Quick Facts
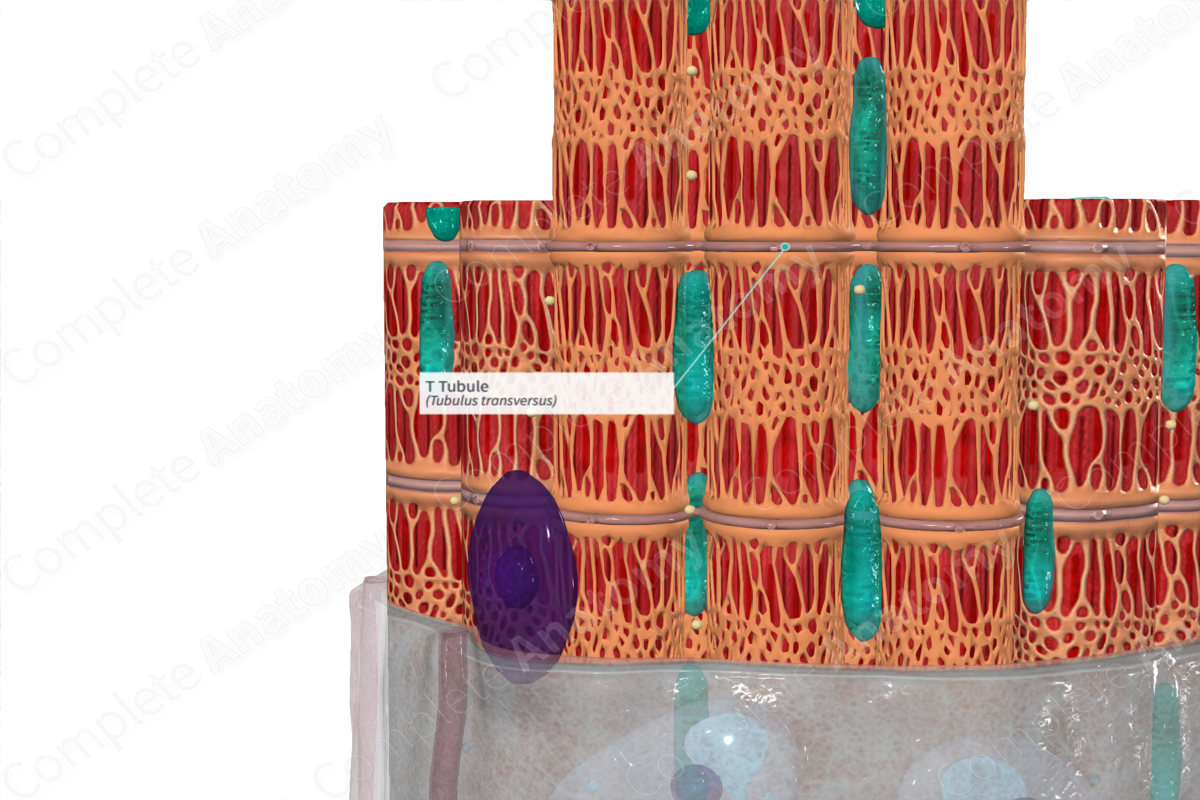
T tubules are the transverse intracellular tubules invaginating from the cell membrane and surrounding the myofibrils of the T system of skeletal and cardiac muscle, serving as a pathway for the spread of electrical excitation within a muscle cell, enabling the nearly simultaneous activation of all myofibrils; in skeletal muscle, a T tubule is the intermediate element of a triad of tubular structures, the other elements being a pair of terminal cisterns (Dorland, 2011).
Related parts of the anatomy
Structure
Transverse (T) tubules are extensions of the sarcolemma, made up of interconnecting rings, each of which surround individual myofibrils. Similar to the sarcolemma, the tubules are composed of two lipid bilayers.
Key Features/Anatomical Relations
Transverse tubules run from the sarcolemma transversely across the fiber at the junction of the A- and I-bands. The sarcolemma is the cell membrane that encloses the muscle fiber (Pocock, Richards and Richards, 2013).
Function
The primary function of transverse tubules is to facilitate the conduction of signals from outside the fiber to the myofibrils. Transverse tubules are the site for excitation-contraction coupling. When an electric signal excites the sarcolemma, the signal travels down along the T tubules to the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which releases Ca2+ for contraction (Standring, 2016).
References
Dorland, W. (2011) Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. 32nd edn. Philadelphia, USA: Elsevier Saunders.
Pocock, G., Richards, C. D. and Richards, D. A. (2013) Human Physiology. Oxford Core Texts 4 edn.: OUP Oxford.
Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Gray's Anatomy Series: Elsevier Limited.
