Quick Facts
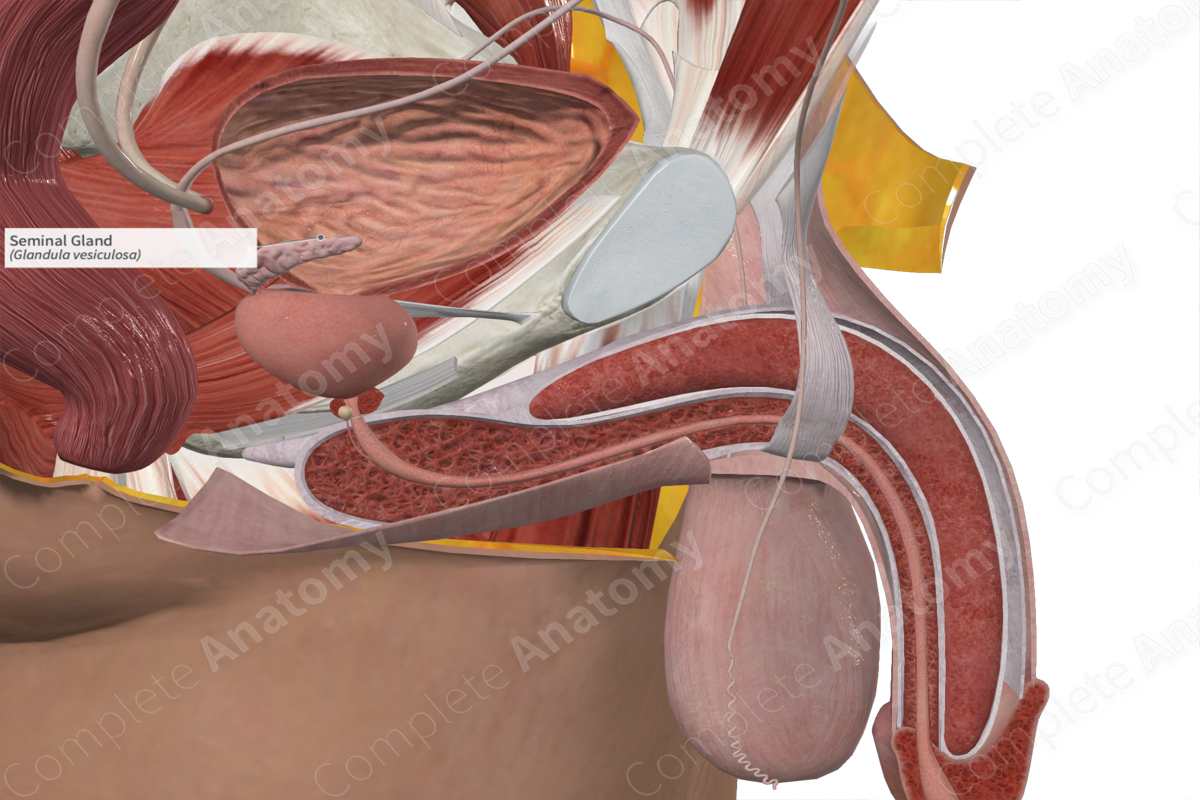
Location: At the base of the prostate, between the bladder and rectum.
Arterial Supply: Artery to ductus deferens and inferior vesical artery.
Venous Drainage: Inferior vesical plexus.
Innervation: Sympathetic: Inferior hypogastric nerve; Parasympathetic: Pelvic and inferior hypogastric nerves.
Lymphatic Drainage: Internal iliac lymph nodes.
Related parts of the anatomy
Structure/Morphology
The seminal gland is an out pouching of the terminal ductus deferens. It is a coiled tube measuring approximately 3–5 cm in adults, with a volume capacity of approximately 13 ml (Standring, 2016). The right seminal vesical is often larger than the left. However, they both decrease in size with age.
The seminal gland consists of a highly convoluted duct, which is surrounded by a capsule of connective tissue.
Anatomical Relations
The seminal glands are posterior to the urinary bladder and prostate, and lateral to the ampulla of the ductus deferens.
The inferior hypogastric plexus lies posterolaterally on either side on the seminal glands.
Function
The seminal glands secrete a thick alkaline seminal fluid with fructose, via the ejaculatory duct, into the prostatic urethra. This seminal fluid mixes with sperm from the ductus deferens, to form semen, which is expelled during ejaculation.
Arterial Supply
The seminal glands are supplied by branches from the Inferior vesical and middle rectal arteries.
Venous Drainage
The seminal glands are drained by the vesical venous plexus into the internal iliac vein.
Innervation
The pelvic and inferior hypogastric nerves supply sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation to the seminal gland. Parasympathetic supply is also supplied by the pelvic nerve.
Lymphatic Drainage
The lymph of the seminal glands is drained into the internal iliac lymph nodes.
References:
Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Gray's Anatomy Series 41 edn.: Elsevier Limited.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Testis, ductus deferens, and seminal vesicle histology: Video, Causes, & Meaning

Testis, ductus deferens, and seminal vesicle histology: Symptoms, Causes, Videos & Quizzes | Learn Fast for Better Retention!





