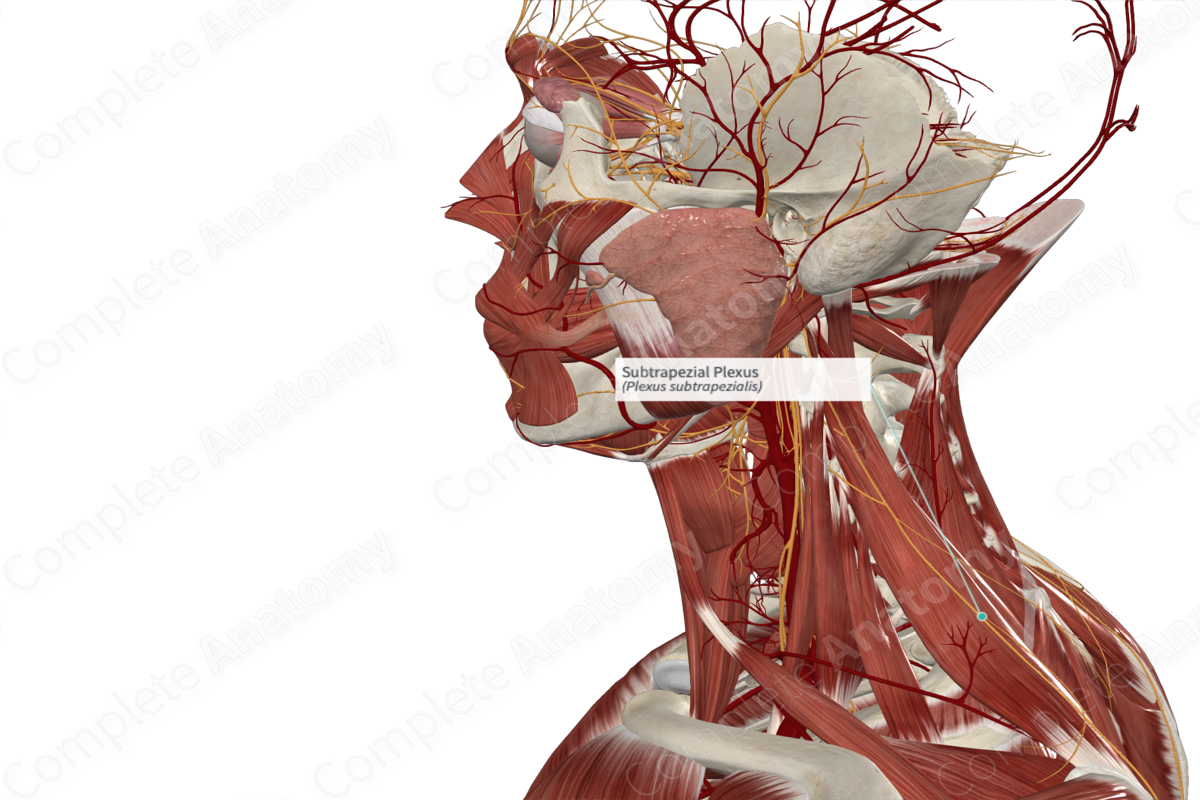
Quick Facts
Origin: Spinal accessory nerve and second and third cervical nerves (C2-3).
Course: From the anastomosis on the transverse deep surface of the trapezius, fibers run laterally and inferiorly to innervate the lower two thirds of the trapezius.
Branches: None.
Supply: Motor innervation to the ascending and transverse fibers of the trapezius muscle.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The subtrapezial plexus on the deep surface of trapezius muscle consists of fibers from two sources, namely the spinal accessory nerve and the second and third cervical nerve levels of the cervical plexus.
Course
The spinal accessory and cervical plexus nerve fibers converge on the deep surface of the trapezius muscle, in the transverse fiber region. From here, fibers run laterally, to the transverse portion, and inferiorly, to the ascending portion, of the trapezius muscle.
Branches
There are no named branches.
Supplied Structures
The subtrapezial plexus is a motor nerve plexus that innervates the transverse and ascending fibers, corresponding to roughly the lower two thirds of the trapezius muscle. The upper third of trapezius is innervated by a separate unnamed branch of the spinal accessory nerve (Kierner et al, 2001).
References
Kierner, A. C., Zelenka, I. & Burian, M. (2001) How do the cervical plexus and the spinal accessory nerve contribute to the innervation of the trapezius muscle? As seen from within using Sihler's stain. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 127(10), 1230-2.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products




