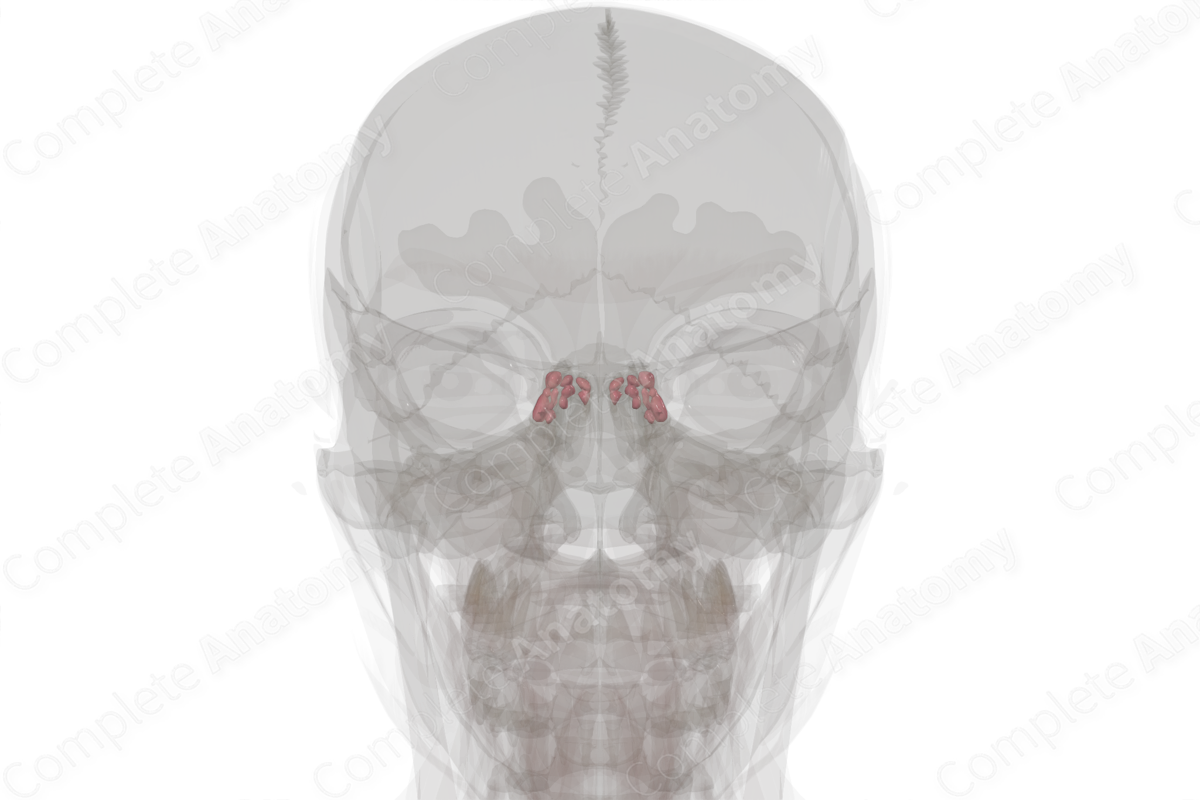
Structure/Morphology
The posterior ethmoidal cells consist of up to seven cells. The sphenoethmoidal cell is the most posterior ethmoidal cell (Standring, 2020).
Related parts of the anatomy
Key Features/Anatomical Relations
The posterior ethmoidal cells typically drain into the superior meatus through a single orifice. This group of air cells lies close to the optic canal and optic nerve. The sphenoethmoidal cell lies lateral and superior to the sphenoid sinus.
Function
The ethmoidal cells contribute to adding resonance to the voice and decreasing the overall weight of the skull.
List of Clinical Correlates
- Endoscopic sinus surgery
References
Standring, S. (2020) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 42nd edn.: Elsevier Health Sciences.




