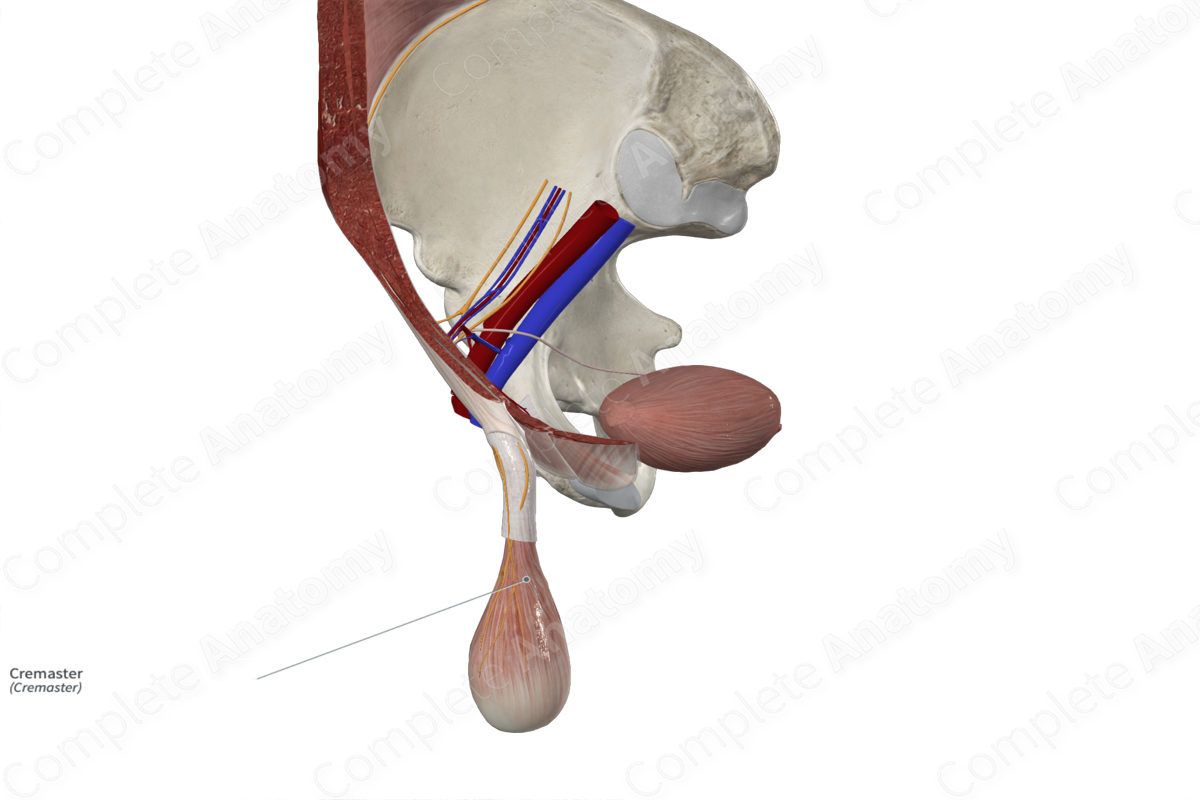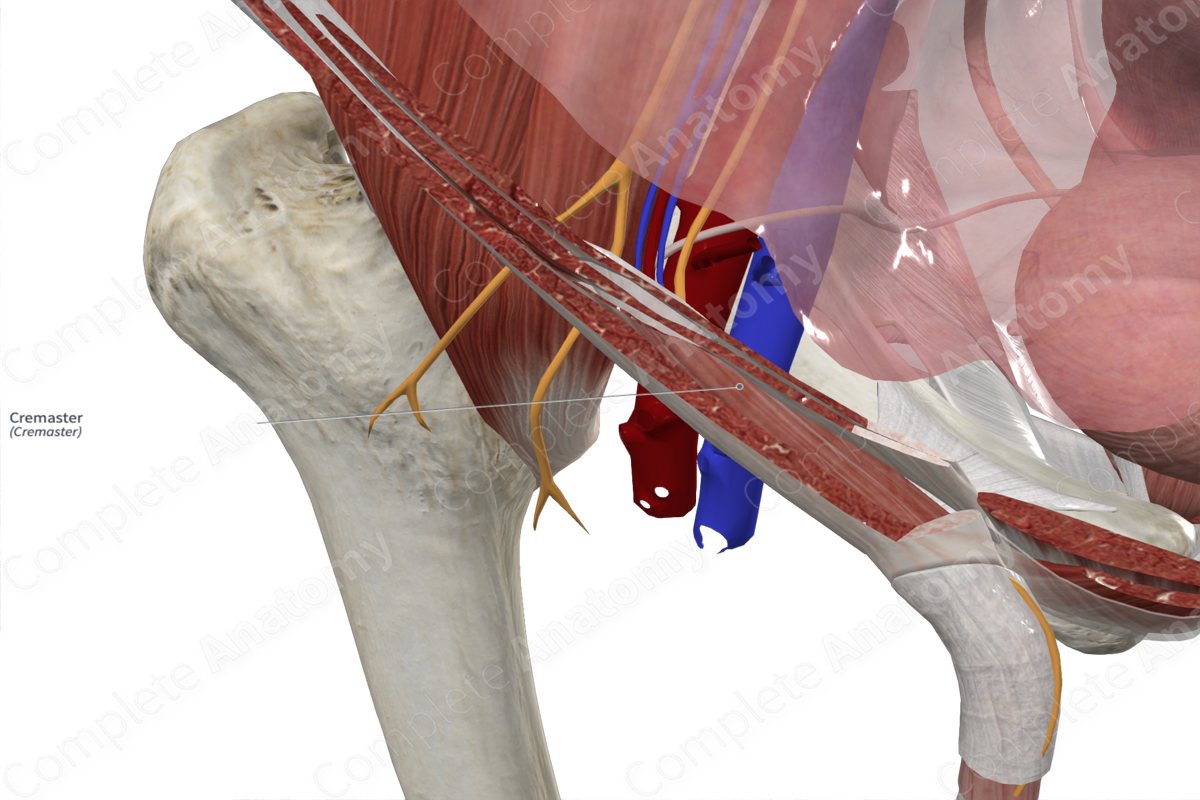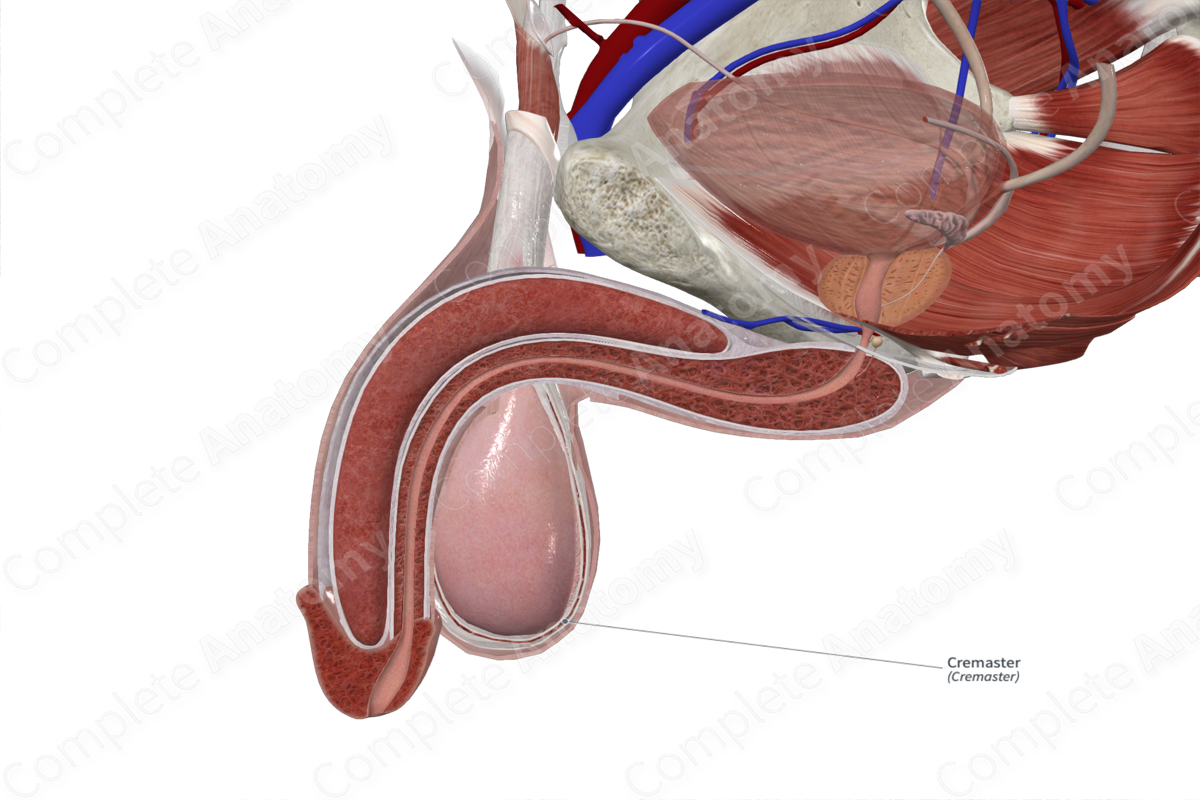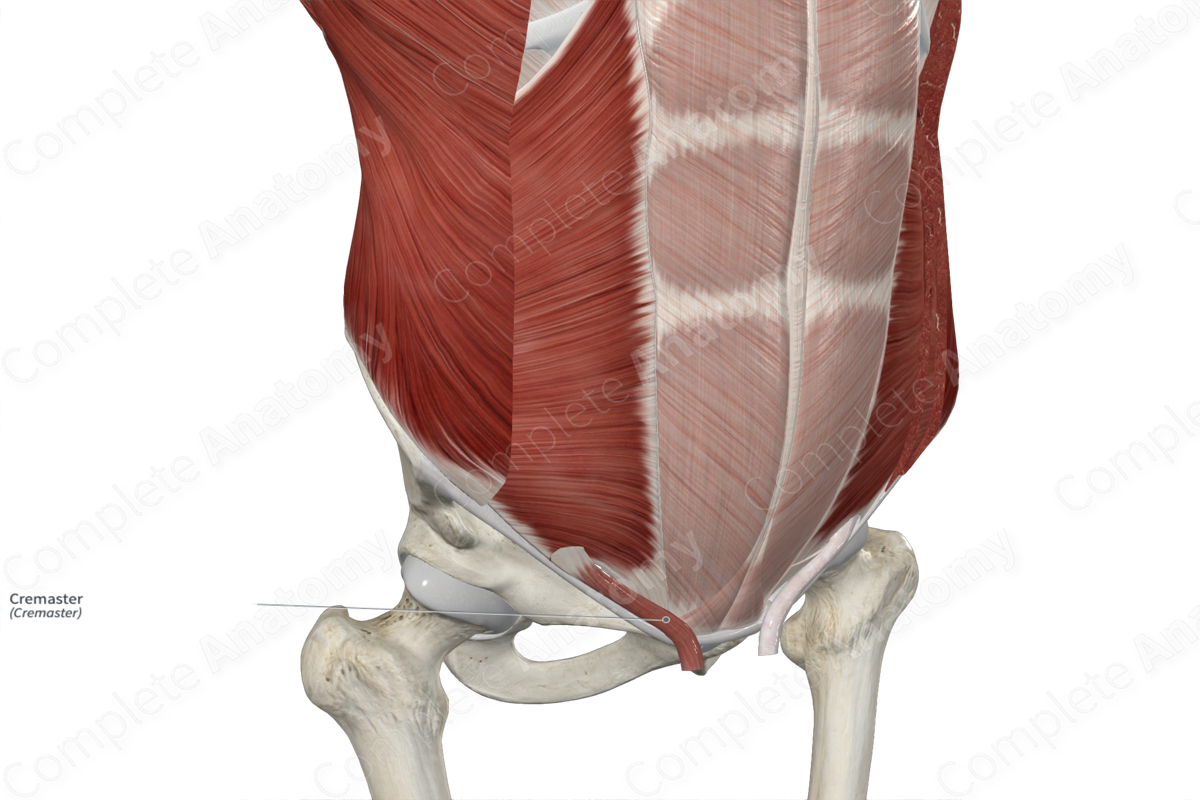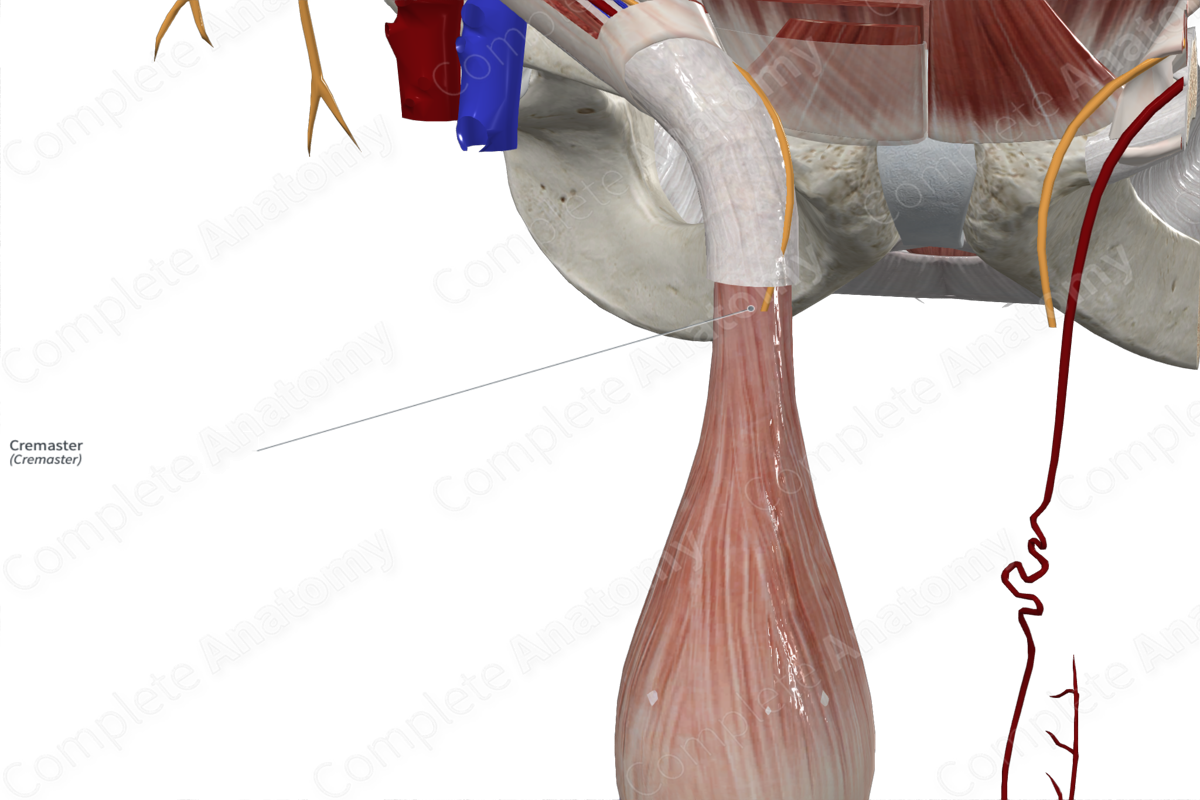
Quick Facts
Origin: Internal abdominal oblique muscle and inguinal ligament.
Insertion: Tunica vaginalis of testis.
Action: Elevation and depression of the scrotum to regulate the temperature of the testes.
Nerve Supply: Genital branch of genitofemoral nerve.
Arterial Supply: Cremasteric artery.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The cremaster muscle originates from the internal abdominal oblique muscle of the anterior abdominal wall and the inguinal ligament.
Insertion
The cremaster muscle inserts on to the tunica vaginalis of testis.
Anatomical Relations
The cremaster muscle is the middle layer covering of the spermatic cord and testes. It lies between the external and internal layers of the spermatic fascia. It is derived from the internal abdominal oblique muscle, as the testis descend in the embryo, from the abdomen to lie outside the pelvis.
The cremaster skeletal muscle fibers are contained within the cremasteric fascia. The cremaster muscle is also present in females; however, the muscle fibers are sparse.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Cremaster Muscle

Cremaster muscle The cremaster muscle is a one-layer muscle fiber bundle.