Quick Facts
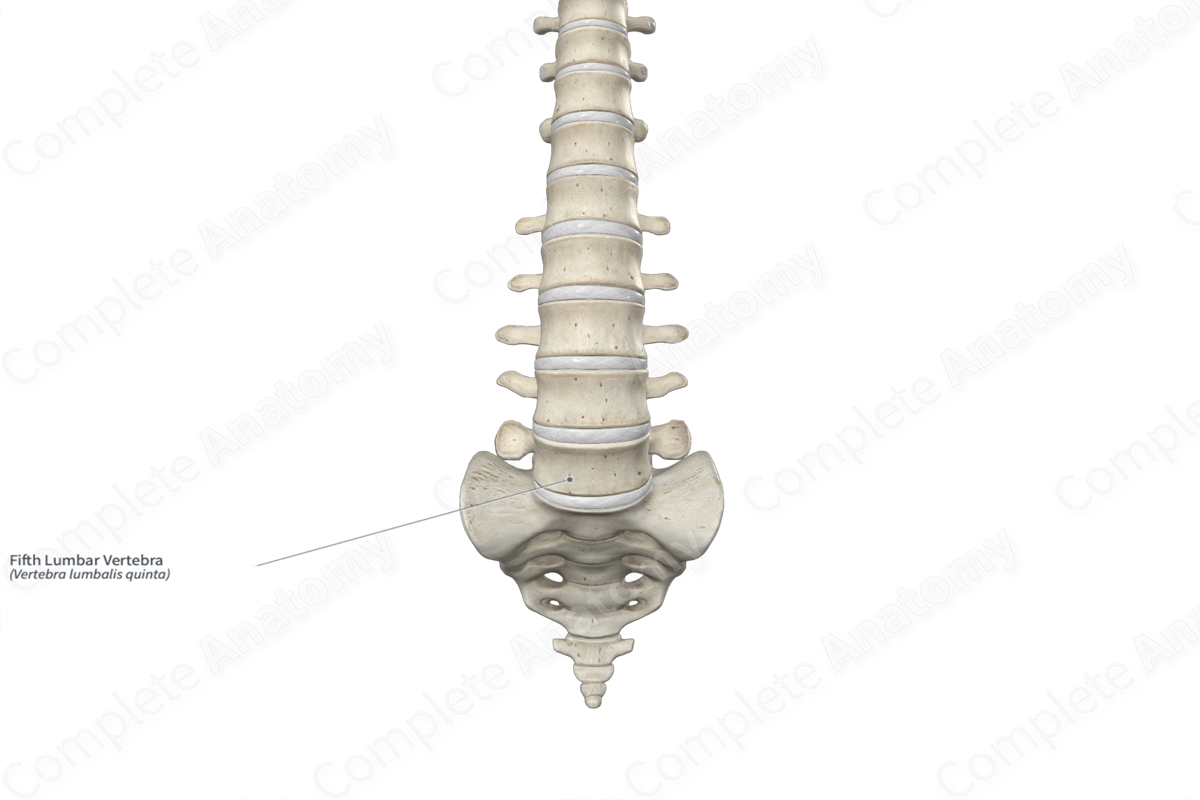
Location: Vertebral column.
Bone Type: Irregular bone.
Key Features: Vertebral body, laminae, pedicles, superior and inferior articular processes, and transverse and spinous processes.
Articulates With: Fourth lumbar vertebra and sacrum.
Arterial Supply: Lumbar arteries.
Key Features & Anatomical Relations
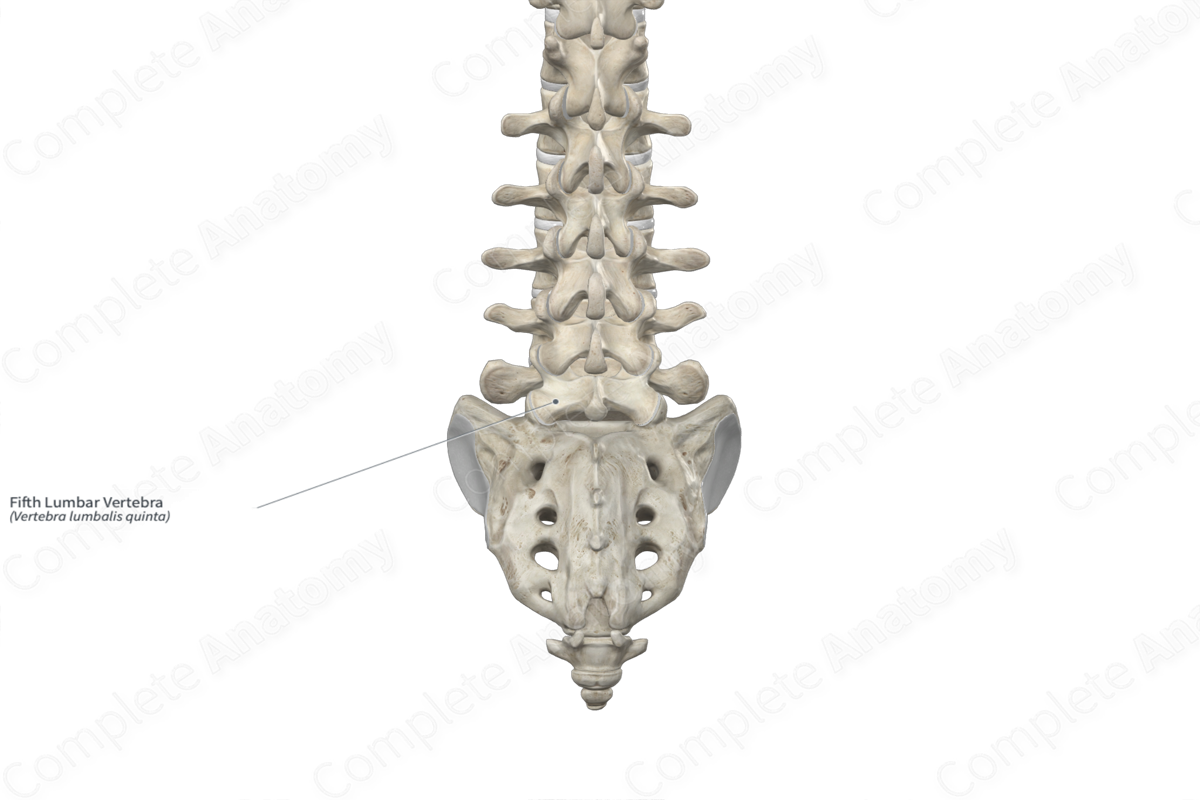
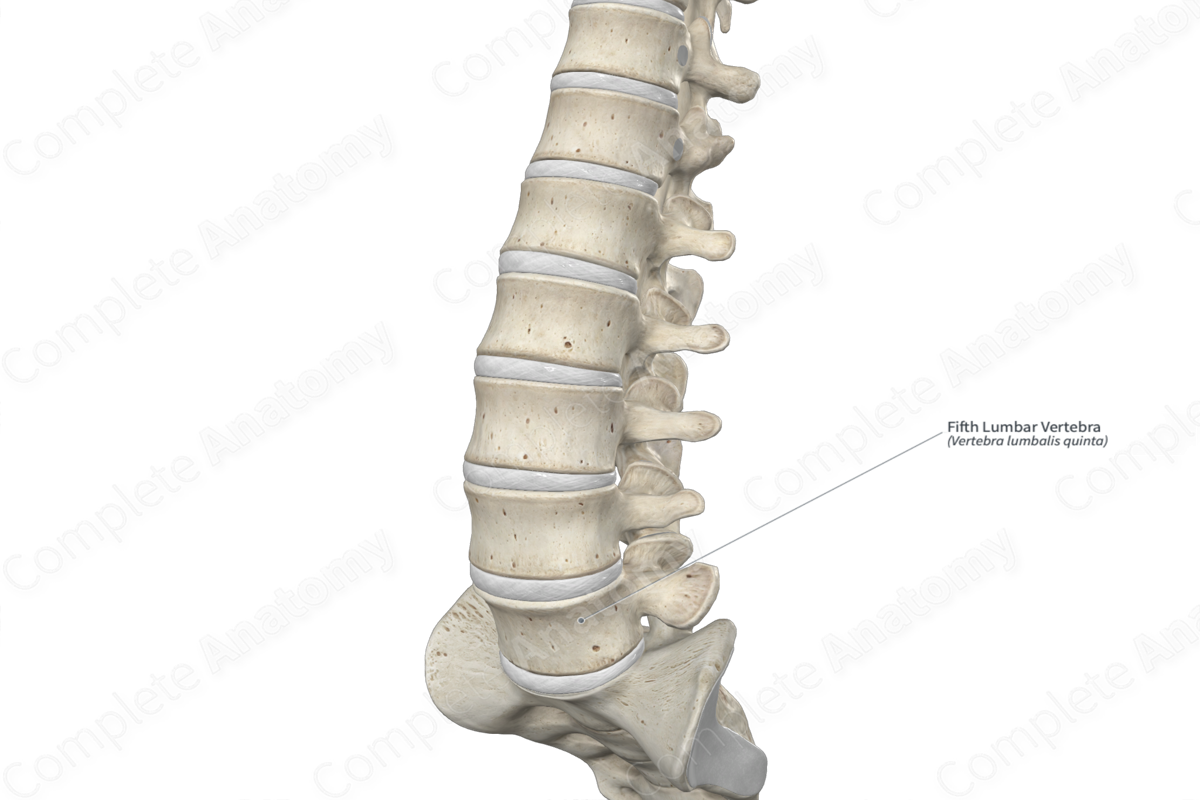
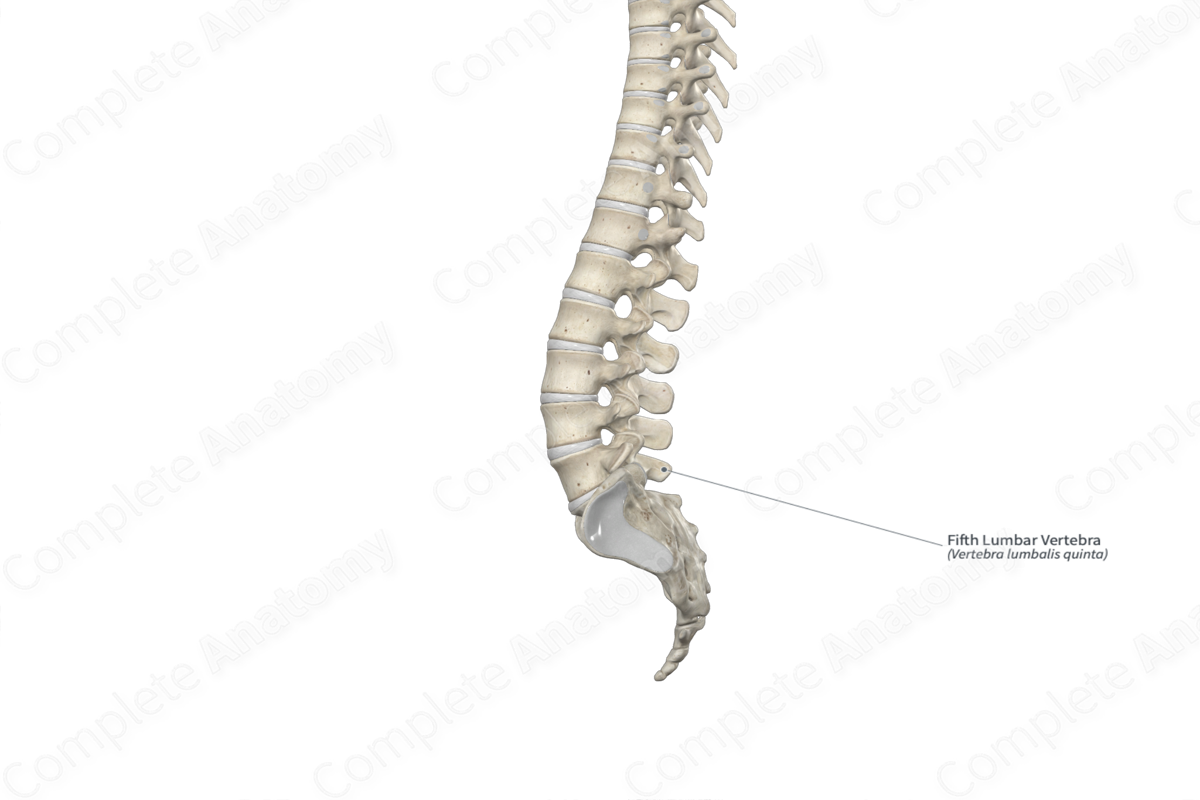
The fifth lumbar vertebra (vertebra L5) is the largest of the five lumbar vertebrae of the vertebral column. It is classified as an irregular bone and includes the following bony features:
- parts: vertebral body, laminae, pedicles, superior and inferior articular processes, and transverse and spinous processes;
- surfaces: superior and inferior intervertebral surfaces, superior and inferior annular epiphyses, and vertebral arch;
- landmarks: superior and inferior vertebral notches, mammillary and accessory processes, and superior and inferior articular facets.
More information regarding these and other bony features can be found in the Parts, Surfaces, and Landmarks tabs for this bone.
The fifth lumbar vertebra is located:
- superior to the sacrum;
- inferior to the fourth lumbar vertebra.
It articulates with the fourth lumbar vertebra at the intervertebral symphysis and zygapophyseal joints and the sacrum at the lumbosacral joint.
Ossification
Ossification of all lumbar vertebrae occurs at ten ossification centers, these are found in the:
- vertebral body, which appears in utero during the second to fourth months;
- right and left halves of the vertebral arch, with one center found in each, which appear in utero during the third month;
- right and left transverse processes, with one center found in each, which appear during puberty;
- spinous process, which appears during puberty;
- superior and inferior annular epiphyses, with one center found in each, which appear during puberty;
- right and left mammillary processes, with one center found in each, which appear during early adolescence.
The ossification centers for the right and left halves of the vertebral arch fuse with each other during the first year after birth. The vertebral arch fuses with the vertebral body during the third year. The remaining centers fuse with the vertebral arch and body during early adulthood (Standring, 2016).
Variations
In some individuals:
- the superior or inferior articular processes of lumbar vertebrae may occasionally present an accessory ossicle, known as an Oppenheimer ossicle;
- the fifth lumbar vertebra may be fused with the sacrum, which is known as sacralization of the fifth lumbar vertebra (Tubbs, Shoja and Loukas, 2016).
Surface Anatomy
The spinous process of the fifth lumbar vertebra can be palpated, especially during flexion of the trunk.
List of Clinical Correlates
- Fracture
- Osteoporosis
- Spinal stenosis
- Scoliosis
- Spondylosis
- Spondylolisthesis
- Spondylolysis
References
Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Gray's Anatomy Series 41st edn.: Elsevier Limited.
Tubbs, R. S., Shoja, M. M. and Loukas, M. (2016) Bergman's Comprehensive Encyclopedia of Human Anatomic Variation. Wiley.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Fifth Lumbar Vertebra

The fifth lumbar vertebra represents the transition from the lumbar to the sacral spine.