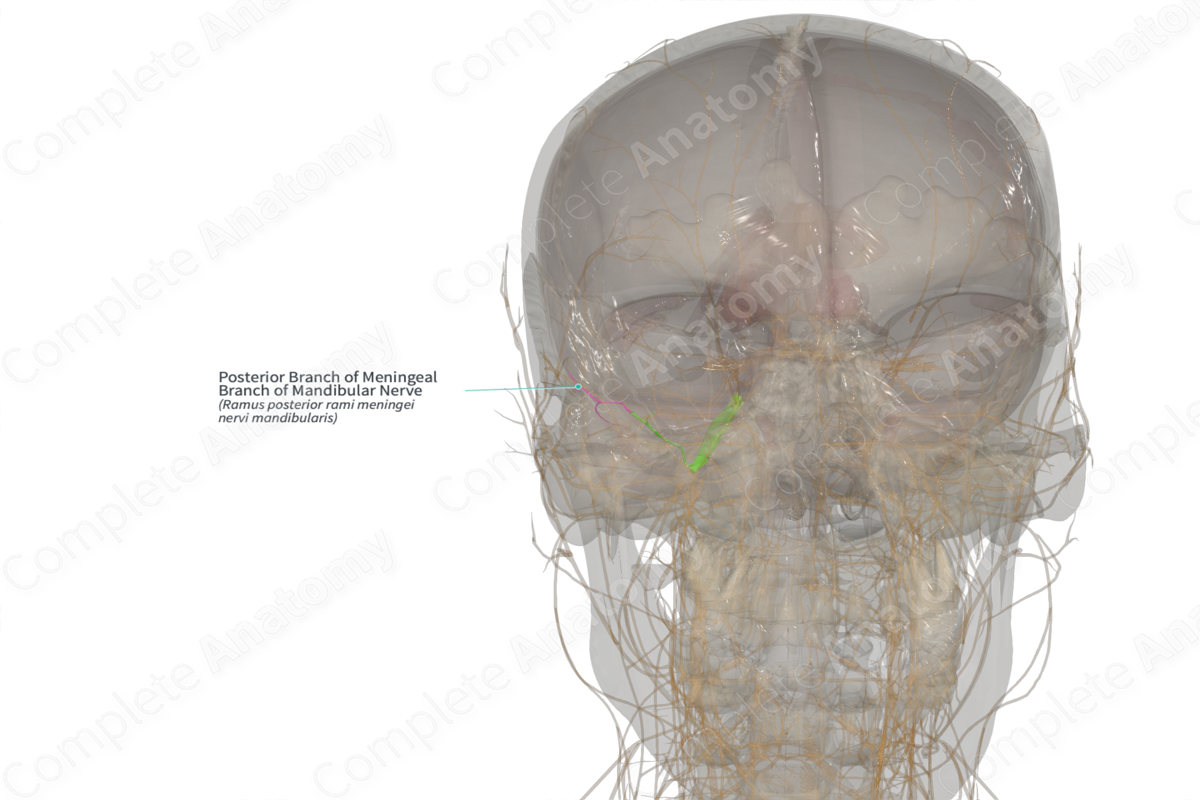
Posterior Branch of Meningeal Branch of Mandibular Nerve (Left)
Ramus posterior rami meningei nervi mandibularis
Read moreQuick Facts
Origin: Meningeal branch of trigeminal nerve.
Course: Roughly follows the middle meningeal artery branches that distribute to the dura mater of the middle cranial fossa.
Branches: None.
Supply: Conveys general sense fibers from the dura of the middle cranial fossa and the mucosal lining of the mastoid air cells.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The posterior branch of the meningeal branch of trigeminal nerve is one of two branches. It originates intracranially after the meningeal branch of the trigeminal nerve passes through the foramen spinosum and bifurcates. Its sensory fibers have cell bodies located in the trigeminal ganglion.
Course
The posterior branch of the meningeal branch of trigeminal nerve follows branches of the middle meningeal artery to be distributed to dura of the posterior half of the middle cranial fossa. Fibers run posteriorly to the mastoid air cells of the temporal bone.
Branches
There are no named branches.
Supplied Structures
The posterior branch of the meningeal branch of trigeminal nerve is a sensory nerve. It conveys general sense fibers from the dura of the posterior half of the middle cranial fossa and the mastoid air cells.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products


