Structure/Morphology
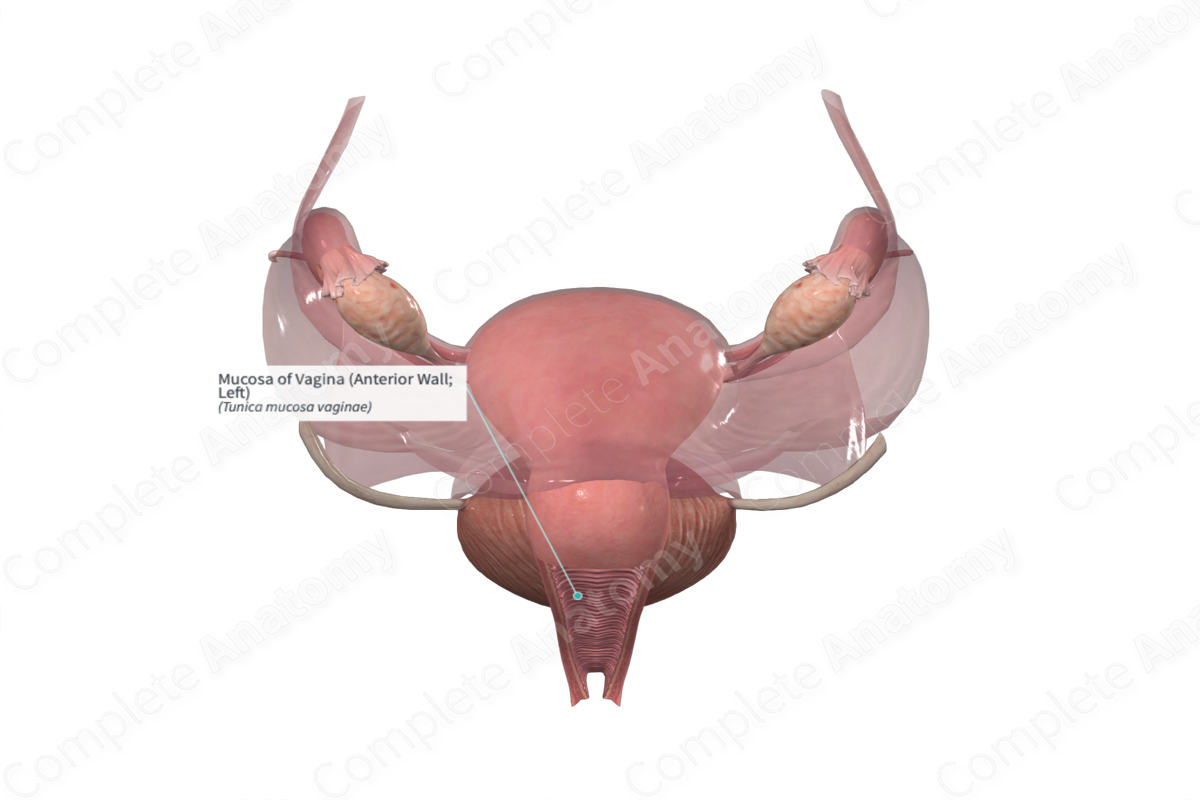
The mucosal layer of the vagina consists of a nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium that has several transverse folds called rugae. The epithelial cells produce glycogen due to the presence of estrogen. The glycogen is metabolized into lactic acid, which creates the lower pH environment of the vaginal canal (Standring, 2020).
Related parts of the anatomy
Key Features/Anatomical Relations
The mucosal layer of the vagina adheres directly to the outer muscular layer and to the uterine cervix superiorly.
Function
The mucosal layer provides protection from pathogens outside of the body from entering the body through the vagina.
References
Standring, S. (2020) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 42nd edn.: Elsevier Health Sciences.



