Quick Facts
Sympathetic Contribution: Preganglionic efferent fibers from T5-T9 spinal cord levels travel via the greater splanchnic nerve to the celiac ganglion. Postganglionic efferent fibers originating here run to the phrenic plexus.
Parasympathetic Contribution: Preganglionic efferent fibers from the vagus nerve travel via the vagal trunks to the celiac ganglion and then to the phrenic plexus.
Course: Lies on the surface of the inferior phrenic artery.
Sympathetic Supply: These efferent fibers innervate the vascular smooth muscle of the inferior diaphragmatic surface, inferior vena cava, and suprarenal glands.
Parasympathetic Supply: These efferent fibers innervate glandular tissue of the suprarenal glands.
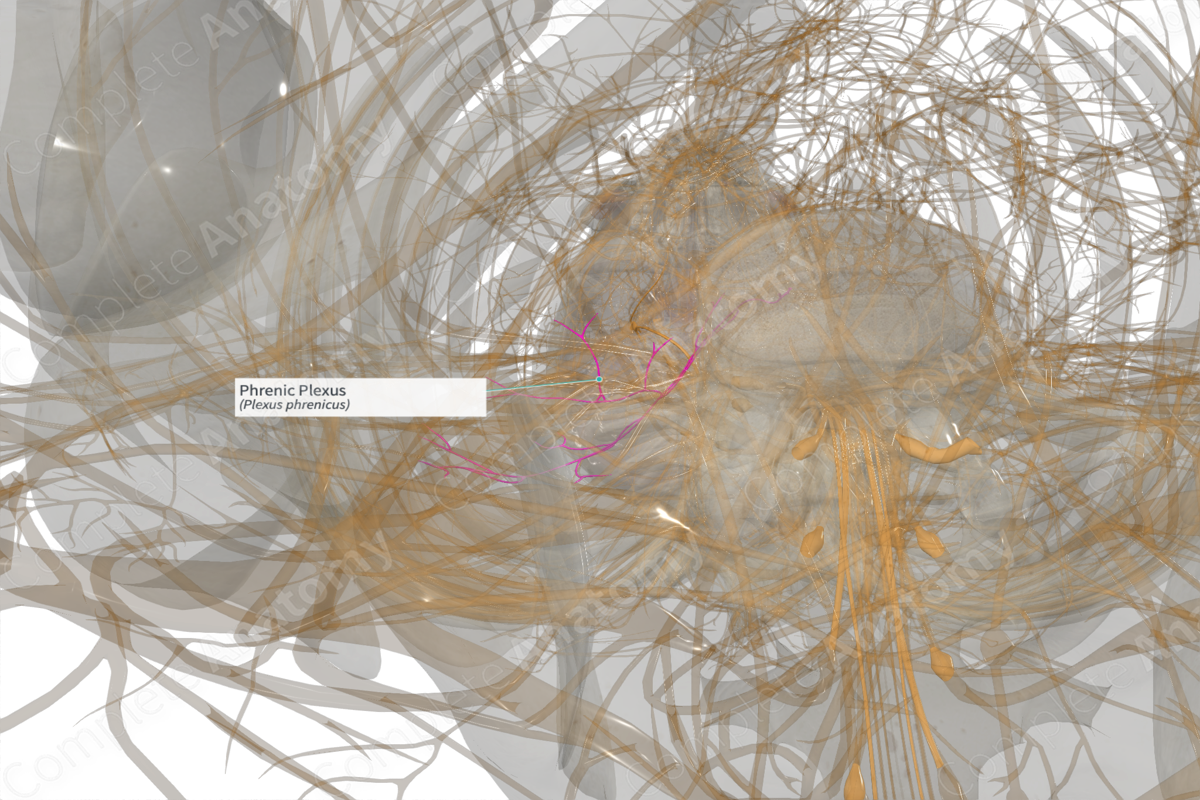
Contributing Nerves
The phrenic plexus is continuous with the celiac plexus. It also receives fibers from the phrenic nerve.
Sympathetic fibers originating from T5-T9 spinal cord levels travel via the greater splanchnic nerve to the celiac ganglion. Postganglionic efferent fibers originating here run to the phrenic plexus.
Parasympathetic fibers from the vagus nerve travel via the vagal trunks to the celiac ganglion and then to the phrenic plexus.
Visceral sensory afferent fibers from the inferior surface of the diaphragm, peritoneum, and suprarenal glands travel via the phrenic plexus on their way to the CNS.
Somatic motor efferent fibers from the phrenic nerve (C3-C5) pass through the phrenic plexus on their way to the inferior surface of the diaphragm muscle.
Course
The phrenic plexus is a bilateral plexus found on the inferior phrenic artery, just superior to the celiac trunk and near the diaphragmatic crura.
Branches
The phrenic plexus does not give rise to named branches. It is connected to the celiac plexus and receives fibers from the phrenic nerve.
Supplied Structures
The phrenic plexus is a mixed plexus conveying somatic, sympathetic, and parasympathetic nerves to the diaphragm or its vascular tissues, the inferior vena cava, and the suprarenal glands. It also conveys visceral sensory nerves back to the CNS.
Sympathetic efferent fibers of the phrenic plexus innervate vascular smooth muscle of the inferior phrenic arterial territories on the diaphragm, suprarenal glands, and the inferior vena cava.
Parasympathetic efferent fibers of the phrenic plexus innervate the suprarenal glands.
Somatic efferent fibers of the phrenic plexus innervate muscle fibers on the inferior surface of the diaphragm.
Visceral sensory fibers carrying afferents from the diaphragm and suprarenal glands run through the phrenic plexus.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products





