Quick Facts
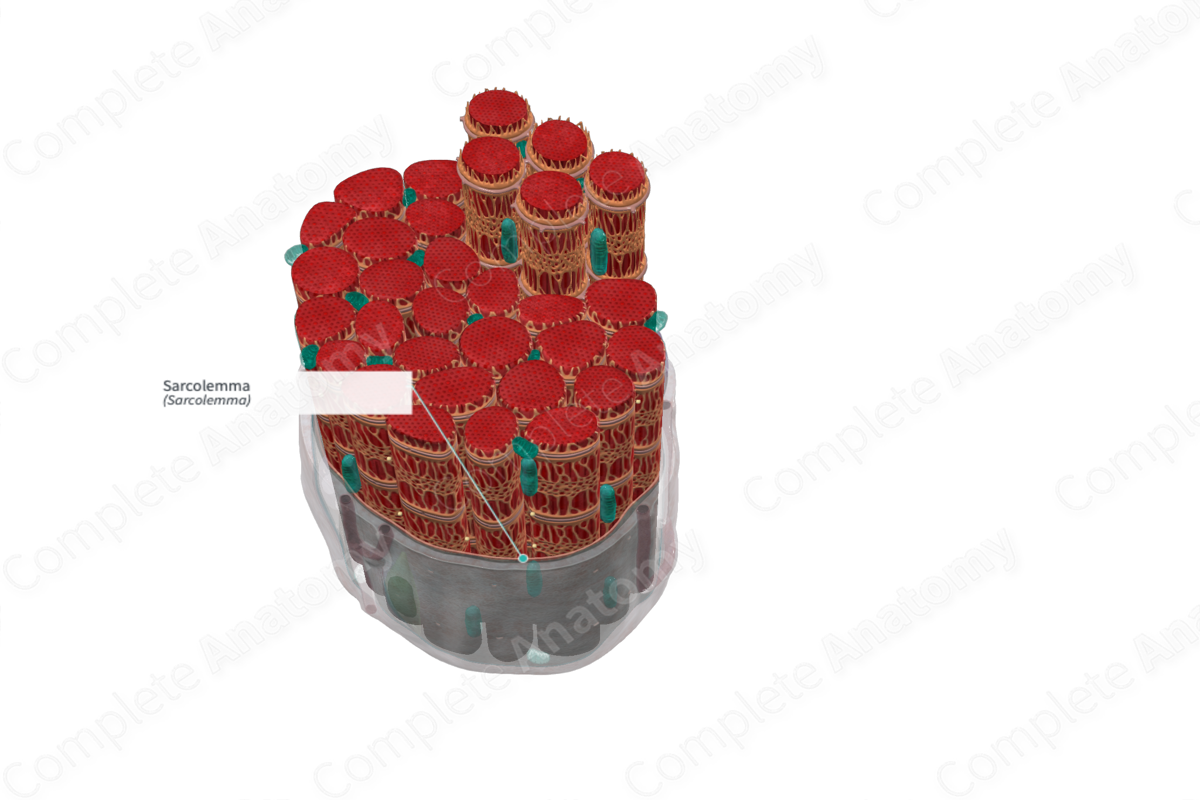
The sarcolemma is the delicate plasma membrane that invests every striated muscle fiber (Dorland, 2011).
Structure
The sarcolemma is the fine, delicate, extensible membrane surrounding each muscle fiber. It is composed of a cell, or plasma, membrane which presents an extracellular matrix of collagen fibrils and polysaccharides that make contact with the basal lamina. The sarcolemma also contains tunnel-like invaginations into the sarcoplasm, which are known as transverse tubules (Standring, 2016).
Key Features/Anatomical Relations
Transmembrane proteins found within the sarcolemma facilitate a physical connection between the actin cytoskeleton of the muscle fiber and the extracellular basal lamina (Martini et al., 2017).
Function
Like other types of cell membranes, the sarcolemma forms a defined barrier between extracellular and intracellular environments.
References
Dorland, W. (2011) Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. 32nd edn. Philadelphia, USA: Elsevier Saunders.
Martini, F. H., Nath, J. L. and Bartholomew, E. F. (2017) Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology. Pearson Education.
Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Gray's Anatomy Series: Elsevier Limited.
