Structure/Morphology
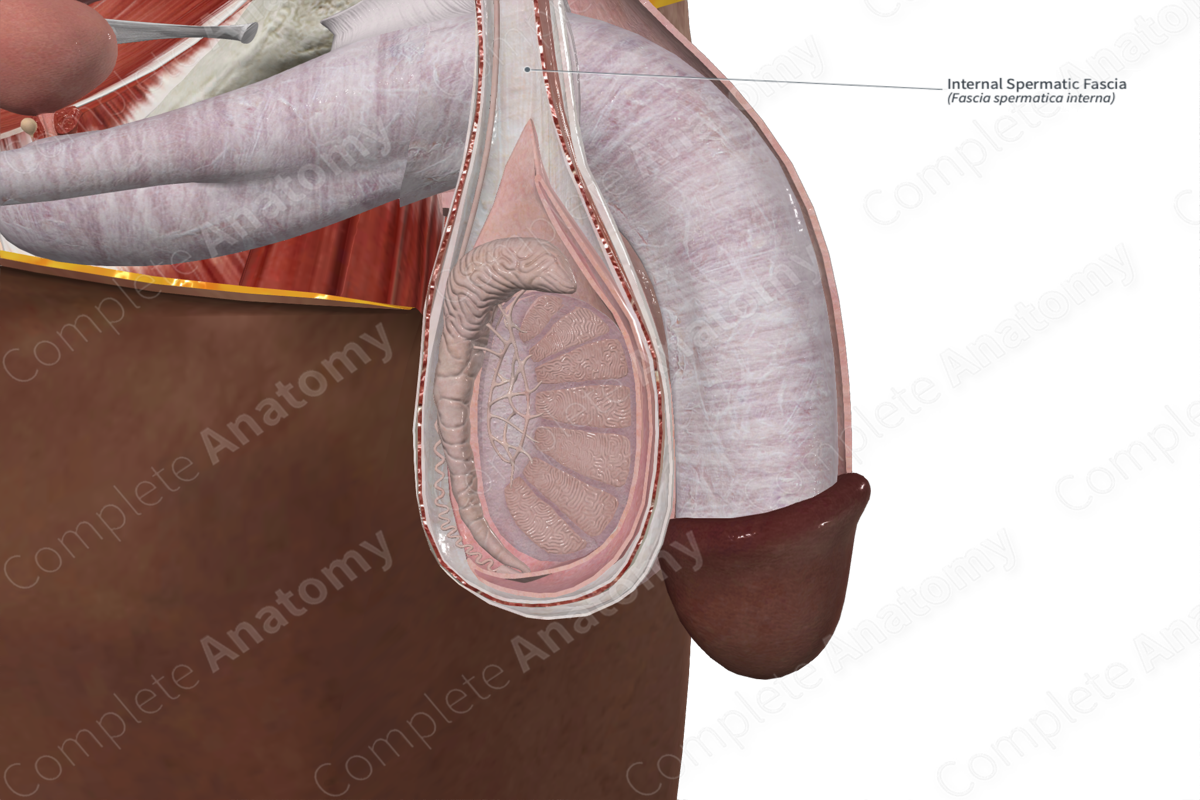
The internal spermatic fascia is a thin membrane that lies deep to the cremaster muscle. It is loosely attached to the parietal layer of the tunica vaginalis testis.
Related parts of the anatomy
Key Features/ Anatomical Relations
The internal spermatic fascia is the deepest of three layers that surround the spermatic cord and testes. It is derived from the transversalis fascia as the testes descend from the abdomen to lie outside the pelvis in the embryo.
Function
The internal spermatic fascia permits a degree of motility between the facial coverings and overlying skin. This movement helps to control the temperature of the testes.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Fascia

A fascia is a connective tissue that surrounds muscles, groups of muscles, blood vessels, and nerves.




