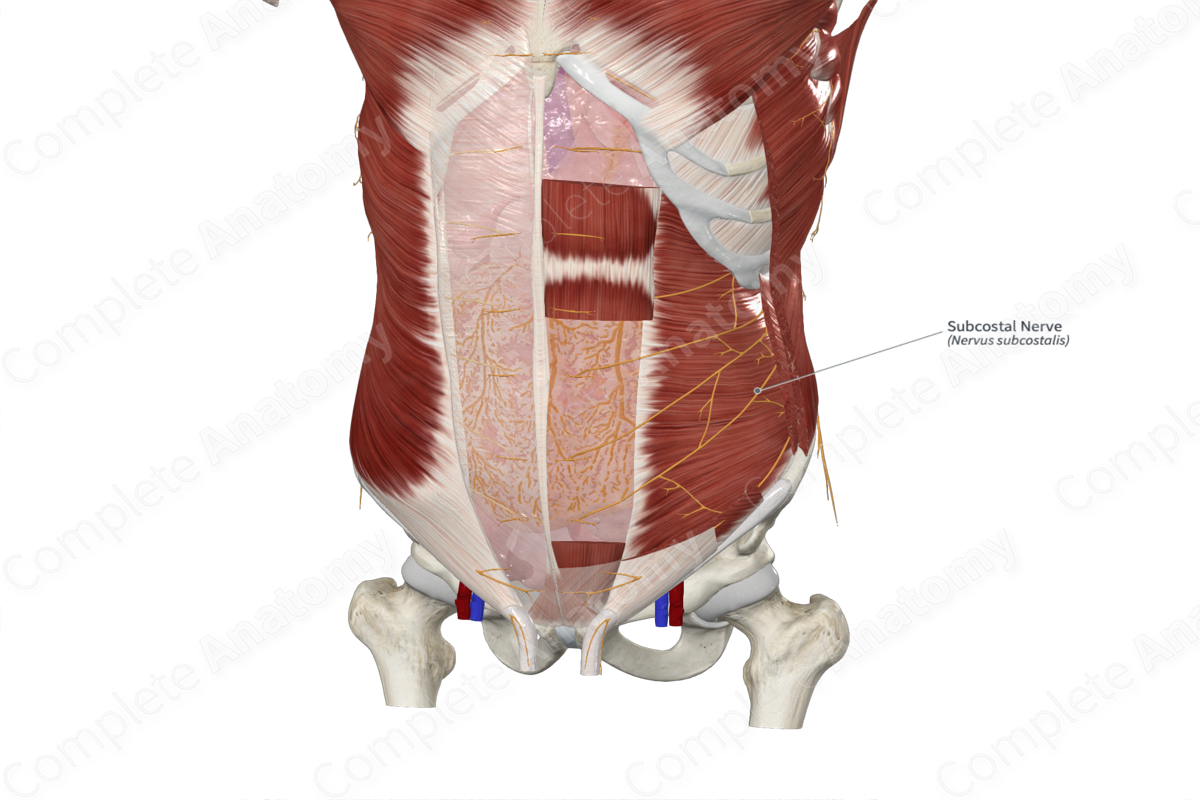
Quick Facts
Origin: Twelfth thoracic nerve.
Course: Lateral, just inferior to the twelfth rib.
Branches: Communicating branch to iliohypogastric nerve, lateral cutaneous and anterior cutaneous branches.
Supply: Abdominal muscles and skin of abdominal and anterior gluteal regions.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The anterior ramus of twelfth thoracic nerve (or subcostal nerve) is one of two branches of the twelfth thoracic nerve, the other being the posterior ramus.
Course
The bulk of the anterior ramus of the twelfth thoracic nerve runs laterally from the spinal nerve, inferior to the twelfth rib and between the lateral arcuate ligament and the quadratus lumborum muscle. It is also accompanied by an intercostal artery and vein, where the vein sits closest to the rib above, followed by the artery and nerve.
The anterior ramus continues laterally and ventrally between the transversus abdominis and internal abdominal oblique muscles.
Branches
Soon after its origin, the anterior ramus of the twelfth thoracic nerve can send a communicating branch to the iliohypogastric nerve (or the dorsolumbar nerve). It also gives off lateral and anterior cutaneous branches during its course.
Supplied Structures & Function
The subcostal nerve supplies the transversus abdominis, internal abdominal oblique, and external abdominal oblique muscles. It contributes to the iliohypogastric nerve, thus supplying the pyramidalis muscle. Its anterior and lateral cutaneous branches serve the skin of the abdominal wall and the skin of the lateral gluteal region.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products





