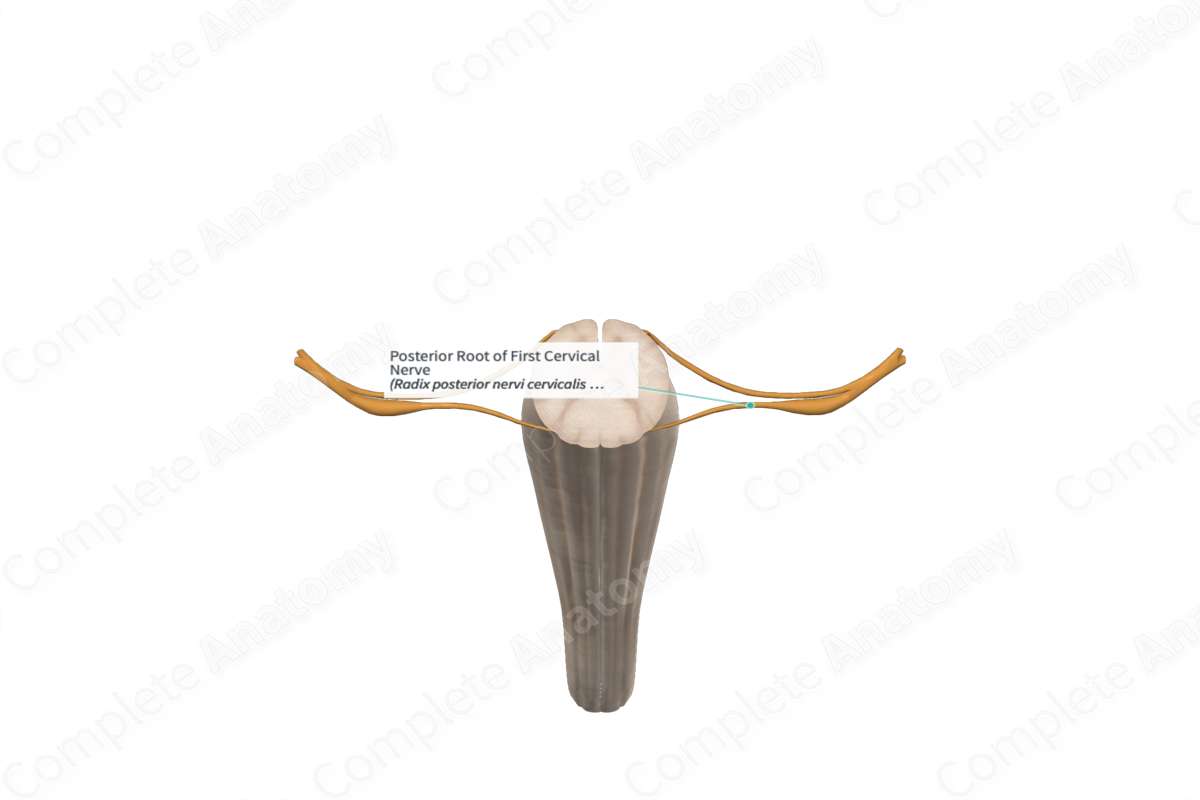
Posterior Root of First Cervical Nerve
Radix posterior nervi cervicalis primi
Read moreQuick Facts
Origin: First cervical nerve.
Course: Medially towards the posterior side of the spinal cord.
Branches: None.
Supply: Afferent fibers from somatic and visceral sensory receptors send information from the meninges and atlantooccipital joint to the spinal cord.
Origin
The posterior root of the first cervical nerve originates just lateral to or in the intervertebral foramen, between the occipital bone and the atlas (C1 vertebra). This corresponds to the point where the cervical nerve splits into anterior and posterior roots.
The posterior root of the first cervical nerve is much smaller in comparison to its corresponding anterior root. It is often absent in about 8% of the population, while others report that is it frequently or never present (Tubbs, Shoja and Loukas, 2016).
Course
The posterior root of the first cervical nerve runs medially towards the posterior side of the spinal cord. Adjacent to the appropriate spinal cord level, the posterior root splits into smaller rootlets, which enter the posterior spinal cord in line with the dorsal horn of the gray matter.
Branches
There are no branches of the posterior root of the first cervical nerve. The proximal end of the posterior root has a bulge called the spinal (or dorsal root) ganglion, which is the location of the neuronal cell bodies of the neurons that form the posterior root.
Supplied Structures
The posterior root of the first cervical nerve carries all afferents from the first cervical nerve to the first cervical spinal segment of the spinal cord.
Small filaments from the meninges and the atlantooccipital joint join the suboccipital nerve (or the posterior ramus) which conveys sensory information to the first cervical nerve and its posterior root (Ouaknine & Nathan, 1973).
References
Ouaknine, G. & Nathan, H. (1973) Anastomotic connections between the eleventh nerve and the posterior root of the first cervical nerve in humans. J Neurosurg, 38(2), 189-97.
Tubbs, R. S., Shoja, M. M. & Loukas, M. (2016) Bergman's Comprehensive Encyclopedia of Human Anatomic Variation. Wiley.



