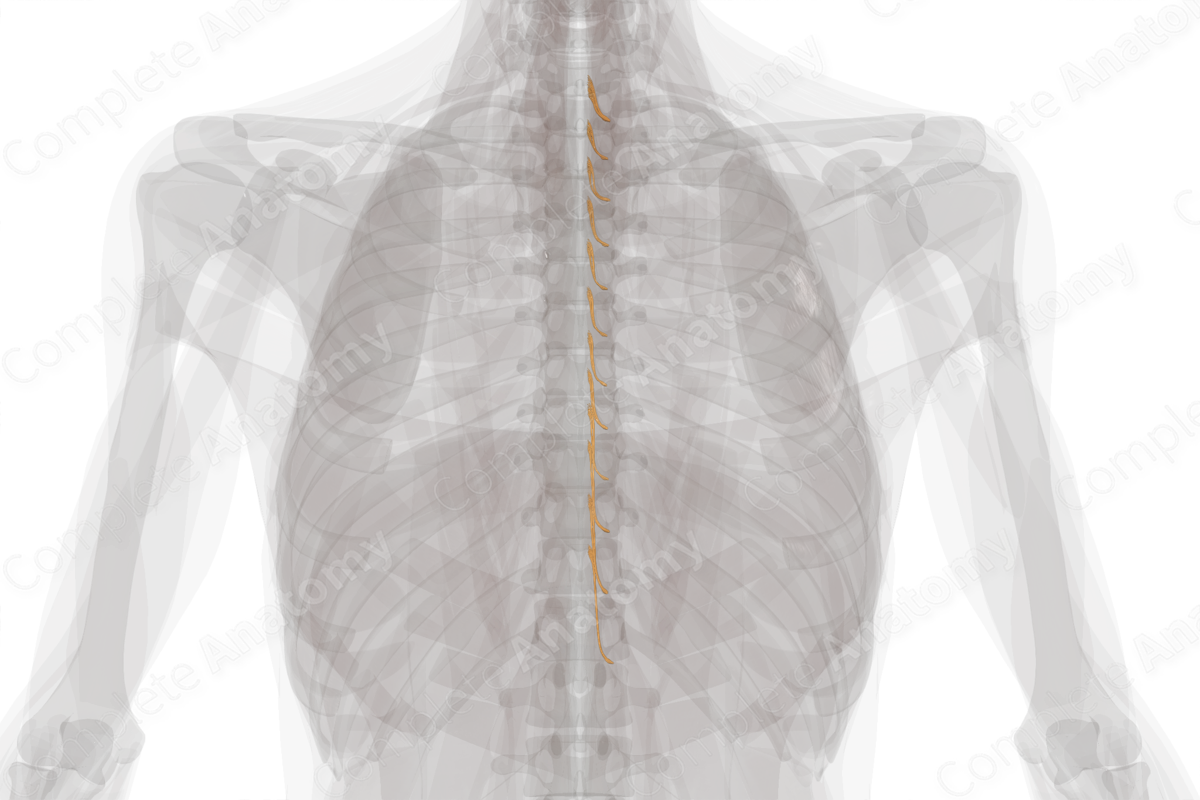
Thoracic Spinal Roots & Ganglia (Left)
Radicis et ganglia spinalia thoracici
Read moreThoracic Spinal Roots & Ganglia (Left) Description
Anterior and posterior roots emerge from each level of the spinal cord. The anterior roots carry motor (efferent) information away from the spinal cord to their targets in the body. The posterior roots carry sensory (afferent) information to the spinal cord.
Within the intervertebral foramina, the anterior and posterior roots unite to form a spinal nerve. Therefore, spinal nerves are “mixed nerves” and contain both afferent and efferent axons, or nerves traveling towards or away from the central nervous system (CNS), respectively. A spinal nerve emerges bilaterally at each thoracic vertebral level, with the first thoracic nerve emerging below the first thoracic vertebra, and so on.
The spinal ganglia are located at the proximal ends of the posterior roots, either inside or just exterior to the intervertebral foramina. Ganglia are swellings in which the cell bodies of afferent sensory neurons are situated.
Related parts of the anatomy
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Nerve Root

The lateral nerve root canal is a tubular region in which the nerve root passes from the thecal sac to the intervertebral foramen.




