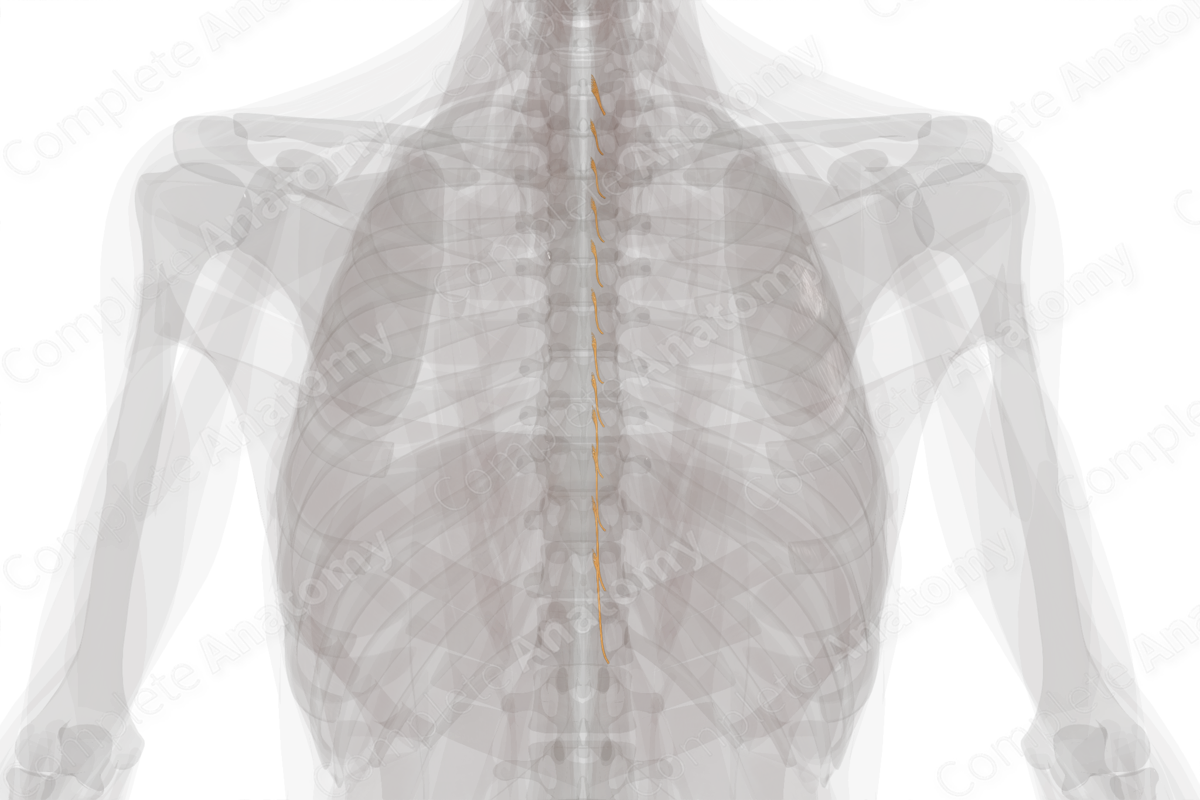
Posterior Roots of Thoracic Nerves (Left)
Radices posteriores nervorum thoracicorum
Read moreDescription
The posterior root of the thoracic nerve (dorsal or sensory root) originates just lateral to or in the intervertebral foramen, corresponding to the point where the thoracic nerve splits into anterior and posterior roots.
The posterior roots consist of afferent fibers that convey sensory signals from the body to the central nervous system. This includes somatic sensation conveying signals, such as touch, temperature, and pain, as well as visceral sensation from organs, viscera, glands, and blood vessels.
Afferent neurons of the posterior root are primarily pseudounipolar. Their axons carry information from the periphery and terminate in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord, passing their cell bodies which lay in the spinal ganglion (or dorsal root ganglion).
At their distal ends, the posterior roots typically join their anterior root counterparts to form a spinal nerve, which consists of both sensory and motor nerve fibers.
Related parts of the anatomy
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products





