Quick Facts
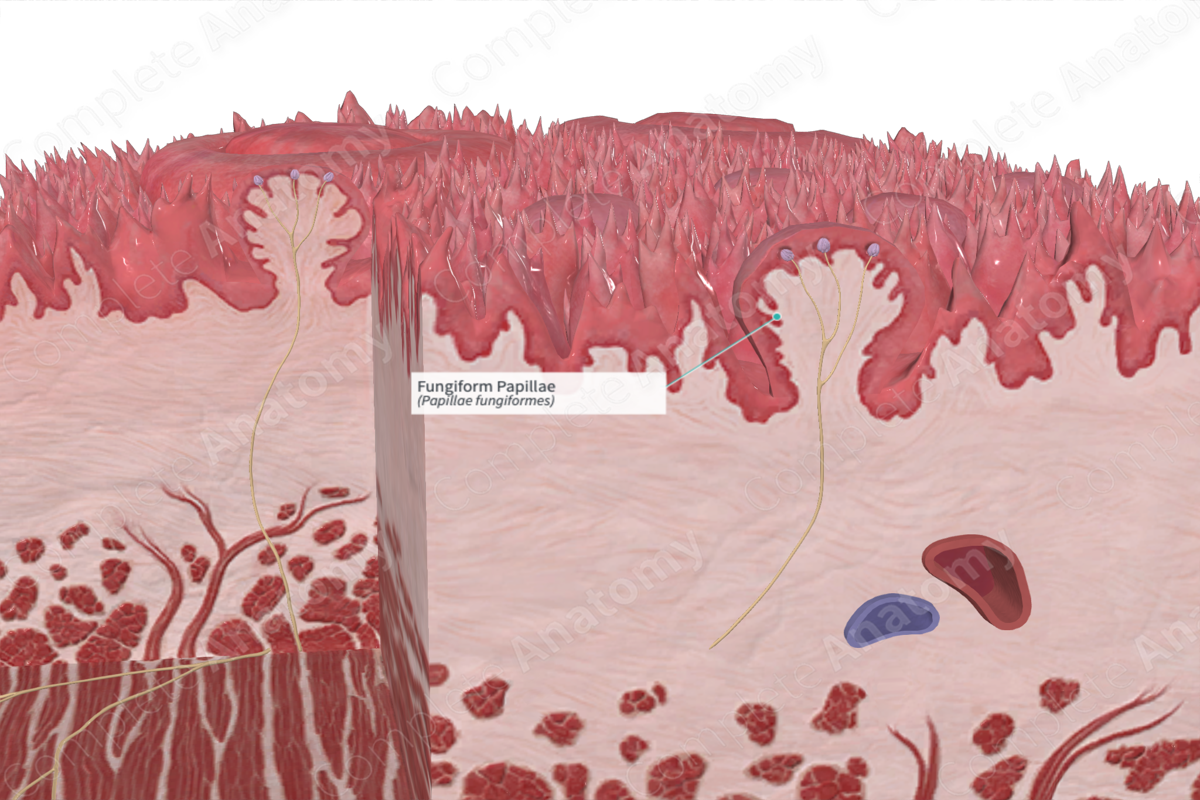
The fungiform papillae are the knoblike projections on the tongue, scattered singly among the filiform papillae (Dorland, 2011).
Related parts of the anatomy
Structure and/or Key Features
The majority of the fungiform papillae are located at the anterior margin of the tongue, including the tip of the tongue. There are some located among the filiform papillae along the dorsum of the tongue.
The fungiform papillae have broad spherical heads; hence their name is derived from the Latin for mushroom. Their taste buds are located at the apex of the papillae, readily in contact with any food particles that they come into contact with. The papillae tend to be larger and slightly flatter than the filiform papillae. They are red due to their densely vascularized core and thin epithelium.
The fungiform papillae are protected by stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium and participate in gustation.
Function
The fungiform papillae are one of the three types of lingual papillae involved in gustation, which is the detection of the different tastes of salty, bitter, sour, and sweet, and savory (Ikeda, 2002). It is important that all areas of the tongue are responsive to the different modalities of taste. However, some taste buds respond to a greater amount of chemical activation, while some respond to less. The simultaneous activation of different taste buds is what leads to the recognition of specific tastes.
References
Dorland, W. (2011) Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. 32nd edn. Philadelphia, USA: Elsevier Saunders.
Ikeda, K. (2002) New seasonings. Chem Senses, 27(9), 847-9.
