Quick Facts
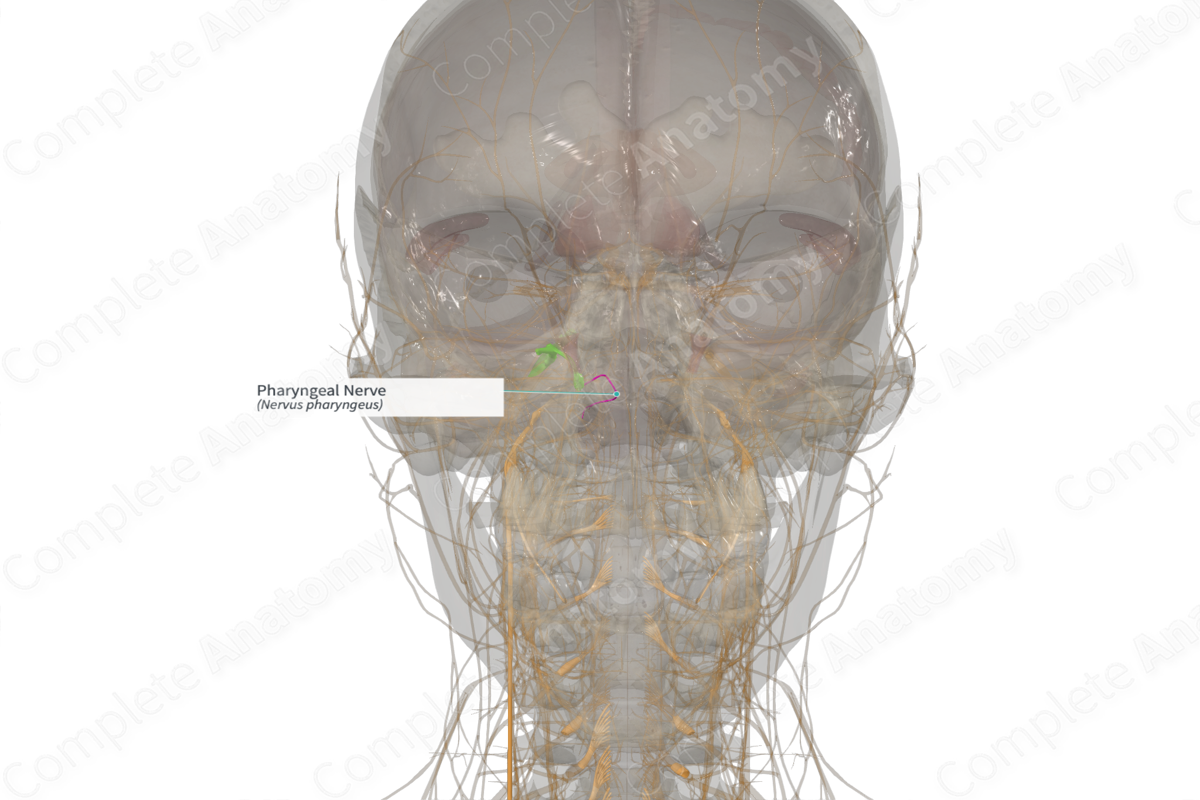
Origin: Pterygopalatine ganglion.
Course: Runs posteriorly through the pharyngeal canal, exiting into the nasopharynx.
Branches: None.
Supply: Sensory: conveys general sensation from the mucosa of the nasopharynx; Parasympathetic: innervation to mucosal glands of the same territory.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The pharyngeal nerve originates as a branch of the maxillary nerve. It branches off the posterior aspect of the pterygopalatine ganglion.
Course
From its origin, the pharyngeal nerve runs posteriorly through the pharyngeal or palatovaginal canal. It emerges into the upper lateral nasopharynx between the sphenoid and palatine bones together with the pharyngeal branch of the maxillary artery.
Branches
There are no named branches; however, the pharyngeal nerve can communicate with fibers of the glossopharyngeal nerve in the lower boundary of the nasopharynx.
Supplied Structures
The pharyngeal nerve is a mixed nerve carrying sensory and parasympathetic fibers. The sensory fibers have cell bodies located in the trigeminal ganglion while the parasympathetic fibers originate in the pterygopalatine ganglion.
The sensory fibers convey general sense information from the mucosa of the nasopharynx.
The parasympathetic fibers innervate the small mucosal glands of the same territory.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products


