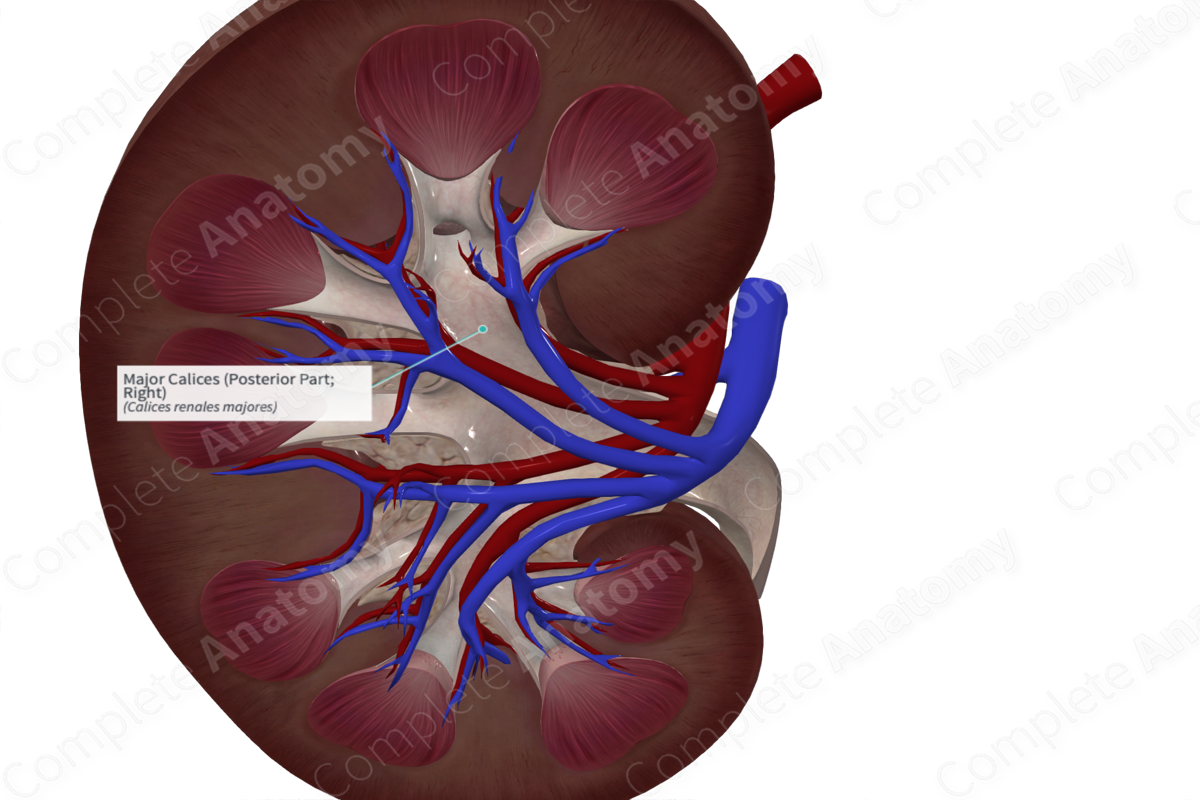
Structure/Morphology
The major calices are tubular chambers formed by the merging of two or more minor calices. The major calices are lined with smooth muscles, which helps to propel urine distally.
Related parts of the anatomy
Key Features/Anatomical Relations
There are usually two or three major calices per kidney (Standring, 2016). The major calices are located closer to the renal hilum in comparison to the minor calices.
Function
The major calices drain the excreted urine into the large singular renal pelvis.
List of Clinical Correlates
—Kidney stones
References
Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Gray's Anatomy Series 41 edn.: Elsevier Limited.



