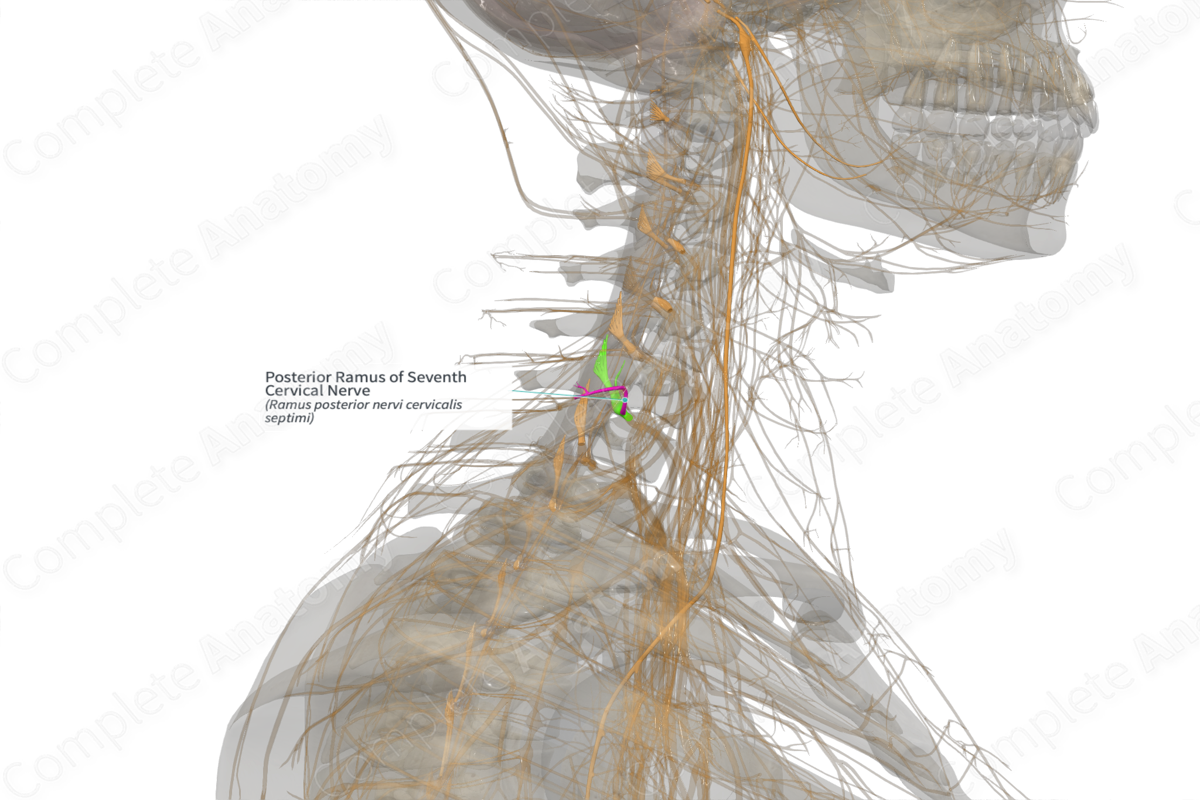
Posterior Ramus of Seventh Cervical Nerve (Left)
Ramus posterior nervi cervicalis septimi
Read moreQuick Facts
Origin: Seventh cervical nerve.
Course: Winds posteriorly around the C7 articular pillar and divides into its branches.
Branches: Medial and lateral branches.
Supply: Motor innervation to semispinalis capitis, multifidus, interspinales, longissimus colli, splenius colli, and iliocostalis colli muscles. Sensory innervation to the skin just below the neck.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The posterior ramus of seventh cervical nerve is one of two branches of the seventh cervical nerve, the other being the anterior ramus.
Course
The posterior ramus of the seventh cervical nerve runs backwards and winds around the articular pillar of C7 vertebra.
Branches
The posterior ramus of the seventh cervical nerve gives rise to medial and lateral branches.
Supplied Structures
The lateral branch of the dorsal ramus provides motor somatic innervation to the longissimus colli, splenius colli, and iliocostalis colli muscles. Those which pass through the medial branch provide motor innervation to multifidus, semispinalis colli, semispinalis capitis, splenius colli, and trapezius, before becoming cutaneous.
The sensory afferent neurons, which provide innervation to the skin above the trapezius, transmit general sensory information regarding pain, touch, pressure, vibration, etc. via the medial branch of the dorsal ramus.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products




