Quick Facts
Origin: Cervicothoracic ganglion.
Course: Ascends and accompanies the vertebral artery.
Branches: None.
Supply: Sympathetic. Provides innervation to the adjacent zygapophyseal joint capsules and intervertebral discs, anterior aspect of the cervical dura mater, and the vertebral artery.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
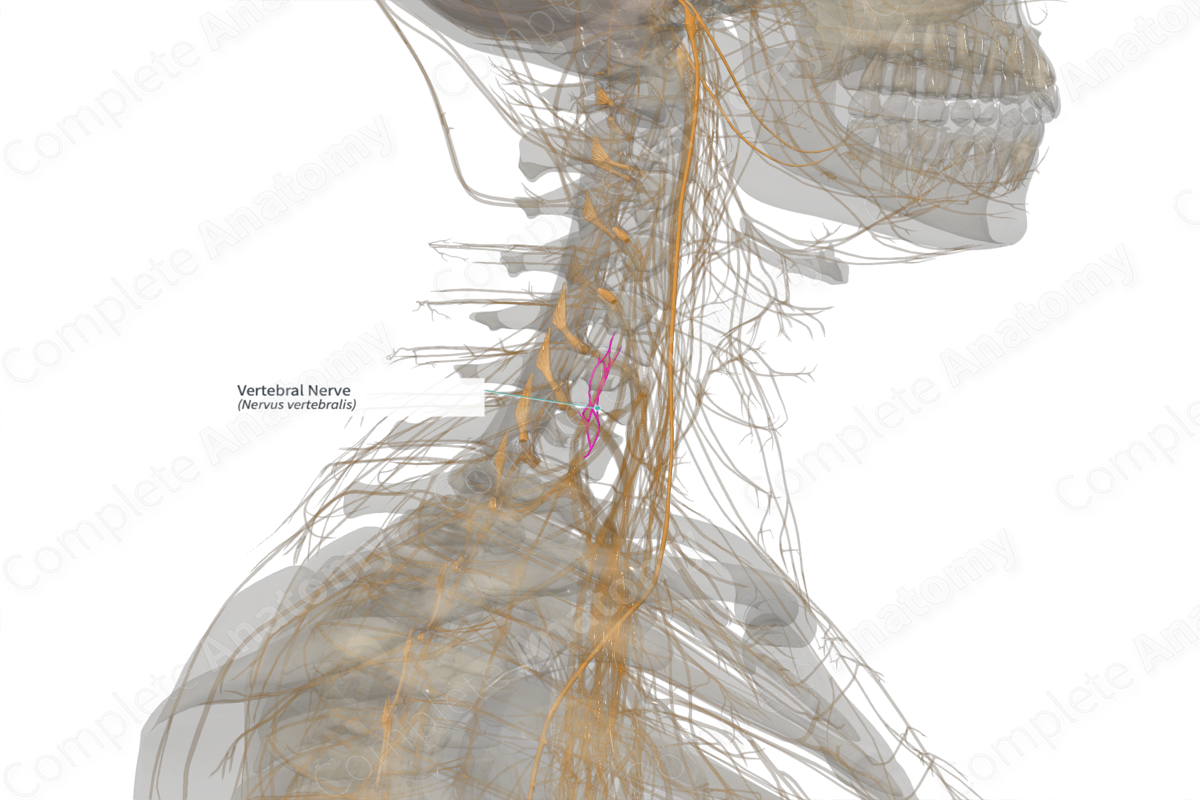
The vertebral nerve refers to the plexus of nerves which surround the vertebral artery. It arises from the cervicothoracic ganglion.
The vertebral nerve is a gray ramus communicantes (postganglionic fibers) connecting the cervicothoracic ganglion or the inferior cervical ganglion to the anterior rami of the sixth and seventh cervical nerves (Tubbs, 2015).
Course
The vertebral nerve usually courses from the cervicothoracic ganglion to the posterior and medial aspect of the vertebral artery to reach the superficial plexus of nerves surrounding the vertebral artery. Next, the vertebral nerve accompanies the vertebral artery through the foramen transversarium of the sixth cervical vertebra.
Branches
There are no named branches.
Supplied Structures
The vertebral nerve innervates the adjacent zygapophyseal joint capsules and intervertebral discs, and sometimes provides branches to the anterior aspect of the cervical dura mater and the deep component of the vertebral artery sympathetic nerve plexus.
References
Tubbs, R. S. (2015) Nerves and Nerve Injuries. Academic Press.



