Quick Facts
The nucleus is a spheroid body within a eukaryotic cell, separated from the cytoplasm by the nuclear envelope (which is penetrated by pores to allow communication with the cytoplasm), and containing chromatin, a nucleolus or nucleoli, and nucleoplasm. In the nucleus, the cell's genetic information is stored on the chromosomes and RNA transcription and processing occur (Dorland, 2011).
Related parts of the anatomy
Structure and/or Key Feature(s)
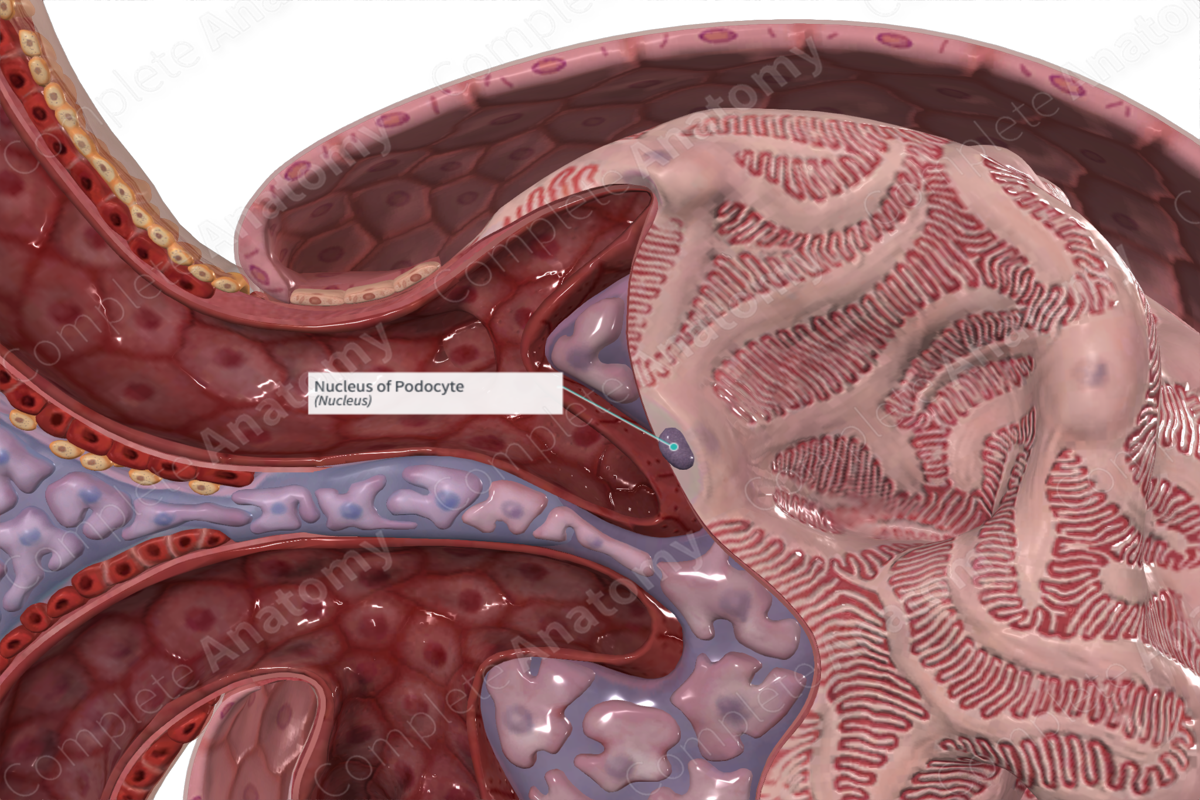
The shape of podocyte nuclei may often appear elongated, spherical, and often more obvious when they project into the subpodocyte space.
Anatomical Relations
The nucleus is surrounded by a minimal amount of cytoplasm as most of the cytoplasmic volume is within the primary and secondary processes (foot processes or pedicels).
Function
The nucleus is the cell's control, coordination, and information center.
References
Dorland, W. (2011) Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. 32nd edn. Philadelphia, USA: Elsevier Saunders.
