Quick Facts
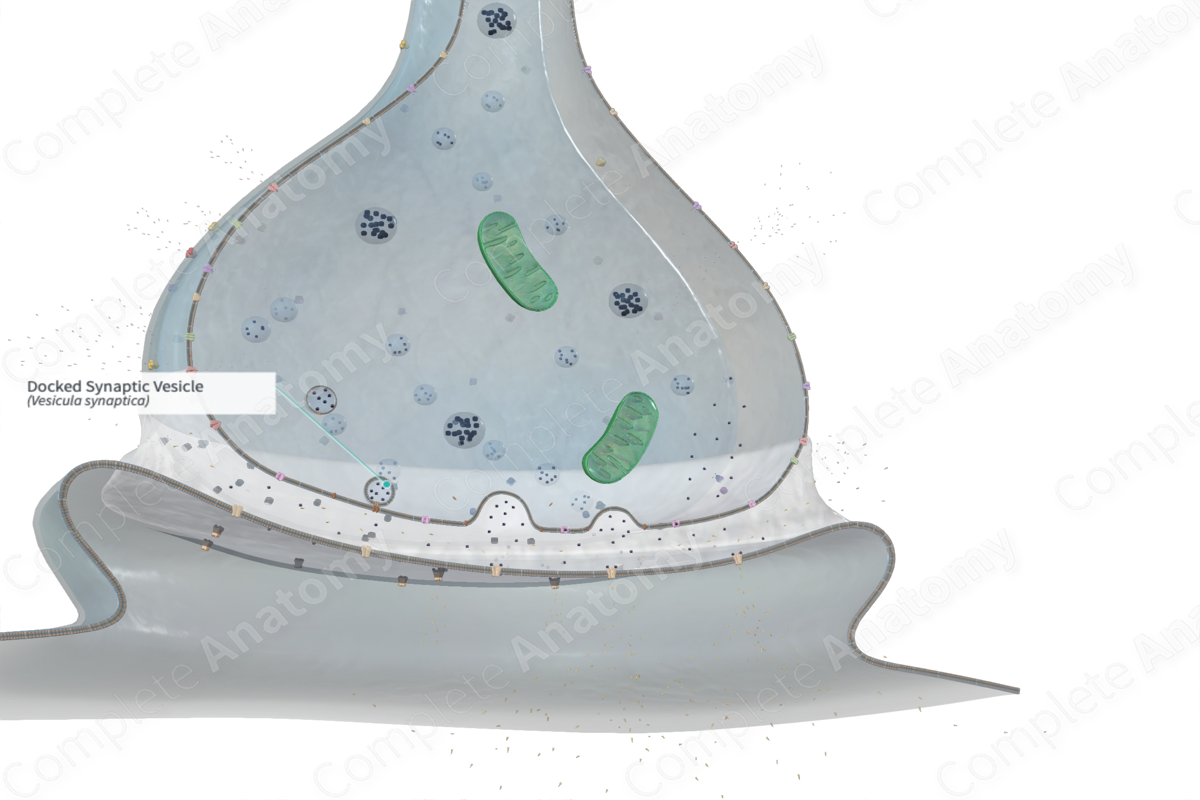
Docked synaptic vesicles are those that fuse with the presynaptic plasma membrane before releasing their contents (neurotransmitter) into the synaptic cleft.
Structure
Docked synaptic vesicles are vesicles loaded with neurotransmitters that have migrated adjacent to the presynaptic membrane, ready to fuse with the membrane and subsequently release the neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft via exocytosis. Synaptic vesicles can only be secreted at the active zones after they have.
A group of transmembrane proteins called Soluble NSF Attachment Receptors (SNAREs), particularly the vesicle-bound v-SNARE and the target-membrane-bound t-SNARE, facilitate the binding of the synaptic vesicles to the presynaptic plasma membrane. Synaptotagmin 1, a vesicle-bound protein, subsequently supersedes the SNARE complex which is later disintegrated and recycled by NSF/SNAP25 protein complexes. This process yields concentrated collections of proteins on the cytoplasmic aspect of the presynaptic plasma membrane which depict the active zones (Ross and Pawlina, 2006).
The membrane of the synaptic vesicle fused to the presynaptic membrane is salvaged by endocytosis and recycled by the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (Ross and Pawlina, 2006).
Anatomical Relations
Docked synaptic vesicles are situated in the presynaptic region. More specifically, they are situated in the active zone, adjacent to the presynaptic membrane.
Function
Synaptic vesicles store and release neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft in order to facilitate the transmission and propagation of nerve impulses (Ross and Pawlina, 2006).
References
Ross, M. H. and Pawlina, W. (2006) Histology: A text and atlas. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
