Quick Facts
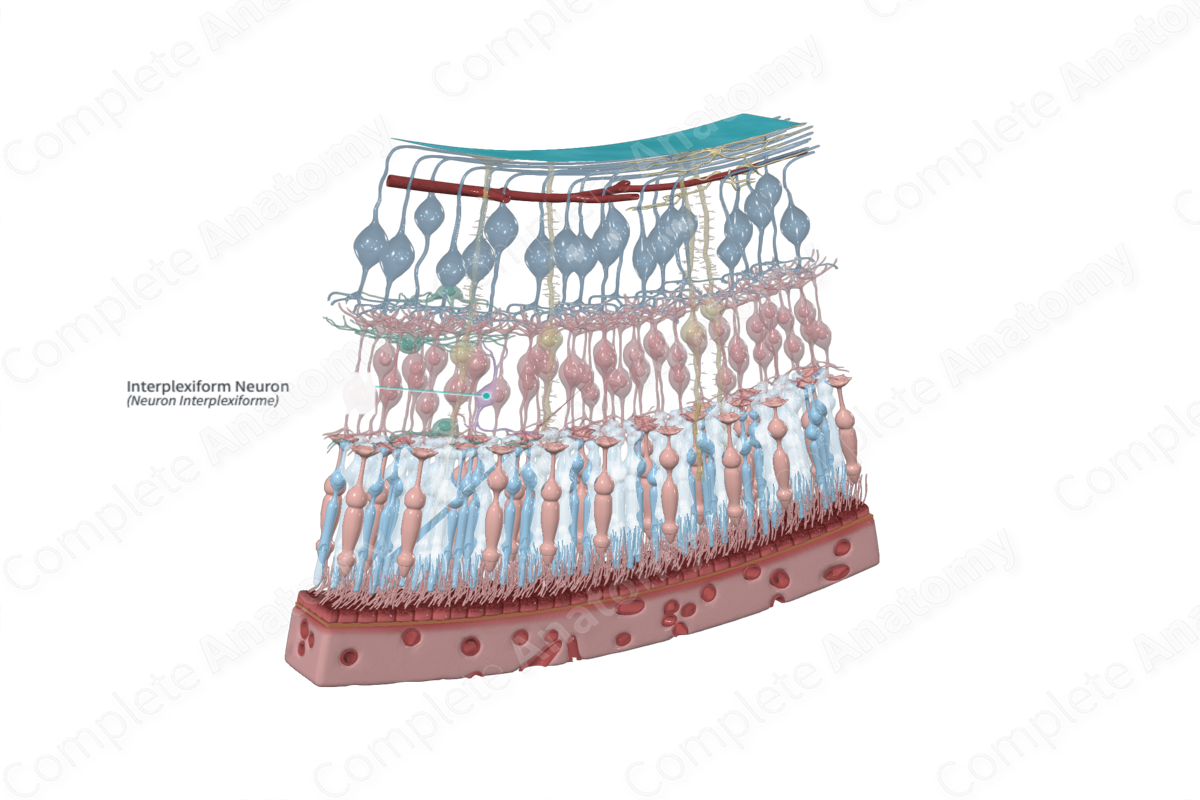
Interplexiform neurons are multipolar neurons that link the inner and outer plexiform layers (Dorland, 2011).
Structure and/or Key Features
Interplexiform neurons are multipolar neurons that link the inner and outer plexiform layers. They receive synaptic input from the inner plexiform layer and transmit synaptic outputs to the outer plexiform layer. Therefore, they serve a “feedback” function, conveying signals against the general flow of information in the retina (Kolb, 1995a).
Anatomical Relations
The cell bodies of the interplexiform neurons are usually located in the inner nuclear layer of the retina. They are postsynaptic neurons that receive input from bipolar, horizontal, and amacrine cells and feedback to photoreceptor cell terminal spherules and pedicles or rods and cones, respectively, in the outer plexiform layer (Standring, 2016).
Function
The function of interplexiform neurons has yet to be elucidated; however, some have been identified as GABAergic and dopaminergic and may play a role in adjusting sensitivity of the retina (Standring, 2016).
List of Clinical Correlates
- Gliosis
- Reactive Gliosis
References
Dorland, W. (2011) Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. 32nd edn. Philadelphia, USA: Elsevier Saunders.
Kolb, H. (1995a) 'Feedback Loops in the Retina', in Kolb, H., Fernandez, E. and Nelson, R. (eds.) Webvision: The Organization of the Retina and Visual System. Salt Lake City (UT): University of Utah Health Sciences Center.
Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Gray's Anatomy Series 41 edn.: Elsevier Limited.
