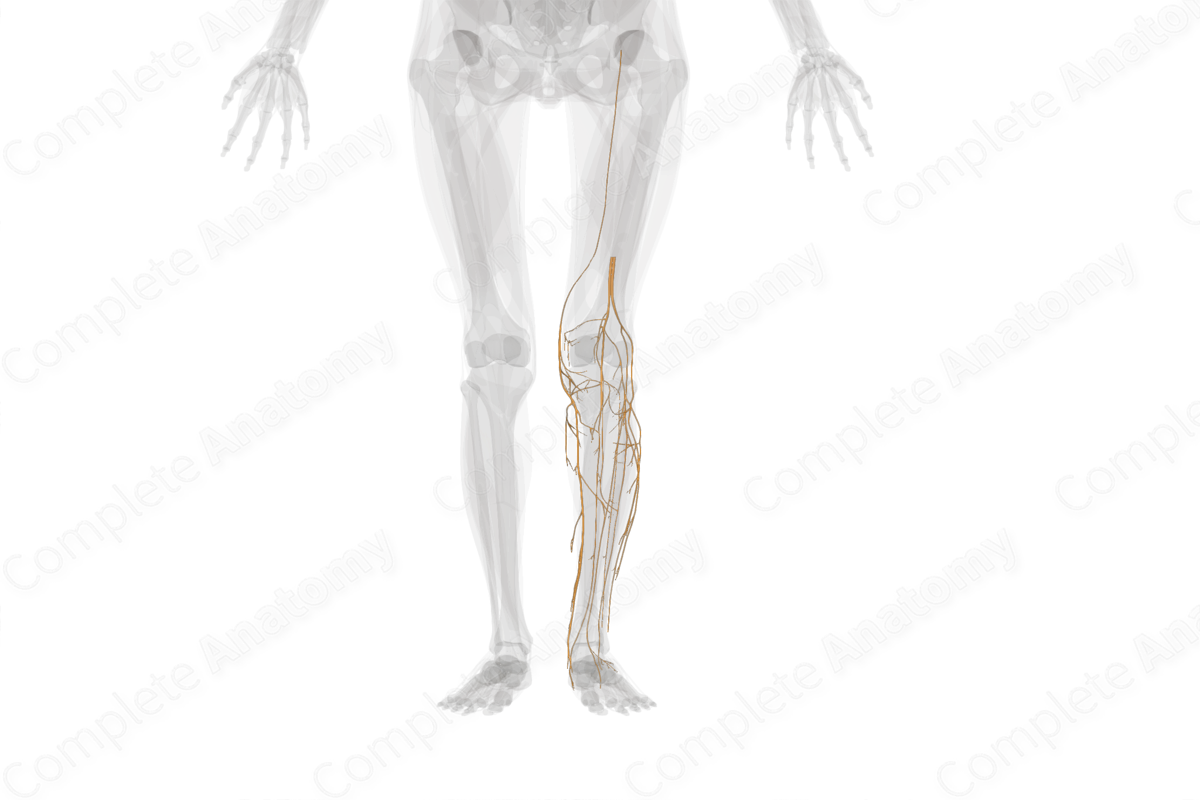
Description
The principal nerves of the knee and leg are the tibial, common fibular, and saphenous nerves.
The tibial and the common fibular nerves are the terminal continuation of the sciatic nerve. The tibial nerve innervates all muscles in the posterior compartment of the leg, while its terminal branches (medial and lateral plantar nerves) innervate most intrinsic muscles in the sole of the foot. In addition, the sural nerve, a branch of the tibial nerve, provides cutaneous innervation to the skin on the posterolateral side of the leg and lateral aspect of the ankle and foot.
The common fibular nerve innervates muscles in the anterior and lateral leg compartments, extensor digitorum brevis on the dorsum of the foot, and first two dorsal interossei in the sole of the foot. In addition, the superficial peroneal nerve, a branch of common peroneal nerve, provides cutaneous innervation to skin on lateral aspect of the leg, ankle, and dorsum of the foot.
The posterior femoral cutaneous nerve arises from the sacral plexus and gives off cutaneous branches in the gluteal, perineal, and posterior thigh regions. It extends further down to provide sensory innervation to the skin of the upper posterior leg.
The saphenous nerve is a long cutaneous branch of the femoral nerve, which provides sensory innervation to the skin as far distally as the medial side of the knee, leg, and the foot.




