Quick Facts
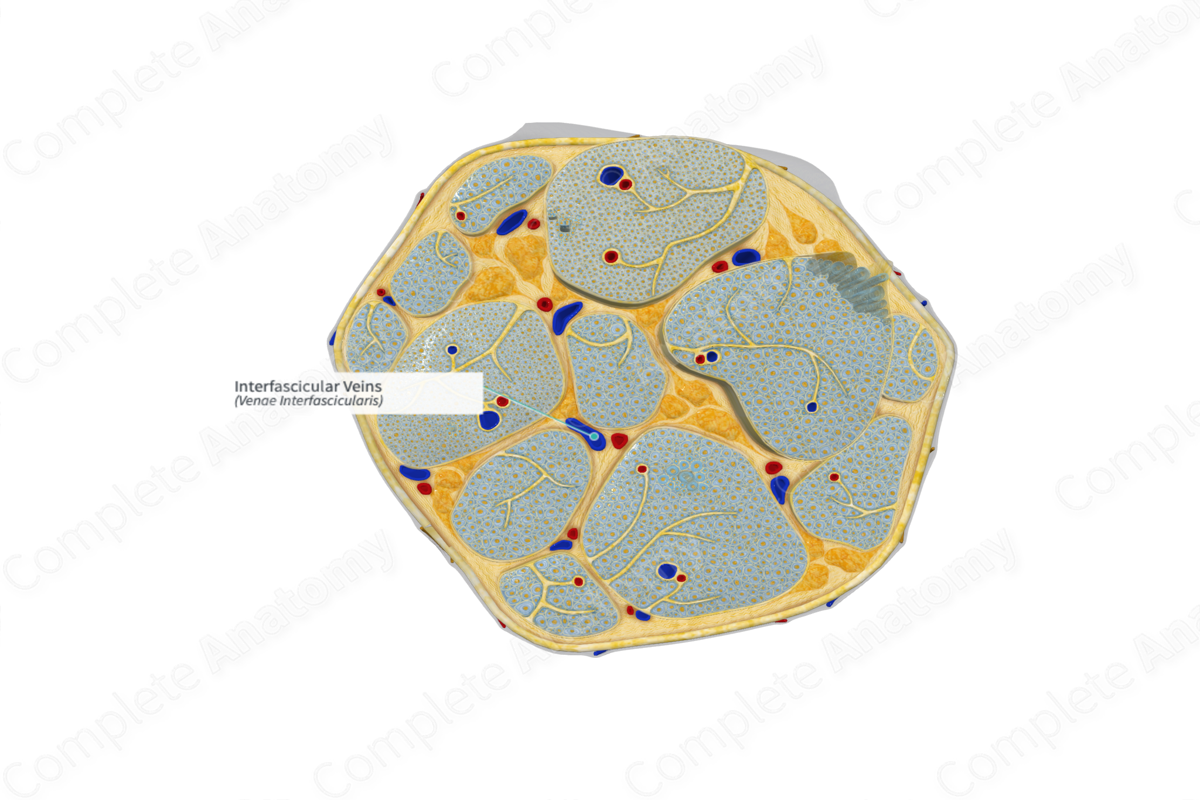
The intrafascicular veins are part of the vasa nervorum and help drain the nerve.
Related parts of the anatomy
Structure/Morphology
The interfascicular veins are located within the internal epineurium and form part of the vasa nervorum, small vessels that supply blood to peripheral nerves. This network of vessels supplies blood to the interior parts of the nerves and their coverings. The vasa vasorum are located within the connective tissue of the nerve scattered between the fascicles (Boissaud-Cooke, Pidgeon and Tunstall, 2015).
Anatomical Relations
The vasa nervorum are the smallest vessels in the epineurial, perineurial, and endoneurial layers.
Function
The vasa nervorum supply the peripheral nerves with the molecular nutrients needed to carry out their cellular functions and for survival (Carp, 2015).
References
Boissaud-Cooke, M., Pidgeon, T. E. and Tunstall, R. (2015) 'Chapter 37 - The Microcirculation of Peripheral Nerves: The Vasa Nervorum A2 - Tubbs, R. Shane', in Rizk, E., Shoja, M.M., Loukas, M., Barbaro, N. & Spinner, R.J. (eds.) Nerves and Nerve Injuries. San Diego: Academic Press, pp. 507-523.
Carp, S. (2015) Peripheral Nerve Injury An Anatomical and Physiological Approach for Physical Therapy Intervention. EBL-Schweitzer: F. A. Davis Company.
