Quick Facts
Protoplasmic astrocytes are astrocytes found mainly in the gray matter of the brain, having many branching, thick cytoplasmic processes (Dorland, 2011).
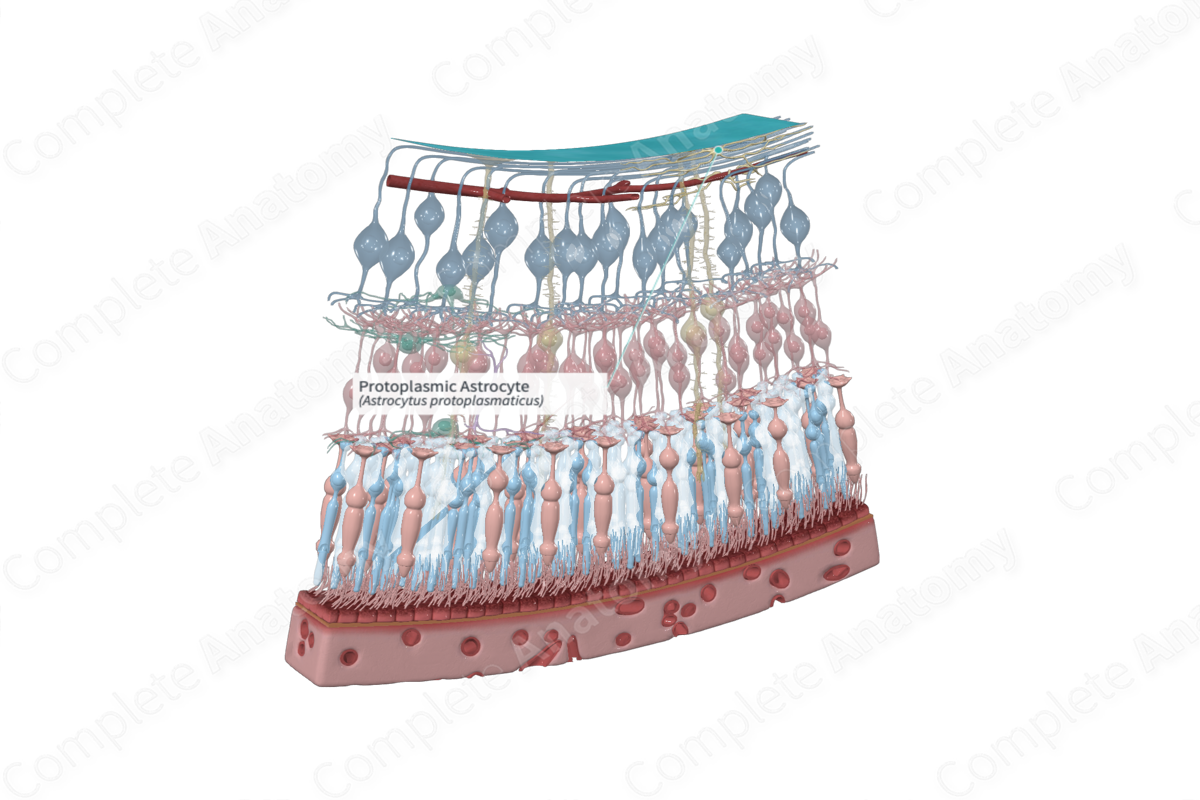
Structure and/or Key Features
Recognizable by their fibrous, star-shaped appearance and flattened cell body, astrocytes are one of the neuroglial cells of the retina. Other neuroglial cells in the retina include radial glial (Müller) cells and microglia. Astrocytes in the retina may also be described as perivascular cells, as they form an irregular supportive network around retinal fibers and capillaries (Kolb, 1995d; Remington and Goodwin, 2011).
Anatomical Relations
In the retina astrocytes are located in the inner layers, typically in the ganglion cell and nerve fiber layers. They are believed to structurally contribute to the inner limiting membrane (Remington and Goodwin, 2011). Astrocytes reach their peak density on the optic nerve head; however, numbers decline in radiating rings traveling away from the nerve head. Astrocytes are absent from the ora serrata and avascular fovea (Kolb, 1995d).
Function
Astrocytes are largely responsible for providing structure and support to retinal neurons, while they additionally play a role in the neural tissue reaction to infection or injury (Remington and Goodwin, 2011). They contain glycogen and are believed to provide a source of nutrition, specifically glucose, to the neurons they encircle. Further, it is believed that astrocytes contribute to maintaining ionic homeostasis, specifically regulating potassium levels and metabolizing neurotransmitters (Kolb, 1995d).
List of Clinical Correlates
- Gliosis
- Reactive Gliosis
References
Dorland, W. (2011) Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. 32nd edn. Philadelphia, USA: Elsevier Saunders.
Kolb, H. (1995d) 'Simple Anatomy of the Retina', in Kolb, H., Fernandez, E. and Nelson, R. (eds.) Webvision: The Organization of the Retina and Visual System. Salt Lake City (UT): University of Utah Health Sciences Center
Remington, L. A. and Goodwin, D. (2011) Clinical Anatomy of the Visual System E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences.
