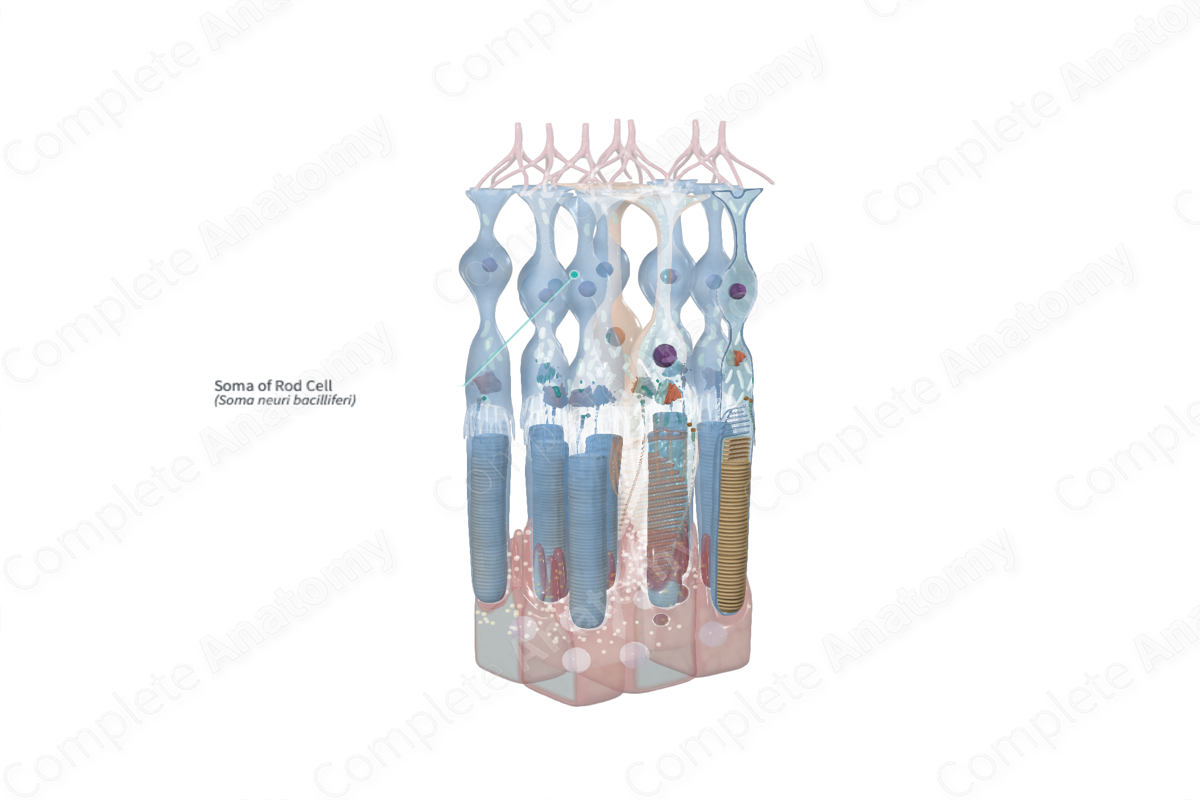
Soma of Rod Cell Quick Facts
The soma, or cell body, is the portion of a cell that contains the nucleus, independent of projections such as an axon or dendrites (Dorland, 2011).
Soma of Rod Cell Structure and/or Key Features
The soma, or cell body, is the region within the photoreceptor cell that houses the nucleus. The soma of the rod cells is large in diameter, measuring 3–5 µm (Dartt et al., 2010).
Soma of Rod Cell Anatomical Relations
The soma of the rod cells is located in the outer nuclear layer of the retina and tend to form several layers vitreal to the soma of the cone cells. It is positioned in between the inner segment and the axonal process of the photoreceptor cells.
Soma of Rod Cell Function
The soma houses the nucleus, which contains the cell’s DNA. It is necessary for the development and maintenance of the cell’s biochemical functions.
Soma of Rod Cell References
Dartt, D. A., Besharse, J., Dana, R., Battelle, B. A., Beebe, D., Bex, P., Bishop, P., Bok, D., D’Amore, P. and Edelhauser, H. (2010) Encyclopedia of the Eye. Elsevier Science, p. 147-152.
Dorland, W. (2011) Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. 32nd edn. Philadelphia, USA: Elsevier Saunders.

