Quick Facts
The tunica intima is the inner coat of a blood or lymph vessel, made up of endothelial cells surrounded by longitudinal elastic fibers and connective tissue (Dorland, 2011).
Structure and/or Key Feature(s)
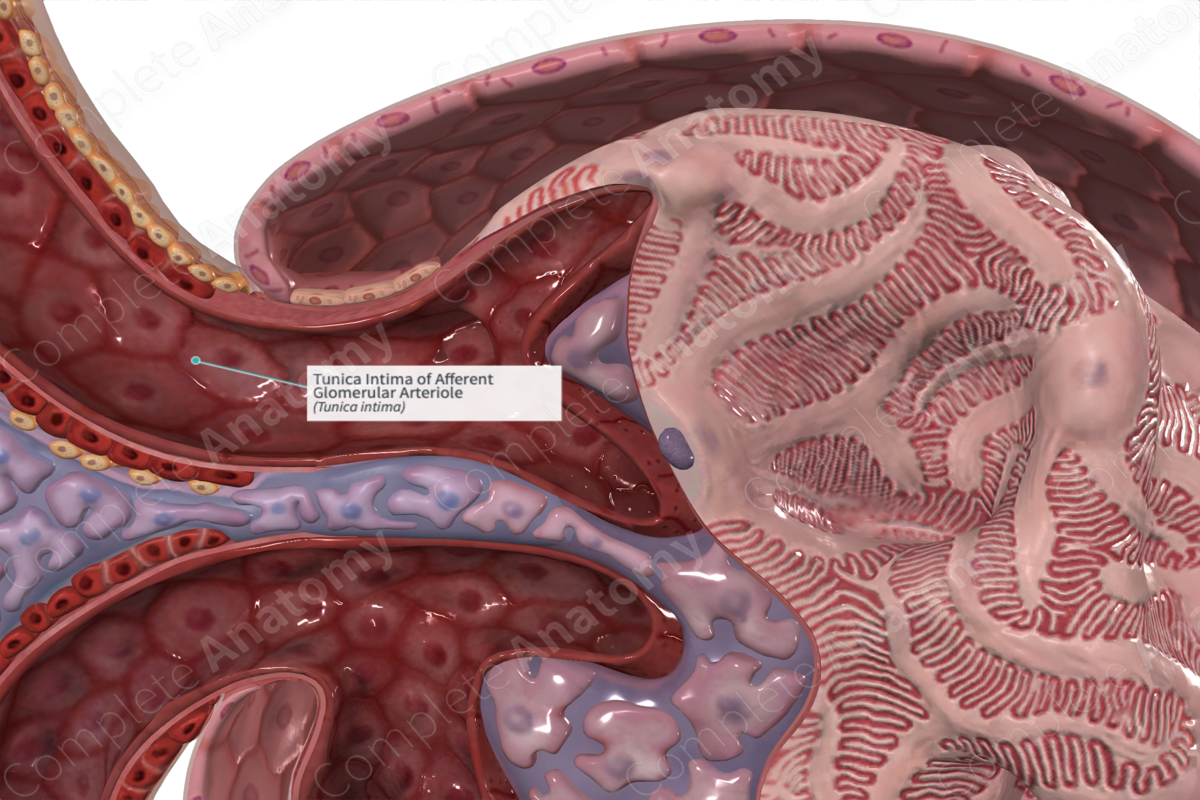
The tunica intima is the innermost layer of the afferent and efferent arteriole of the glomerulus. It consists of a simple squamous epithelium (of endothelial cells or endothelium), the basal lamina of the endothelial cell, and an extremely thin subendothelial connective tissue layer.
Anatomical Relations
An arteriole has three layers (or tunics). The tunica adventitia of an arteriole is the outermost layer of a blood vessel that merges with surrounding loose connective tissue. The tunica media is adjacent to the outer adventitia layer as the middle layer of a blood vessel. The layer adjacent to the blood vessel lumen (or inner layer) is the tunica intima.
Function
The tunica intima is the epithelial layer adjacent to the lumen (or inner layer) of the arteriole.
References
Dorland, W. (2011) Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. 32nd edn. Philadelphia, USA: Elsevier Saunders.
