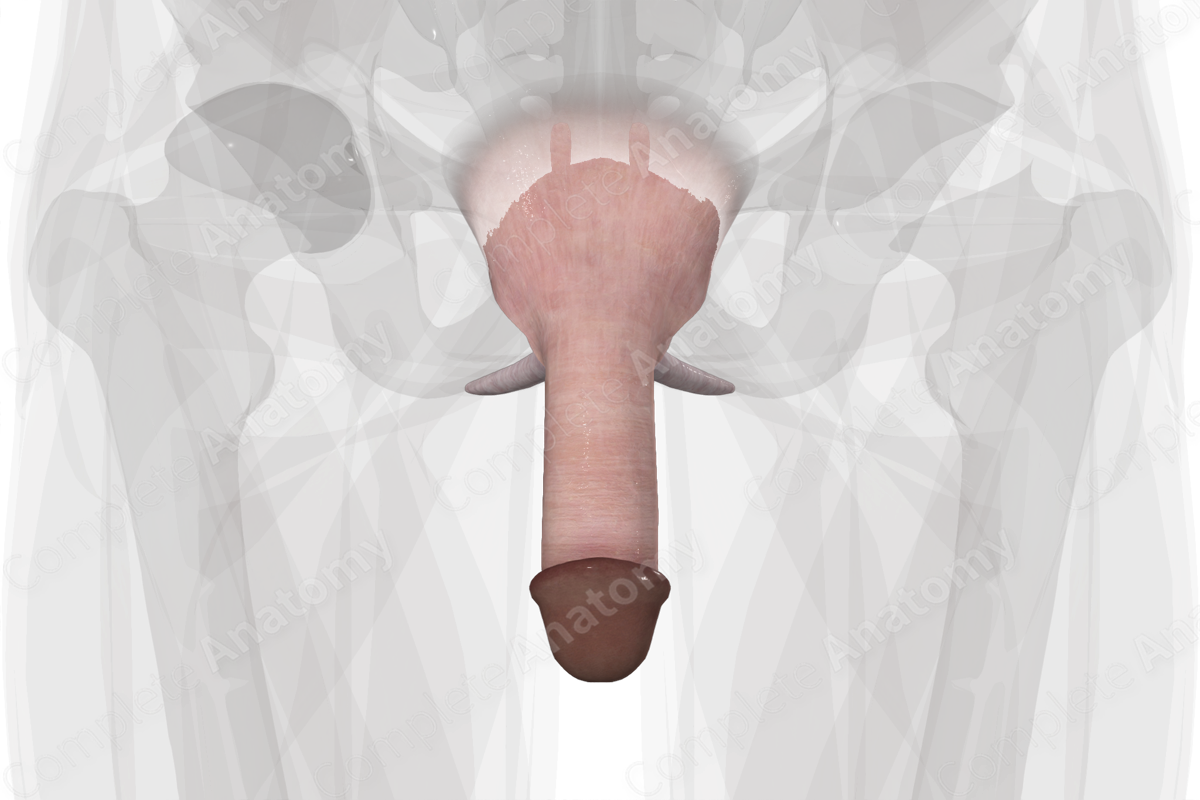
Penis Quick Facts
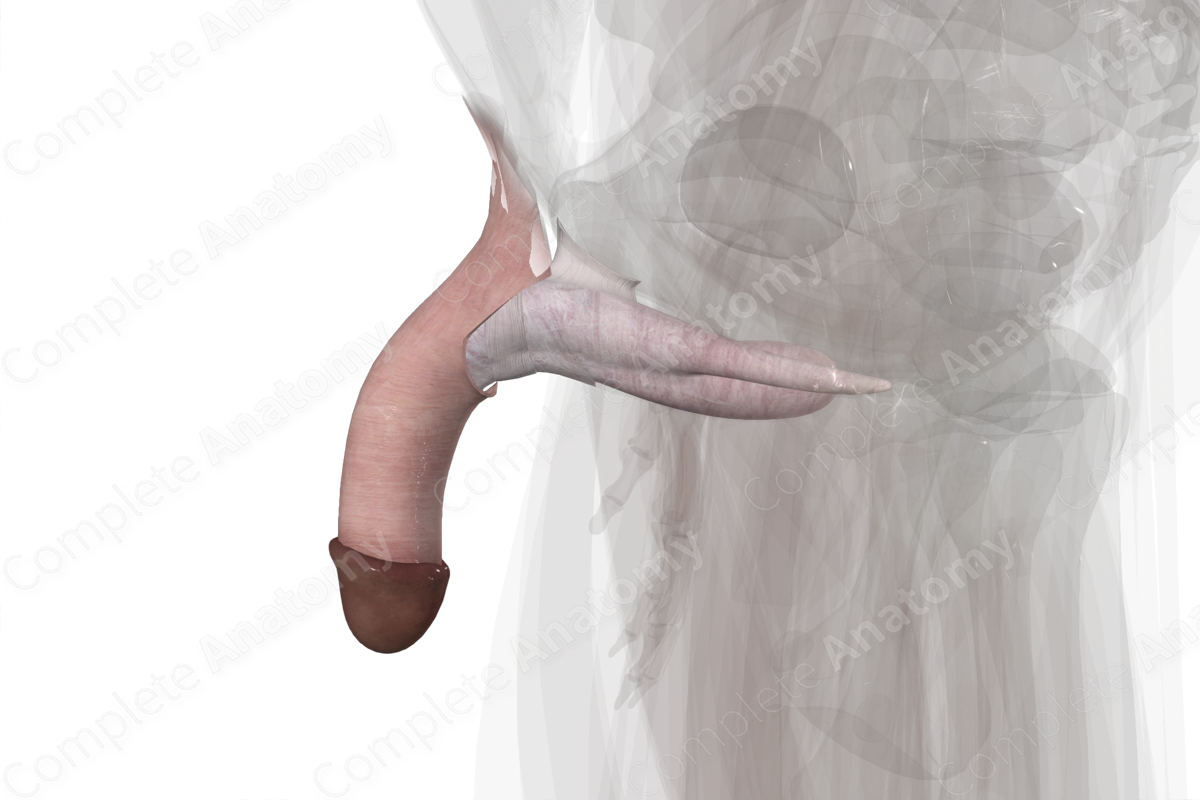
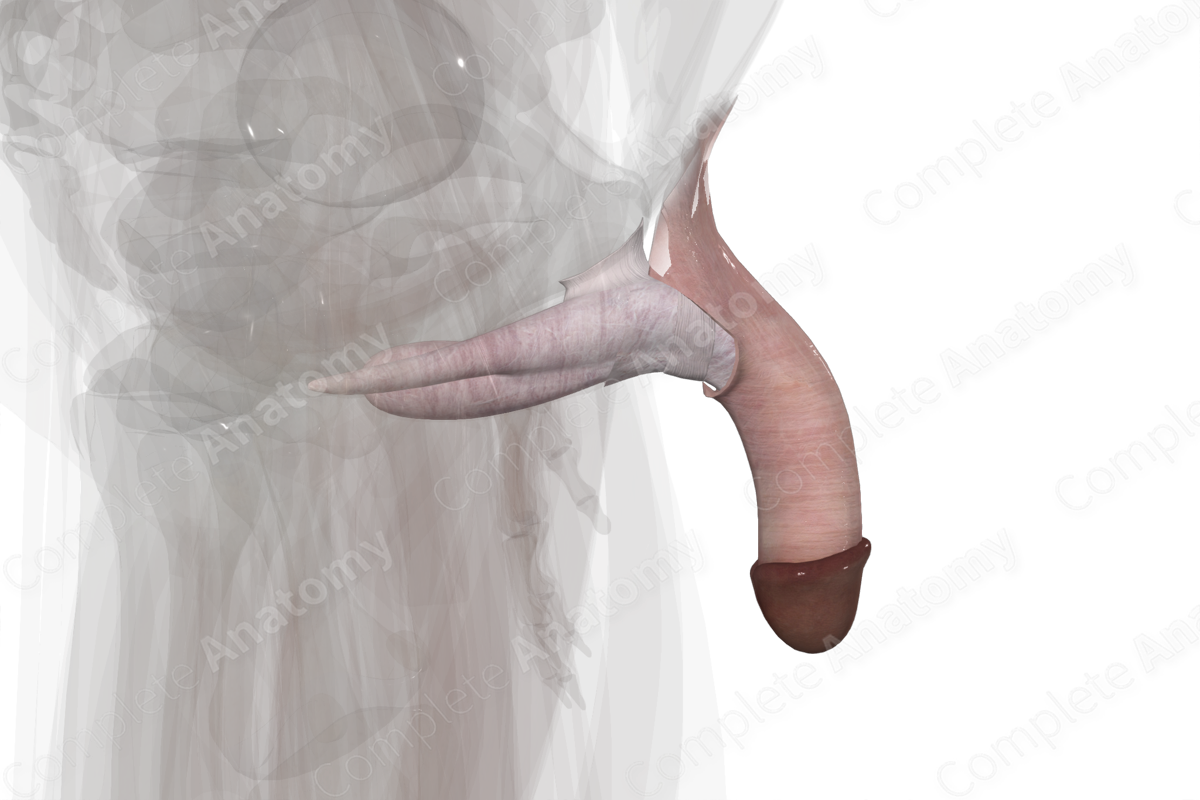
Location: Root of penis is attached to perineum and anchored to pubic symphysis. The shaft of penis lies outside the pelvic cavity.
Arterial Supply: Perineal branch of internal pudendal artery and its tributaries.
Venous Drainage: Superficial dorsal vein of penis, deep dorsal vein of penis, and crural veins.
Innervation: Visceral afferent: Dorsal penile and perineal nerves; Parasympathetic: Pelvic splanchnic and cavernous nerves; Sympathetic: T11–L1 spinal nerves and deep cavernous nerve.
Lymphatic Drainage: Superficial inguinal, deep inguinal, and internal iliac lymph nodes.
Related parts of the anatomy
Penis Structure/Morphology
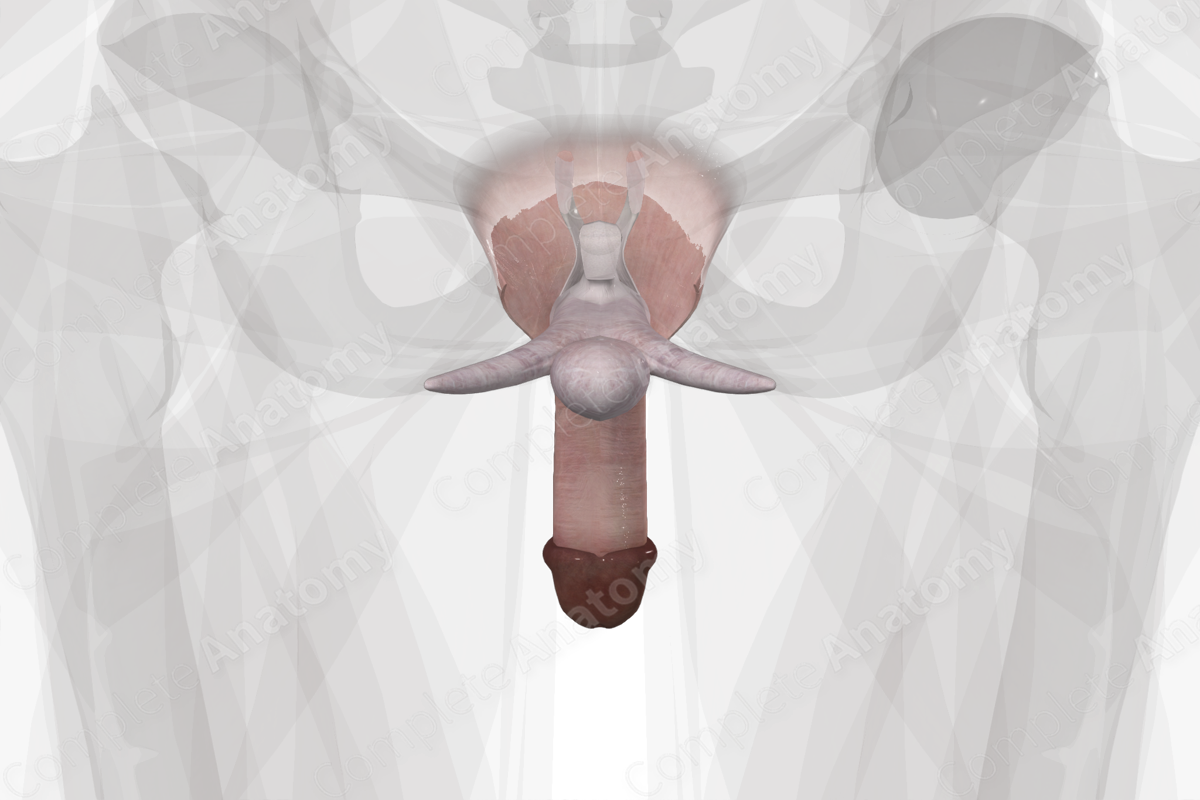
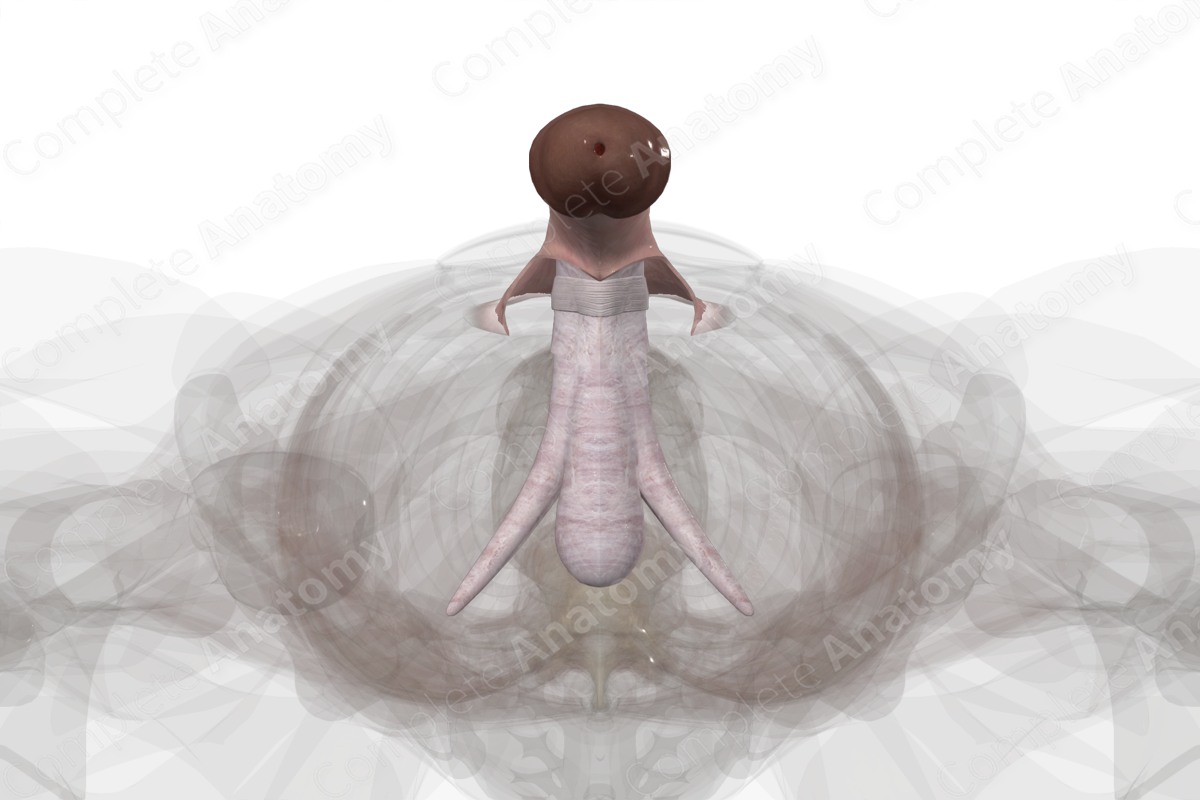
The penis is composed of a free shaft, which is attached to the perineum by the root of the penis. It is anchored to the pubic symphysis by two suspensory ligaments. The shaft contains the erectile bodies of the corpus cavernosum and corpus spongiosum, the penile urethra, blood vessels, and nerves.
Penis Anatomical Relations
The shaft of the penis lies external to the pelvic cavity, anterior to the scrotum. The dorsal shaft of the penis is comprised of corpus cavernosum, separated in the midline by the septum penis. The corpus spongiosum runs on the ventral side of the penis. The distal end of the penis is capped by the bulbous-shaped glans penis.
Penis Function
The penis is involved in copulation, which culminates in the ejaculation of semen, containing sperm for fertilization of the female oocyte. The penis also functions in micturition (the act of passing urine out of the body).
Penis Arterial Supply
The penis is mainly supplied by the perineal artery, a branch of the internal pudendal artery. The artery of bulb of penis penetrates the perineal membrane to supply the bulb of the penis, corpus spongiosum, and glans penis. The dorsal artery of the penis travels between the crus of the penis and the pubic symphysis to supply the dorsal surface of the corpus cavernosum. As it courses through the penis, it travels with the dorsal vein and dorsal penile nerve. The dorsal artery of the penis also gives off circumflex tributaries which supply the corpus spongiosum and the spongy urethra. The deep arteries of penis are paired vessels that pierce the tunica albuginea of the corpus cavernosum and travel in the center of the corporal bodies, towards the glans penis. Along its course, it provides straight and helicine branches, which open into the sinusoidal spaces.
Penis Venous Drainage
The penis is drained by three venous routes: superficial, intermediate, and deep. The superficial veins travel within the dartos fascia of the scrotum and receive blood from the prepuce and penile shaft. The superficial veins unite at the base of the penis forming a single superficial dorsal vein, which empties into the superficial external pudendal vein. The intermediate circumflex and deep dorsal veins are deep to the deep fascia of the penis. They drain blood from the glans penis, corpus spongiosum, and distal two thirds of the penile shaft. The proximal two thirds of the penile shaft is drained by the deep crural veins.
Penis Innervation
Sensory innervation to the penis is supplied by the dorsal nerve of the penis and the perineal nerve. Autonomic innervation to the penis is supplied by the deep cavernous nerve. It travels through the prostate and exits the pelvis with the urethra. It enters the corpus cavernosum and sends branches to the corpus spongiosum. Parasympathetic fibers to the penis travel in the pelvic splanchnic nerves towards the pelvic plexus, where they synapse and give rise to the cavernous nerve.
Sympathetic input (inhibitory) originates from the eleventh and twelfth thoracic and first lumbar nerves and travel to the sympathetic trunk before descending to the pelvis plexuses.
Penis Lymphatic Drainage
The lymph of the penis and perineal skin is drained into the superficial inguinal nodes. The lymph from the glans penis is drained into the deep inguinal and external iliac nodes. Lymph from the erectile tissue and spongy urethra pass into the internal iliac lymph nodes.
Penis List of Clinical Correlates
—Erectile dysfunction
—Hypospadias
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Penis

The penis is the external male sexual organ located superior to the scrotum and inferior to the umbilicus.
Penis histology: Video, Causes, & Meaning

Penis histology: Symptoms, Causes, Videos & Quizzes | Learn Fast for Better Retention!